1.2-Hydrocarbons
advertisement

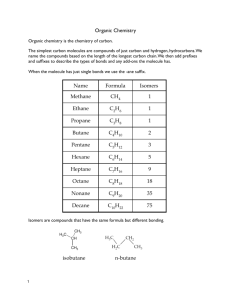
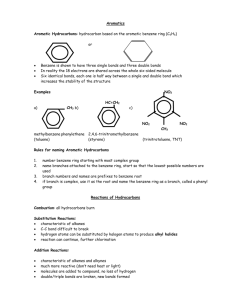
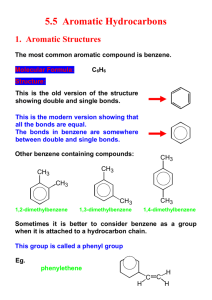
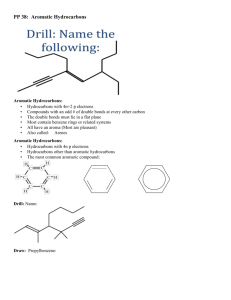
1.2 Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons are the simplest type of organic compounds composed of Carbon and Hydrogen only They are non-polar because they have only single bonds 2 types of Hydrocarbons 1. Aliphatic a. Carbon atoms that are bonded in one or more chains and rings b. contain single, double or triple bonds 2. Aromatic a. Based on the aromatic benzene group b. Benzene is the simplest aromatic compound Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes Alkane has only single bonds do not contain rings general formula is CnH2n+2 Example Cycloalkane ring shape connected by single bonds Example Alkene Has at least one double bond general formula CnH2n a double bond contains 2 bonds (1 strong and 1 weak) these are more reactive Example Alkyne Has at least one triple bond General formula CnH2n-2 even more reactive than alkenes Example Functional Groups a reactive group of bonded atoms that appears in all members of a chemical family these groups determine physical and chemical properties Common Functional Groups Rules For Naming Organic Compounds Three parts to an Organic compound name Prefix + Root + Suffix Root indicates the # of Carbon atoms in the longest chain that contains the functional group root names see tale 1.2 page 13 Suffix indicates the type of compound according to the functional groups present ane = alkane ene = alkene yne = alkyne Prefix indicates the name and location of each branch and/or functional groups attached to the main chain table 1.3 page 14 and your cheat sheets Steps to Naming Hydrocarbons 1. Find the root a. longest chain containing the functional groups b. count # of C’s obtain the root using table c. if cyclic add the prefix “cyclo” before the root 2. Find the suffix a. functional groups determine the suffix. Use your common organic families sheet here b. if more than one functional group use prefix di(2) and tri(3) to indicate the number of them 3. # the Main Chain a. # from the end that is closest to any functional groups b. # so any branches have the lowest position 4. Find the Prefix a. Name each branch as an alkyl group and give its position # b. if more than one branch put in alphabetical order Examples Steps to drawing hydrocarbons 1. Draw the main chain according to the root name # of carbons 2. add double or triple bonds according to the suffix 3. add branches according to the prefix 4. add H atoms so each carbon has 4 bonds Examples Aromatic Compounds hydrocarbons that have a benzene ring Naming Aromatic compounds 1. # the Carbons in the benzene ring if more than 1 branch attached to the ring start numbering at the Carbon with highest priority (page 18) 2. Name any branches attached to Benzene ring and give position #’s. if only one branch this is not necessary 3. Place the position #’s and names of these branches before the root name benzene Worksheets: Extra practise Questions BLM 1-2 BLM 1-3