Unit 4: Geologic Time Study Guide Part 1: Geologic Timescale
advertisement

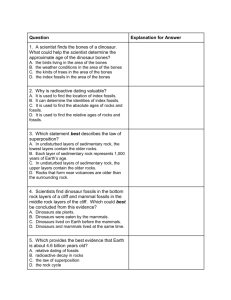
Unit 4: Geologic Time Study Guide Part 1: Geologic Timescale Concept Review: When did: Period Years Mammals Appear __Triassic____ 250-200 mya Reptiles Appear Pennsylvanian 325-300 mya First Amphibians Devonian 400-350 mya First Animal Traces Late Proterozoic 600-550 mya First Birds Appear Jurassic 200-150 mya The picture to the right is of fossil records. Why doesn’t the picture contain any fossils from the Archaean or the Hadean? Hadean there is no evidence of life at all. Archaean had life But the life was a soft organism with no bones or skeletons. What are some major characteristics of the Mesozoic Era? Age of the dinosaurs, first mammals and birds appeared. First Flowering plants and first primates. Ended with dinosaur extinction Part 2: Relative Dating Vocabulary: Index Fossils – fossils used by geologists to date the age of rock layers. Geologic Column – a non-existing model of the Earth’s rock layers pieced together from multiple locations. Law of Superposition – sedimentary rock layers on top are younger than rock layers on bottom. Law of Cross Cutting Relationships – rock layers that cut through other rock layers are younger than the layers they cut through. Law of Original Horizontality- sedimentary rocks are originally laid horizontally due to gravity. Any folds, bends, faults occur later and therefore are older than horizontal rock layers. Inclusion/Intrusion – igneous rocks that are surrounded by other rock types, mainly due to lava/magma flows. Unconformity – missing or irregular layering or shape. Mainly due to erosion, extremely folding from plate tectonic movement, or lava/magma flow melting/cutting through rock layers. Concept Review: Using the fossil record picture above, which types of fossils would make good index fossils? Why? Dinosaur fossils because they have a clear extinction point. Animals from the Paleozoic because they had a massive extinction point as well. Fossils that are unique in shape and easily identifiable, such as shells, trilobites, and certain plant material. What types of specific events could cause folding or tilting in rock layers? Plate tectonic plate movement or pressure. Fault lines, which can cause tilting and movement during earthquakes. Magma chambers from below can cause folding to rock layers above. Determine the sequence of rock layers in chronological order from YOUNGEST to OLDEST for the following picture. B, C, A, F, E, G, D Which laws did you use to determine your answer? Explain each. Law of superposition (C is younger than A, etc) Law of cross cutting relationships (B cuts through all, so is youngest, etc) How do index fossils help scientists determine the age of rock layers? If scientists know the age of the fossils, then the rocks containing those Fossils are the same age or slightly younger. If the dinosaur fossil lived between 75 – 65 million years ago and the leaf fossil was from 70- 50 million years ago, what is the approximate age of the dark rock layer in the picture? Explain your answer. Between 70-65 million years because of the overlap in years. Part 3: Absolute Dating Vocabulary: Radioactivity- process where unstable elements become more stable (by releasing atomic Particles or energy. Half-Life- the amount of time it takes for HALF a substance to radioactively decay. Radiometric Dating- the process of measuring the radioactive decay material to determine The age of the material. Concept Review: 1. Compare and Contrast Relative Dating and Absolute Dating. Absolute Dating – A number age is put on the rock/fossils. Use radiometric dating to determine actual age number of rocks/fossils. Relative Dating – Comparing rock ages to other rocks and fossils. No age given, just an order (i.e. rock A is younger than rock B). Similarities – Both try to put a general age on the rocks. Absolute dating supports/confirms relative dating. 2. If a rock sample originally contained 12 g of Uranium-235, how much will be left after: a. 1 half-life __6g_____ b. 2 half-lives ___3g___c. 3 half-lives ___1.5g___ 3. Iodine-131 is used to destroy thyroid tissue in the treatment of an overactive thyroid. The half-life of iodine-131 is 8 days. If a hospital receives a shipment of 200 g of iodine-131, how much I-131 would remain after 32 days? 0 days = 0 half-life = 200 g start 8 days = 1 half-life = 100 g left 16 days = 2 half-life = 50 g left 24 days = 3 half-life = 25 g left 32 days = 4 half-life = 12.5 g left.