Anti-Ischemic Drugs: MOA, Effects, Contraindications
advertisement
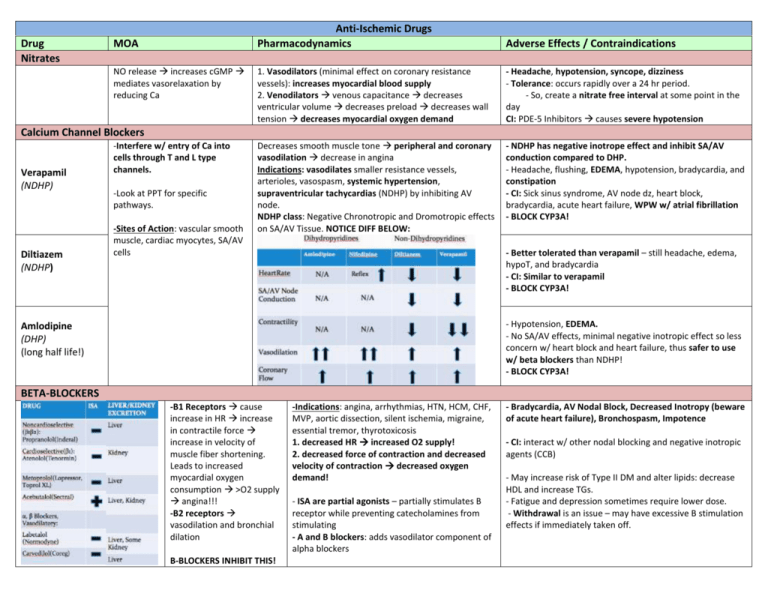
Drug Nitrates MOA NO release increases cGMP mediates vasorelaxation by reducing Ca Anti-Ischemic Drugs Pharmacodynamics Adverse Effects / Contraindications 1. Vasodilators (minimal effect on coronary resistance vessels): increases myocardial blood supply 2. Venodilators venous capacitance decreases ventricular volume decreases preload decreases wall tension decreases myocardial oxygen demand - Headache, hypotension, syncope, dizziness - Tolerance: occurs rapidly over a 24 hr period. - So, create a nitrate free interval at some point in the day CI: PDE-5 Inhibitors causes severe hypotension Decreases smooth muscle tone peripheral and coronary vasodilation decrease in angina Indications: vasodilates smaller resistance vessels, arterioles, vasospasm, systemic hypertension, supraventricular tachycardias (NDHP) by inhibiting AV node. NDHP class: Negative Chronotropic and Dromotropic effects on SA/AV Tissue. NOTICE DIFF BELOW: - NDHP has negative inotrope effect and inhibit SA/AV conduction compared to DHP. - Headache, flushing, EDEMA, hypotension, bradycardia, and constipation - CI: Sick sinus syndrome, AV node dz, heart block, bradycardia, acute heart failure, WPW w/ atrial fibrillation - BLOCK CYP3A! Calcium Channel Blockers Verapamil (NDHP) Diltiazem (NDHP) -Interfere w/ entry of Ca into cells through T and L type channels. -Look at PPT for specific pathways. -Sites of Action: vascular smooth muscle, cardiac myocytes, SA/AV cells - Better tolerated than verapamil – still headache, edema, hypoT, and bradycardia - CI: Similar to verapamil - BLOCK CYP3A! - Hypotension, EDEMA. - No SA/AV effects, minimal negative inotropic effect so less concern w/ heart block and heart failure, thus safer to use w/ beta blockers than NDHP! - BLOCK CYP3A! Amlodipine (DHP) (long half life!) BETA-BLOCKERS -B1 Receptors cause increase in HR increase in contractile force increase in velocity of muscle fiber shortening. Leads to increased myocardial oxygen consumption >O2 supply angina!!! -B2 receptors vasodilation and bronchial dilation B-BLOCKERS INHIBIT THIS! -Indications: angina, arrhythmias, HTN, HCM, CHF, MVP, aortic dissection, silent ischemia, migraine, essential tremor, thyrotoxicosis 1. decreased HR increased O2 supply! 2. decreased force of contraction and decreased velocity of contraction decreased oxygen demand! - ISA are partial agonists – partially stimulates B receptor while preventing catecholamines from stimulating - A and B blockers: adds vasodilator component of alpha blockers - Bradycardia, AV Nodal Block, Decreased Inotropy (beware of acute heart failure), Bronchospasm, Impotence - CI: interact w/ other nodal blocking and negative inotropic agents (CCB) - May increase risk of Type II DM and alter lipids: decrease HDL and increase TGs. - Fatigue and depression sometimes require lower dose. - Withdrawal is an issue – may have excessive B stimulation effects if immediately taken off. Ranolazine - Inhibits late phase of myocyte Na current (late INa) - If you’re ischemic, Na is increased, leading to the exchanger allowing more Ca inside which causes contraction. Impaired relaxation angina. Anti-Platelet Aspirin P2Y12 Antagonists Clopidogrel Prasugrel - Increases Total Exercise Time and Time to Ischemia - Decreases Freq. of Anginal attacks, # of SL NTG taken and recurrent ischemia. - No mortality benefit. - No hemodynamic effects on HR or BP Indications: ACS where Ischemia is rapid and caused by platelet mediated thrombus. Plaque rupture allows platelet adhesion, activation, and aggregation. Thrombus can be either partially or completely occlusive. - Inhibits COX1 - Blocks formation of TXA2, a platelet stimulator. - High doses inhibit COX2 which has anti-inflammatory effects - Irreversible P2Y12 Inhibition - P2Y12 receptor activated by ADP G protein coupled platelet activation and aggregation MOA - Absorbed in GI tract - Enteric Coated Delays Absorption - Irreversible Inhibition - Indication: secondary prevention for stable CAD, Post-ACS, Post-PCI, Post-CABG; reductions in death, MI, recurrent ischemia - Synergistic effect when given w/ aspirin. Indications: Clopidogrel – secondary prevention of recurrent ischemia in pts allergic to ASA post MI, post CVA or w/ PAD Added to Aspirin: Post-ACS, Post-PCI, where dual antiplatelet therapy for 12 mo is recommended Prasugrel – reduce rate of thrombotic events post-PCI in ACS - Bleeding! - CI: NSAIDs- may exacerbate bleeding and compete for COX1 - True aspirin allergy can be life threatening – use clopidogrel as alternative, can desensitize - Prasugrel had much higher rates of major bleeding