Fifteen – Wave-Particle Duality
advertisement

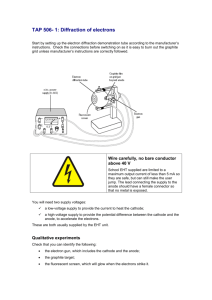
Fifteen - Wave-Particle Duality 1. explain the concept of electron diffraction: -electrons from heated filament are accelerated to high speeds by large p.d.s between the cathode and anode -beam of electrons pass through thin sample of polycrystalline graphite in uniform atomic layers -the spaces between the nuclei act as apertures for diffraction of electrons to take place -electrons emerge from graphite film and produce diffraction rings on phosphor screen -show constructive and destructive interference -slower the electrons, more widely spaced the rings 2. explain that electron diffraction is evidence for the wave nature of particles like electrons 3. select and apply the De Broglie equation: 𝜆= ℎ 𝑚𝑣 4. explain that diffraction of electrons by matter can be used to determine the arrangements of atoms and the size of nuclei 5. argue the wave-particle duality of electrons: WAVEelectrons travel/propagate in space as a wave electrons show diffraction and interference electrons are diffracted by matter such as crystalline graphite nuclei electron show diffraction "ring"/fringes diffraction of electrons occur when λ is comparable to aperture size PARTICLEelectrons have mass electrons have charge electrons interact with matter like a particle electrons can be deflected by charge/electric field 6. explain that wave-particle duality states that all objects exhibit both wave and particle properties