Community and Biomes 3.1 and 3.2 Common Limiting Factors
advertisement
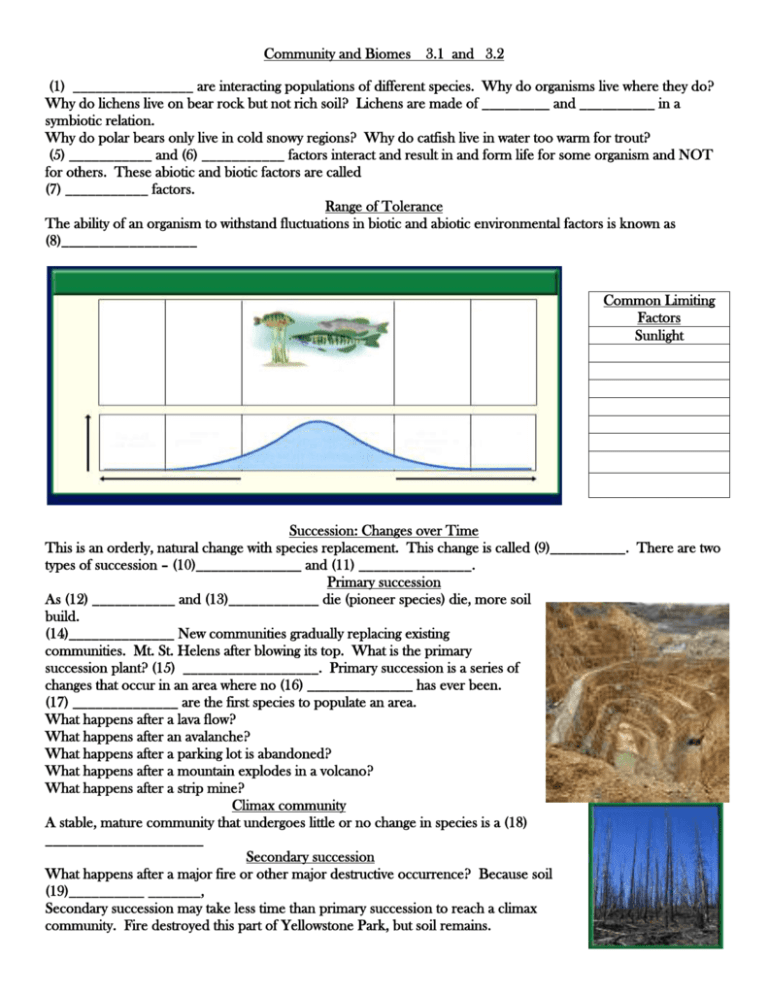
Community and Biomes 3.1 and 3.2 (1) ________________ are interacting populations of different species. Why do organisms live where they do? Why do lichens live on bear rock but not rich soil? Lichens are made of _________ and __________ in a symbiotic relation. Why do polar bears only live in cold snowy regions? Why do catfish live in water too warm for trout? (5) ___________ and (6) ___________ factors interact and result in and form life for some organism and NOT for others. These abiotic and biotic factors are called (7) ___________ factors. Range of Tolerance The ability of an organism to withstand fluctuations in biotic and abiotic environmental factors is known as (8)__________________ Common Limiting Factors Sunlight Succession: Changes over Time This is an orderly, natural change with species replacement. This change is called (9)__________. There are two types of succession – (10)______________ and (11) _______________. Primary succession As (12) ___________ and (13)____________ die (pioneer species) die, more soil build. (14)______________ New communities gradually replacing existing communities. Mt. St. Helens after blowing its top. What is the primary succession plant? (15) __________________. Primary succession is a series of changes that occur in an area where no (16) ______________ has ever been. (17) ______________ are the first species to populate an area. What happens after a lava flow? What happens after an avalanche? What happens after a parking lot is abandoned? What happens after a mountain explodes in a volcano? What happens after a strip mine? Climax community A stable, mature community that undergoes little or no change in species is a (18) _____________________ Secondary succession What happens after a major fire or other major destructive occurrence? Because soil (19)__________ _______, Secondary succession may take less time than primary succession to reach a climax community. Fire destroyed this part of Yellowstone Park, but soil remains. Annual wild flowers were the (20)_______ plant to grow back Previously in the forest, the shade of the trees inhibited wild flower growth. Within three years, grasses, ferns, pine seedling began replacing (21) ____________ (life cycle is on year) Once the pine seedling grow above the shade of grasses the trees will grow more quickly and then the large pole pine, back to the original community. Quiz Biomes 3.2 A large group of ecosystems that shares the same type of climax community is called a (22)______________. Types of Biomes: Those located on land is called a (23) _____________________. Types of Biomes located in streams, oceans, seas, and some inland lakes is called an (24) _____________________. About _____ of the earth surface is covered with water. What are the effects of tides? Gravitational pull of sun and moon cause the rise and fall of ocean tides. The part of the shoreline between the high and low tide is called the (25)__________________. Intertidal ecosystem have high levels of (26)________, and (27) _________ but waves keep production low. Aquatic Ecosystems 1. Where do most marine organisms live? Most of the organisms that live in the marine Biome are (26)_______________. Plankton are tiny organisms that float in the water of the (27)__________ zone. Plankton are (28)_____________; diatoms, eggs and very young marine animals. Plankton are important as the bas of the aquatic (29) _____________ ____________ 3. 2. 4. 5. 6. Freshwater biomes Another abiotic factor that limits life in deep lakes is (30)_________. In deep waters, it is colder and there are fewer species. Dead organisms drift to the bottom where bacteria break down and recycle (31)______________. 1. 3. 2. Terrestrial Biomes vary greatly. Each biome has a characteristic climate and community of organisms Tundra: Circles the (32)____________ pole. Very cold, few grasses and small plants. Thin layer of soil may thaw but soil underneath stays frozen called (33) _____________. Animals include:________________, _________________, _________________, _________________, ______________, _______________, _______________, _____________, ____________, _____________ , ___________________ The land is very cold and (34) ____________. Plants include (35) __________, (36) __________ , (37)_____________and willow trees. Desert Biome: The driest biome is the (38)_______________. Little to no plant life. Little to no rainfall. Leaves, stems and coatings conserve water, (39) __________________ and protective coatings. Usually less than ________ cm annually. With rainfall as the major (40) ____________ _________, vegetation in deserts varies greatly. The driest deserts are drifting sand dunes. Many desert plants are (41) _________ that germinate from seed and grow to maturity quickly after sporadic rainfall. The leaves of some desert plants (42) _________, or even drop off altogether, thus reducing water loss during extremely dry spells. Many desert mammals are small (43)________________ that remain under cover during the heat of the day, emerging at night to forage on plants. Life in the desert: _________, ___________, ___________ and _______________ are carnivores that feed on ___________, _____________, and small mammals of the desert. Grasslands or Prairies Biomes: Are covered with rich (44)___________, grasses and other grassland plants. Are known as breadbasket of the world. ________ and __________, ___________, ____________ and ___________ dogs. _________, reptiles and insects are also plentiful. Grasslands are large communities and occur principally in climates that experience a (45) ______ season, where insufficient water exists to support forests. Temperate Rain Forests Are (46)_________ common Also have large amounts of (47) ______________ Tropical Rain Forest: (48)______temperatures (49)_____ weather Lush plant growth Located near (50) _____________. A tropical Rain Forest: Canopy: A canopy layer, 25-45 meters high, is a (51)______________. The tree tops are exposed to rain, sunlight, and strong winds. The tree tops are exposed to (52)__________, (53)_________, and strong (54)__________. A few giant trees called emergent pole through the canopy. ________ frequently pass through. Birds, such as scarlet _______, live on the fruits and nuts of the trees. A tropical Rain Forest: Understory: In the understory, the air is (55)_______, (56)_______, and (57)_________. Vines grow from the soil to the canopy. (58) ____________ ants harvest leaves and bring them to the ground. Plants include _________, broad-leaved shrubs, and dwarf palms. Tree frogs are common understory amphibians. Reptiles include ______________ and ____________. A tropical Rain Forest : Ground: The ground layer is a moist forest floor. Leaves and other organic materials decay (59)________. Roots spread throughout the top (60)______ inches of soil. There is great competition for nutrients. Mammals living on the ground include: _________ and _________ such as the jaguar. ______, ____________, _____________, ___________ and ___________ live in the soil and quickly (61)_____________ organic materials. Life in rain forests: (62)________________ land is not common in rain forests. Some rain forests are important sources of(63)_______________ products and hardwood trees and have provided a sources of income for people. Soils in rain forests do not have substantial amounts of organic matter because leaf matter, which contains nutrients, disappears so (64)__________. Without organic matter, once rain forest soil is exposed and farmed, it becomes (65)____________, almost bricklike, and nutrient-poor in a matter of a few years. Temperate or deciduous Forest: Precipitation ranges from ______ to _______ cm annually. Soil is (66)____________. Forests are dominated by (67)_________________ hardwood trees that lose their foliage annually. The soil of temperate forest usually consists of a top layer that is (68) _________ in humus and a deeper layer of clay. The animals that live in the temperate deciduous forest include ________, _______, _________, ________, and _________. The weather in this area changes with the seasons. It becomes very (69)_______ in the winter and (70)_______ in the summer. There is enough rainfall to support (71)______________. Animals include: __________, __________, ___________, and bears. Latitude and climate: (72)_____________ and climate are abiotic factors that affect what plants and animals will survive in a given area. The two main factors that determine the biome are: __________ and ______________. 1. Groups of ecosystems that reach similar climax communities are ______________. A. stable B. biomes C. terrestrial D. populations 2. Explain the difference between the photic and aphotic zones of a marine biome. 3. Compare an estuary to an intertidal zone. 4. The floating protists, animal eggs and larvae in photic zones are known as ___________.A. tide pool collections B. foraminifera C. barnacles D. plankton 5. Describe the oxygen levels at different depths of a freshwater lake. 6. Which of the following biomes has the lowest annual precipitation? __________. 7. Grasslands are another name for which of the following? ___. A. savannas B. taiga C. tundra D. temperate forest 8. What is the Biome that is represented by the graph? 9. What is the Biome that is represented by the graph? 10. In which layer of a tropical rain forest are you most likely to find tree frogs? A. canopy B. understory C. ground D. root 11. Describe the importance of Bacteria in a healthy ecosystem? 12. As you travel north from a tropical rain forest, what are some of the variations you would observe? 13. In which biome would you expect the greatest biomass? A. tropical rain forest B. temperate deciduous forest C. desert D. taiga 14. In which biome would you expect to find only shallow-rooted grasses and small plants? A. grassland B. deciduous forest C. taiga D. tundra







