7C22

Section 1 Matter
1.
Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass; matter is composed of tiny particles.
2.
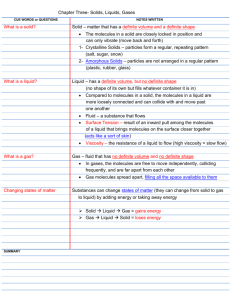
Three usual states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
3.
Plasma, a fourth state, occurs only at very high temperatures and is not common on Earth.
4.
Solids have definite shape and volume because particles are packed closely together and merely vibrate in place.
5.
Solids in which particles are arranged in a repeating, three-dimensional pattern are called crystals or crystalline solids.
6.
Amorphous solids have a random arrangement of particles.
7.
Matter with a definite volume but no definite shape is a liquid; a liquid’s particles move more freely than those of a solid.
8.
Viscosity is a liquid’s resistance to flow and increases when particles are more strongly attracted to each other.
9.
Surface tension is uneven forces acting on the particles of a liquid’s surface.
10.
Gas is matter that does not have a definite shape or volume; gas particles spread out evenly as far apart as possible.
Section 2 Changes of State
11.
Particles are in constant motion; amount of movement depends on their kinetic energy.
12.
Thermal energy is the total energy of all the particles in a sample of matter
13.
The average kinetic energy of particles in a substance is its temperature.
14.
Heat is the movement of thermal energy from a substance with a higher temperature to one with a lower temperature.
15.
Matter can change states as energy is absorbed or released.
16.
A change from the solid to the liquid state is called melting.
17.
A change from the liquid to the solid state is called freezing.
18.
A change from liquid to gas is called vaporization.
19.
Boiling is vaporization that occurs below the liquid’s surface at its boiling point.
20.
Evaporation is vaporization that occurs at the surface of a liquid; molecules must be at or near the surface and at the right speed to evaporate.
21.
Condensation is a change from gas to liquid
22.
Changes between solid and gas states—during sublimation the surface particles of a solid gain enough energy to become a gas.
Section 3 Behavior of Fluids
23.
Pressure equals the force exerted on a surface divided by the total area over which the force is exerted, or P = F / A.
24.
If force increases over an area, the pressure increases; if force over an area decreases the pressure decreases.
25.
Atmospheric pressure is air presses down on Earth with force.
26.
Pressure can be balanced as the pressure pushing down equals the pressure pushing up.
27.
As altitude increases, air pressure decreases.(so the farther I am from the Earth’s surface, the less the air pressure)
28.
Gas pressure in a closed container changes with volume and temperature changes.
29.
Decreasing volume increases pressure; increasing volume decreases pressure.
30.
Increasing temperature increases pressure; decreasing temperature decreases pressure.
31.
Density is mass divided by volume.
32.
An object will float in a fluid that is denser than the object. (object is less dense than the fluid.)
33.
An object with the same density as the fluid will stay at the same level in the fluid.
34.
An object will sink in a fluid if the object is more dense than the fluid.