Acid & Base Notesheet 15-1 Defining Acids and Bases Name ___________________________________
advertisement

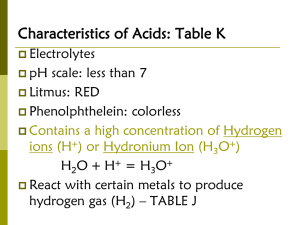
Acid & Base Notesheet Name ___________________________________ 15-1 Defining Acids and Bases Period________Date_______________________ 1. Properties of Acids and Bases: Taste Touch Reactions with Metals Electrical Conductivity Acid Base 2. Indicators: Turn 1 ___________________ in an acid and another color in a __________________. A. Litmus Paper: An aciD turns blue litmus paper _______ A Base turns red litmus paper ________. B. Phenolphthalein: C. pH paper: D. pH meter: 3. Neutralization: A reaction between an ___________ and ___________. When an acid and base neutralize, _________________ form. “Salts” are any _______________ compound formed from the metal ______________ of the base and ____________ from the acid. _______+ ______ → _______+ ______ Ex) HCl + NaOH → 4. Arrhenius Definition: A. An acid dissociates in water to produce ______________________, __________. B. A base dissociates in water to produce _______________________, __________. C. Problems with Definition: •Restricts acids and bases to _______________ solutions. •Oversimplifies what happens when ____________ dissolve in water. •Does not include certain compounds that have characteristic properties of acids & bases. Ex) 1 5. BrØnsted-Lowry Definition: A. An acid is a substance that can ____________ hydrogen ions. Ex) B. A base is a substance that can _____________ hydrogen ions. Ex) C. Advantages of BrØnsted-Lowry Definition •Acids and bases are defined independently of how they behave in ____________. •Focuses solely on __________________ ions. D. Hydrogen ion is the equivalent of a ______________. Therefore, acids are often called proton _________________ and bases are called proton _______________. 6. Hydronium Ion: A. Hydronium Ion – H3O+ This is a complex that forms in water. B. To more accurately portray the BrØnsted-Lowry, the _________________ ion is used instead of the ________________ ion. C. Amphoteric: A substance that can act as either an ___________ or a ____________. Ex.) 7. Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs: A pair of compounds that differ by only one ____________________ A. When an acid loses a hydrogen ion, it becomes its ________________________________. B. When an base gains a hydrogen ion, it becomes its ________________________________. Ex. NH3 ____ + H2O ____ ↔ NH4+ ____ + OH____ HCl ____ + H2O ____ ↔ Cl____ + H3O+ ____ A strong acid will have a _____________ conjugate base. A strong base will have a _____________ conjugate acid. C. A strong acid or base will ______________________ _____________________(break apart) in water. This is represented by a ___________________________ arrow. Ex) 2 D. A weak acid or base will _____________________ _____________________in water. This is represented by a _____________________________________ arrow. Ex) 8. Naming Acids Review Ch 7: A. Binary – H + one anion Prefix “hydro” + anion name + “ic” acid Ex) HCl _________________________________ Ex) _________ hydrophosphoric acid B. Tertiary – H + polyatomic anion no Prefix “hydro” end “ate” = “ic” acid end “ite” = “ous” acid Ex) H2SO4 _______________________________ Ex) _________ sulfurous acid 15-2 The Self-ionization of Water and pH 1. Water is amphoteric, it acts as both an acid and a base in the same reaction. Ex) H2O(l) + H2O(l) ↔ H3O+(aq) + OH-(aq) 2. In pure water at 25C, both hydronium ions and hydroxide ions are found at concentrations of _____________________. Because they are at ______________________ and you do not include liquid water in the equilibrium expression, Keq or Kw (water) can be expressed as follows: A. Formula for Kw = [H3O+] [OH-] 1.0 x 10-14M = [1.0 x 10-7M] [1.0x10-7M] 1.0 x 10-14M = [H3O+] [OH-] B. Using Kw in calculations: If the concentration of H3O+ in the blood is 4.0 x 10-8 M, what is the concentration of OH- ions in the blood? Is blood acidic, basic or neutral? 3 3. The pH scale: A. Used to determine if something is an ___________ or a ____________. A way to express _________ concentration based on logarithms. pH changes by a factor of ______. Ex) 10,000 = ________ therefore log 10,000 = ______ 0.001 = ________ therefore log 0.001 = ______ B. pH 1- 6.9: pH 7.1-14: pH of 7.0: _________ _________ _________ C. Copy the pH scale: pH [H3O+] sci. not. decimal [OH-] OH- D. pH = -log [H3O+] E. [H3O+] [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-14M F. pH + pOH = ______ H3 O+ H. Significant Digits Rule: The number of digits after the decimal point in your answer should be equal to the number of significant digits in your original number. Ex) –log[8.7 x 10-4 M] Calculator Answer = 3.060480747 Sig. Fig. pH = 3.06 Ex #1) [H3O+] = 7.3 x 10-5 M What is the pH value? Is it an acid, base or neutral? Ex #2) [OH-] = 5.0 x 10-2 M What is the pH value? Is it an acid, base or neutral? 4 Ionization of Acids & Bases: • H2SO4 2 H+ + SO4-2 • H3PO3 • Ca(OH)2 ~Sulfuric acid donates 2 H+ ions per mole. _____________ acid 15-3 Acid-Base Titration 1. An acid-base titration is a carefully controlled ____________________________ reaction which can determine the ________________________________ [ ] of an unknown solution. 2. To determine the concentration of an unknown substance, a ________________________________ is needed. This solution has a ____________________ concentration. 3. An indicator, usually ___________________________________, is used in a titration. 4. The point at which enough standard solution is added to neutralize the unknown solution is called ________________________________ ________________________. 5. The point at which the indicator changes color is called the ________________________________. 6. Therefore: [H3O+] = [OH-] at the equivalence point (which is usually the endpoint) Volume (acid) Conc.(acid) = Volume (base) Conc.(base) VaMa = VbMb Ex #1) Solutions of sodium hydroxide are used to unclog drains. A 43.0 mL volume of sodium hydroxide was titrated with 32.0 mL of 0.100 M hydrochloric acid. What is the molarity of the sodium hydroxide solution? Write the equation first: ______________ + ______________ → ______________ + ______________ ACID BASE SALT WATER 5 Ex #2) A volume of 25.0 mL of 0.120 M sulfuric acid neutralizes 40.0 mL of a sodium hydroxide solution. What is the concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution? Write the equation first. Ex #3) 24.9 mL of 2.88 M calcium hydroxide completely neutralizes 38.9 mL of a hydrobromic acid solution. What is the molarity of the hyrdobromic acid? Write the equation first. 6