Chapter 4 Notes
advertisement

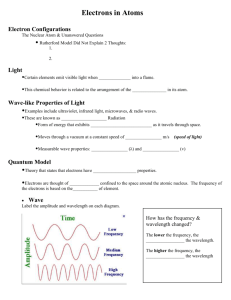
Quantum Model of the Atom – Chapter 4 Notes: What is a Quantum? Electrons are found in . When electrons get , they can from one energy level to another. An electron that has jumped to a new energy level is in an . The electron in its original position its in the . A is the amount of it takes to jump from one energy level to another. When an electron is excited, it gives off a burst of , called a . Different give off different of light. The Quantum Mechanical Model The was created in the 1920s. This model is very similar to . But, electrons don’t orbit the nucleus is neat paths. They are actually found in fuzzy cloud-like regions called . This model states that it is impossible to know the of an electron. It just illustrates places where electrons are . Where the cloud appears , the probability of finding an electron is . Where there is , the probability of finding an electron is . These clouds are called . Atomic Orbitals: An orbital is a area around the of an atom where you are likely to find . There are four types of orbitals: . The s-sublevel contains s-orbital. It can hold electrons and is shaped like a . The p-sublevel contains p-orbitals. It can hold electrons and is shaped like a . The d-sublevel contains d-orbitals. Most are shaped like a with 4 petals. The d-sublevel can hold electrons. There are types of f-orbitals. The f-sublevel can hold electrons. Draw an s-orbital: Draw a p-orbital: Draw a d-orbital: Quantum Numbers: 1. 2. 3. 4. There are four quantum numbers: quantum number quantum number quantum number quantum number Each number indicates a certain about electrons. Principal Quantum number – tells what the electron is in. Angular momentum quantum number indicates what the electron is in ( ). Magnetic quantum number indicates the way the orbital is . Spin quantum number describes which direction the electron is . Principal Quantum Number: Symbolized by the letter “ ” Indicates what an electron is in. When the electron is the first energy level, you would write n = For an electron in the second energy level, n = . An electron is in the 4th energy level. What is the value of n? For a particular electron n = 3. What energy level is it in? . The 1st energy level can hold electrons. This energy level only contains an . There are no -orbitals in the first energy level. The 2nd energy level can hold electrons total. It has an -orbital and a -orbital. rd The 3 energy level can hold electrons. It has -orbitals. th The 4 energy level can hold electrons. It has -orbitals. This number is usually combined with the orbital letter, like 2p or 4s. Angular Momentum Quantum Number Symbolized by the letter “___” Indicates the _________ of the orbital. Recall that type of orbital has a different shape. Value of L Orbital Shape If L = 1, what type of orbital is the electron in? _________________ What would be the value of L for an electron in an f-orbital? ____________ For a particular electron L = 2. Draw the shape of that orbital below. Magnetic Quantum Number Symbolized by the letter _______. Indicates the _________________ of the orbital around the _____________. Recall that there are three different p-orbitals. Each of these orbitals has a figure-eight shape. But, each is turned differently with respect to the nucleus. One is _________________, one ____________, and the other is ______________ _______________. The magnetic quantum number is used to describe what ______________ the orbital is in. There is only one type of ___orbital. So, there is only _______ possible value of m. For the s-orbital, m is always equal to ________. For the p-orbital, there are _________ possible values of m. For a p-orbital, m can equal _________________. The d-orbital has ________different values of m. The f-orbital has ________ possible values of m. Type of Orbital Possible Values of “m” Spin Quantum Number Symbolized by the letter “___.” Electrons __________ on an _________, the same way the Earth does. Electrons can spin or . The spin quantum number indicates which the electron is ________________ in. For any electron, the spin quantum # has two possible values: ________________. If the electron is spinning in a direction, spin = If the electron is spinning , spin = . An orbital can only hold _________ electrons. These electrons must have ____________________ ______________. This means for one of these electrons s= ½ and for the other s= - ½ When electrons are paired in an orbital, they must have different spins. This means for one of these electrons s= ½ and for the other s= - ½ Electron Configurations: There are three rules that guide how electron configurations are written: 1. Aufbau Principle - states that electrons are placed in orbitals one electron at a time AND that you always place electrons in the lowest energy orbital. That means start with the first energy level and work your way up. 2. Pauli-Exclusion principle – States that no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers. This means that electrons are sometimes paired together in orbitals, but they aren’t moving the same way. One electron is spinning counterclockwise and one is clockwise. 3. Hund’s Rule – states that when multiple orbitals are available (like in the p, d, or f sublevel), put one electron in each energy level first. Then pair electrons up.