A X0 w BTFA 0.374 1.588 0.0437 BPFB 0.520 1.583 0.0601 BTFP
advertisement
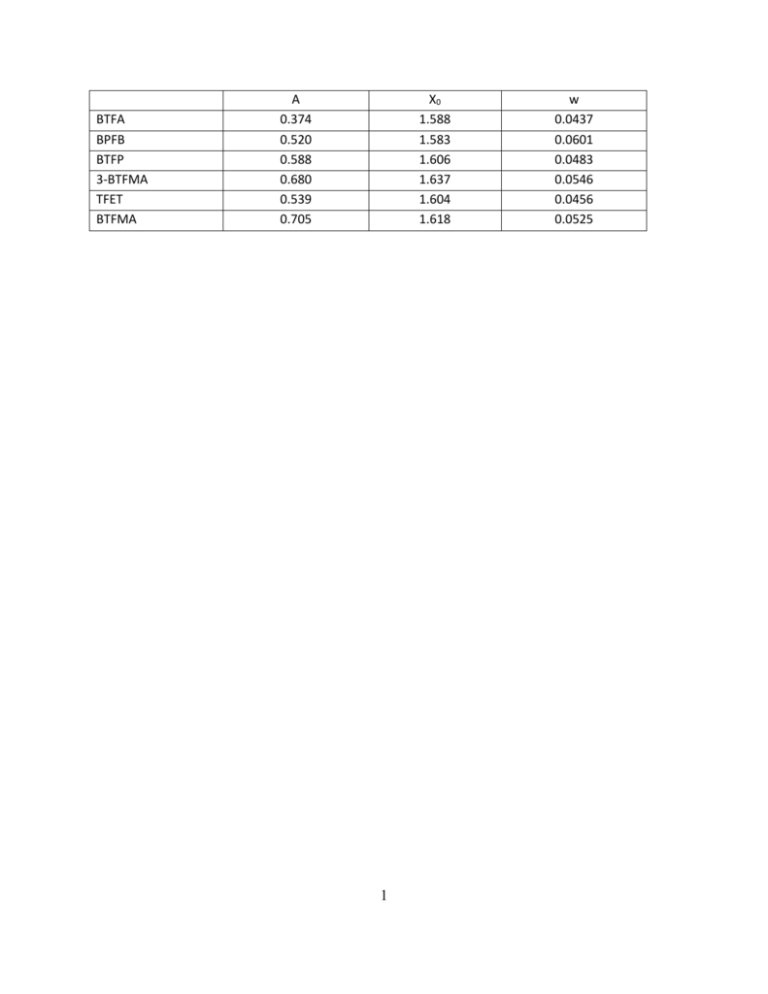
BTFA BPFB BTFP 3-BTFMA TFET BTFMA A 0.374 0.520 0.588 0.680 0.539 0.705 X0 1.588 1.583 1.606 1.637 1.604 1.618 1 w 0.0437 0.0601 0.0483 0.0546 0.0456 0.0525 Supplementary Table 1. Fitting parameters (A, xo and w) used to interpret the dependence of chemical shift change of CF3 tags to solvent polarity, using the formula = A/(1+exp(-(Pyx0)/w)). Methanol:H2O 4:1 3:1 2:1 1:1 1:2 1:3 1:4 Difference BTFA -85.239 -85.214 -85.139 -85.003 -84.911 -84.873 -84.860 0.379 BPFB -79.465 -79.348 -79.248 -79.148 -79.025 -78.976 -78.959 0.506 BTFP -78.320 -78.296 -78.192 -78.000 -77.837 -77.768 -77.729 0.591 TFET -66.518 -66.497 -66.406 -66.220 -66.063 -66.007 -65.974 0.544 3-BTFMA -63.217 -63.194 -63.124 -62.933 -62.724 -62.631 -62.575 0.642 BTFMA -62.595 -62.561 -62.461 -62.248 -62.046 -61.952 -61.907 0.688 Supplementary Table 2. 19F NMR spectra of each of the probes in different solvent systems composed of methanol and water. Note that the difference in the rightmost column in the above table designates the difference between the chemical shift in the highest water sample from that of the highest methanol sample. 2 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. 19F NMR spectra of each of the probes shown in Figure 1, for both water to MeOH ratios of 0.25 (black) to 4.0 (red). Note that TFET labeling of the peptide proved to be incomplete and in water the peptide-bound and peptide-free signals appear downfield and upfield, respectively. The expected triplet in TFET spectra arises from the 3-bond scalar coupling to the methylene 1H nuclei. 3 Figure S2. 19F NMR chemical shifts (normalized to 19F shifts in H2O) as a function of solvent polarity. This plot uses a relative solvent polarity scale where H2O is arbitrarily assigned a polarity = 1. This relative polarity scale is defined by chromophore absorbance in various solvents. See Christian Reichardt, Solvents and Solvent Effects in Organic Chemistry, Wiley-VCH Publishers, 3rd ed.). 4 5