Carbon cycle notes LBMS KEY
advertisement

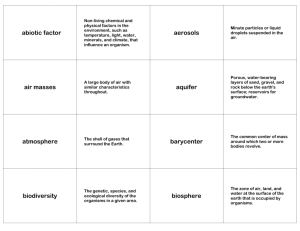
Name _______________________________________________________ Class ________ Date _______________________________________________ The Carbon-Oxygen Cycle Background: Carbon and oxygen are constantly being recycled in ecosystems. They can be found as compounds in living things, in the atmosphere as a gas, and in the soil as other compounds. These processes are linked and all producers and consumers play an important part in allowing the cycles to continue. Directions: Fill in the table below. Each box should explain how a transition can occur from one location to another. Organisms Atmosphere Atmosphere Organisms Organisms Soil Through respiration Through respiration heterotrophs breathe heterotrophs take in out CO2 O2 When organisms die the carbon compounds get returned into the soil Through Through photosynthesis photosynthesis autotrophs take in autotrophs release O2 CO2 When organisms produce waste carbon molecules are returned into the soil Air mixes with water When organisms burn and transfers CO2 and they release carbon O2 to aquatic plants into the atmosphere and animals Soil Organisms Plants take up nutrients in their roots that can include carbon compounds 1. What do producers release when they conduct photosynthesis? Oxygen 2. What happens to the oxygen released into the atmosphere? It gets taken in by heterotrophs 3. Where do producers get the carbon dioxide they need? From the atmosphere 4. What would prevent this cycle from continuing on indefinitely? If there were no plants, CO2 would not be taken out of the atmosphere and O2 would not be provided to the hetertrophs 5. In what ways can humans impact the exchange of carbon and oxygen in the atmosphere? List two. 1. Burning more fuel (releases more carbon into the atmosphere) 2. Cutting down trees decreases the amount of O2 being placed in the atmosphere 6. Explain how you think a cow eating grass is part of the carbon and oxygen cycles. Cow breathes in O2, breathes out CO2. Cow eats carbon compounds in the grass, then returns carbon compounds back into the soil through waste products