Heating and Cooling Curve Assignment
advertisement
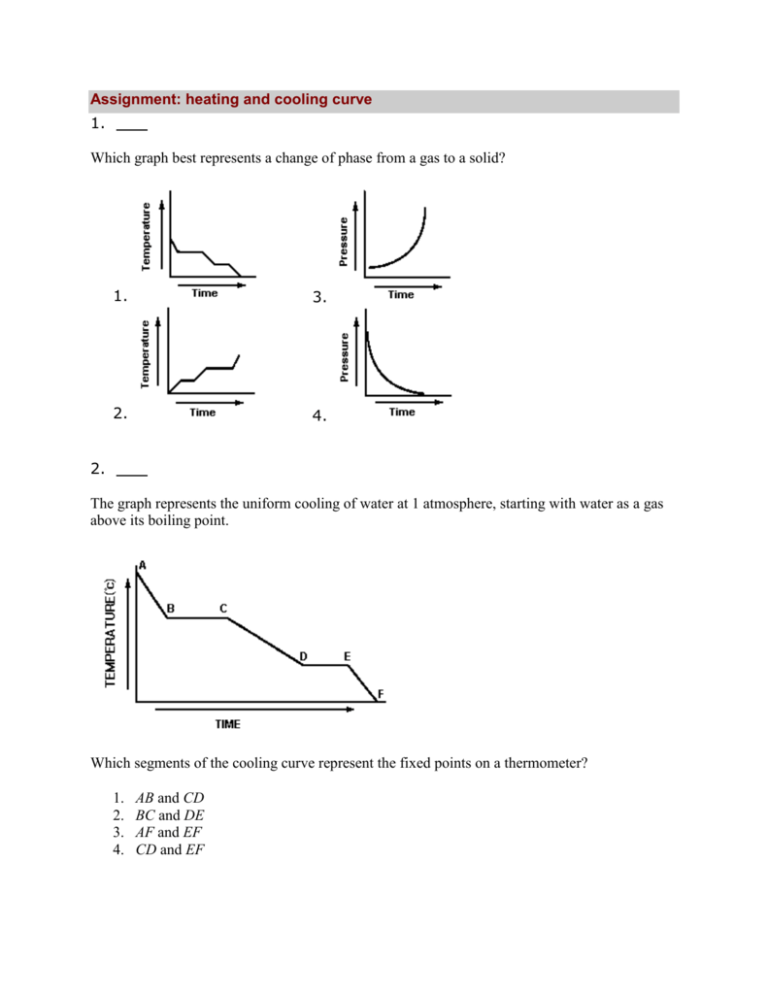
Assignment: heating and cooling curve 1. Which graph best represents a change of phase from a gas to a solid? 1. 3. 2. 4. 2. The graph represents the uniform cooling of water at 1 atmosphere, starting with water as a gas above its boiling point. Which segments of the cooling curve represent the fixed points on a thermometer? 1. 2. 3. 4. AB and CD BC and DE AF and EF CD and EF 3. Which substance will sublime at 298 K? 1. 2. 3. 4. CO2(s) Al(s) Si(s) KOH(s) 4. Which substance takes the shape of and fills the volume of any container into which it is placed? 1. 2. 3. 4. H2O ( ) I2 (s) CO2(g) Hg ( ) 5. The graph represents the uniform heating of a solid, starting below its melting point. Which portion of the graph shows the solid and liquid phase existing in equilibrium? 1. 2. 3. 4. AB BC CD DE 6. What occurs when the temperature of 10.0 grams of water is changed from 15.5°C to 14.5°C? 1. 2. 3. 4. The water absorbs 42 joules. The water releases 42 joules. The water absorbs 4200 joules. The water releases 4200 joules. 7. Which phase change represents sublimation? 1. 2. 3. 4. solid to gas solid to liquid gas to solid gas to liquid 8. A 1-gram sample of which substance in a sealed 1-liter container will occupy the container completely and uniformly? 1. 2. 3. 4. Ag(s) Hg( ) H2O( ) H2O(g) 9. Which change results in a release of energy? 1. 2. 3. 4. the melting of H2O(s) the boiling of water ( ) the evaporation of H2O( ) the condensation of H2O(g) 10. During which change is energy absorbed? 1. 2. 3. 4. the melting of ice the cooling of ice the freezing of water the condensation of water 11. The graph represents a solid heated at a uniform rate, starting at a temperature below its melting point. Once the solid has reached its melting point, how many minutes are required to completely melt the solid? 1. 2. 3. 4. 6 min 2 min 8 min 4 min 12. The cooling graph represents the uniform cooling of a substance, starting with the substance as a gas above its boiling point. How much time passed between the first appearance of the liquid phase of the substance and the presence of the substance completely in its solid phase? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5 minutes 2 minutes 7 minutes 4 minutes 13. The amount of heat needed to change 1 gram of a solid to 1 gram of a liquid at constant temperature is called the heat of 1. 2. 3. 4. vaporization sublimation fusion fission 14. The diagram represents the uniform heating of a substance that is a solid at time t0. What is the freezing point of the substance? 1. 2. 3. 4. 15. 1°C 12°C 60°C 100°C When 200 grams of water cools from 50.°C to 25°C, the total amount of heat energy released by the water is 1. 2. 3. 4. 210 J 21000 J 42000 J 1500 J 16. The temperature of 100 grams of water changes from 16°C to 20°C. What is the total number of joules of heat energy absorbed by the water? 1. 2. 3. 4. 210 J 168 J 42,000 J 1,680 J 17. Approximately how many joules of heat are needed to raise the temperature of a 4.0-gram sample of water 8.0°C? 1. 2. 3. 4. 134,006 J 168 J 134 J 1,680 J 18. The graph represents a substance, X, in the form of a gas uniformly cooled from an initial temperature of 140°C. In which segment of the graph is substance X in the liquid phase only? 1. 2. 3. 4. AB BC CD DE 19. The heat of fusion of a compound is 333.6 joules per gram. What is the total number of joules of heat that must be absorbed by a 15.0-gram sample to change the compound from solid to liquid at its melting point? 1. 2. 3. 4. 1304J 168J 420J 5004J 20. The graph represents a relationship between temperature and time as heat is added uniformly to a substance, starting when the substance is a solid below its melting point. Which portions of the graph represents times when heat is absorbed and potential energy increases while kinetic energy remains constant? 1. 2. 3. 4. A and B B and D A and C C and D 21. As ice melts at standard pressure, its temperature remains at 0°C until it has completely melted. Its potential energy 1. decreases 2. increases 3. remains the same 22. The temperature at which the solid and liquid phases of matter exist in equilibrium is called its 1. 2. 3. 4. melting point boiling point heat of fusion heat of vaporization 23. Which phase change results in the release of energy? 1. 2. 3. 4. H2O(s) → H2O(l) H2O(s) → H2O(g) H2O(l) → H2O(g) H2O(g) → H2O(l) 24. The graph represents the heating curve of a substance that starts as a solid below its freezing point. What is the melting point of this substance? 1. 2. 3. 4. 30°C 55°C 90°C 120°C 25. At STP, fluorine is a gas and iodine is a solid. This observation can be explained by the fact that fluorine has 1. 2. 3. 4. weaker intermolecular forces of attraction than iodine stronger intermolecular forces of attraction than iodine lower average kinetic energy than iodine higher average kinetic energy than iodine 26. What amount of heat is required to completely melt a 29.95-gram sample of H2O(s) at 0°C? 1. 334 J 2. 2260 J 3. 1.00 ×103 J 4. 1.00 ×104 J 27. Base your answer to the question on the information below. A 5.00-gram sample of liquid ammonia is originally at 210. K. The diagram of the partial heating curve below represents the vaporization of the sample of ammonia at standard pressure due to the addition of heat. The heat is not added at a constant rate. Some physical constants for ammonia are shown in the data table below. Calculate the total heat absorbed by the 5.00-gram sample of ammonia during time interval AB. Answer: J 28. Base your answer to the question on the information below. A 5.00-gram sample of liquid ammonia is originally at 210. K. The diagram of the partial heating curve below represents the vaporization of the sample of ammonia at standard pressure due to the addition of heat. The heat is not added at a constant rate. Some physical constants for ammonia are shown in the data table below. Determine the total amount of heat required to vaporize this 5.00-gram sample of ammonia at its boiling point. Answer: J 29. What is the total amount of heat absorbed by 100.0 grams of water when the temperature of the water is increased from 30.0°C to 45.0°C? 1. 2. 3. 4. 418 J 6270 J 12 500 J 18 800 J 30. Which process is exothermic? 1. 2. 3. 4. boiling of water melting of copper condensation of ethanol vapor sublimation of iodine 31. The graph below represents the relationship between temperature and time as heat is added to a sample of H2O. Which statement correctly describes the energy of the particles of the sample during interval BC? 1. 2. 3. 4. Potential energy decreases and average kinetic energy increases. Potential energy increases and average kinetic energy increases. Potential energy increases and average kinetic energy remains the same. Potential energy remains the same and average kinetic energy increases. 32. The temperature of a sample of water changes from 10°C to 20°C when the sample absorbs 418 joules of heat. What is the mass of the sample? 1. 1 g 2. 10 g 3. 100 g 4. 1000 g 33. A 36-gram sample of water has an initial temperature of 22°C. After the sample absorbs 1200 joules of heat energy, the final temperature of the sample is 1. 2. 3. 4. 8.0°C 14°C 30.°C 55°C 34. Given the diagram representing a heating curve for a substance: During which time interval is the average kinetic energy of the particles of the substance constant while the potential energy of the particles increases? 1. 2. 3. 4. AC BC CD DF 3234366 False 0 0 1






