Worksheet Unit 1
advertisement

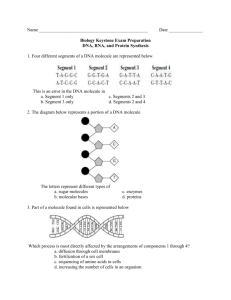
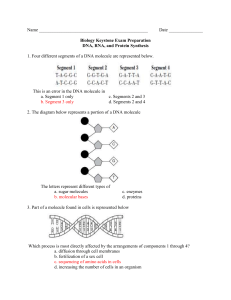
Bio 101 Blinderman Worksheet Unit 1 1 Name _________________________________________ 1. Arrange in the correct order from least to most complex cell organism ecosystem population biosphere organelle tissue organ system 2. Arrange in the correct order from least to most complex Amino acid nitrogen atom protein polypeptide 3. Place in the correct order from least to most complex Chromosome Gene Nucleotide Genome Deoxyribose sugar molecule 4. Place in the correct order of energy flow through and ecosystem consumer sunlight producer secondary consumer decomposer 5. Match the molecule to the function _____ carries the code for primary structure of protein _____ product of photosynthesis _____ allows cohesion to aid transport in plants _____ the solvent in aqueous solutions _____ a storage polysaccharide _____ a structural polysaccharide _____ hydrophobic biomolecule with maximum H _____ major component of membrane bilayer A. phospholipid B. DNA C. Cellulose D. Saturated Fat E. Water F. Water G. Glycogen H. C6H12O6 6. A double-blind controlled trial was conducted to test methods of transmission of viruses and the protective ability of vitamin C. 24 male volunteers were recruited for the study. Half of the men were pretreated for 3 weeks with 2,000 mg of vitamin C daily (4 X 500 mg) and the other half were given 4 placebo pills daily. The men were all infected with RV16 cold virus by direct inoculation into the nose. The men were observed for 7 days and during the week continued to take the pills. All developed colds. a. Identify the hypothesis b. Identify the experimental variable in the experiment: c. Identify the control group: d. List 3 controlled variables e. What is the dependent variable (what is measured)? f. Why is the data considered to be quantitative? g. Was the hypothesis supported, or was it falsified? 7. Organic? 8. Circle the functional groups What is the molecular formula for this molecule? Bio 101 Blinderman Worksheet Unit 1 2 9. Add the appropriate number of hydrogen atoms to this organic molecule. Remember, each carbon must have 4 bonds C-C-C-C 10. Fill in the number Thousands 3 75% 4 1 7 _____ Amount of the Earth covered by water _____ Body temperature in degrees Celsius _____ Neutral pH _____ Hydrogen atoms in glucose _____ Glucose units in starch _____ Types of nucleotide bases that compose DNA _____ Named species on earth . _____ Domains of life _____ Amino acids _____ Cells in a bacteria 20 37 1.8 million 12 11. List 1 organism (common name) that represents each of the following taxonomic categories a. Domain Bacteria _____________ Domain Eukarya _______________ b. Kingdom Fungi _______________ Kingdom Plantae _______________ c. Kingdom Protista _______________ 12. Fill in the corresponding strand of DNA. Follow the rules of nucleotide base complementation in which a certain purine hydrogen bonds to a certain pyrmidine TTAGCCCATTGC 13. Hydrophilic or hydrophobic? Unsaturated fat NaCl Monosaccharide Triglyceride ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ 14. Place and X by the statements that ARE consistent with natural selection. Traits vary in populations in a non-random fashion More offspring are generated than can survive and there is competition for resources The strongest always reproduce the most Traits are heritable Over time, more individuals in a population will have the advantageous traits Organisms can pass on traits that were acquired in life Ancestral species cannot give rise to descendant species Fossils provide evidence of organisms that once populated earth 15. Circle the words not associated with proteins (may choose more than one) Polypeptide sheet Peptide bond Organic Chitin Hemoglobin and melanin Amino acid Polymer Biomolecule Enzyme Nucleic acid Disaccharide Steroid 20 building blocks Tertiary structure Bio 101 Blinderman Worksheet Unit 1 3 16. What is the name of the functional group? -CH3 -COOH -SH -C=O -NH2 -PO4 -OH 17. Fill in using the word bank Trace element Atom Electron Hydrogen Isotope Matter Reactant Compound Isomer Ionic Covalent _____________________ takes up space and has mass _____________________ required by the body in very small amounts _____________________composed of two or more elements in a fixed ratio _____________________ a strong bond due to electron sharing _____________________ a weaker bond in which charged molecules are attracted _____________________ a negatively charged subatomic particle _____________________ an element whose atoms differ in the number of neutrons _____________________ starting material in a chemical reaction _____________ two molecules with the same molecular formula, but different structural _____________________ bond between T and A nucleotides in a DNA molecule ________________ smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of the element 18. Fill in Temperature Evaporative cooling a. b. c. d. e. f. Specific heat Heat Buffer Surface tension Cohesion of water molecules at the water/air interface _____________________ Amount of heat absorbed or lost for 1 g to change temperature by 1ºC ________ Lowering of temperature upon the transformation of water from liquid to gas ____ Intensity of heat dependent on movement of molecules ___________________ Will stabilize pH of an aqueous solution _____________________ Total amount of energy due to molecular motion _____________________ 19. Monomer or polymer a. Starch b. Polysaccharide c. Glucose d. Lactose e. DNA f. Nucleotide g. Amino acid h. Cellulose i. Chitin j. Glycogen k. G, A, T, and C l. Sucrose