WITH CAUTION - Cardiology Update FK UNAND
advertisement

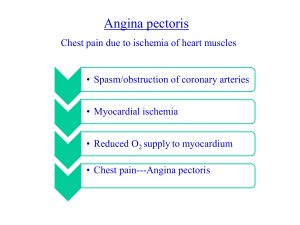
New Paradigm of Anti Anginal Therapy dr.Yerizal Karani SpPD,SpJP(K) Angina Pectoris • Angina pectoris sudden severe pressing chest pain or heaviness radiating to the neck, jaw, back and arms associated with diaphoresis, tachypnea and nausea. • Angina insufficient coronary flow to meet oxygen demands of the myocardium precipitated by any activity/process that creates an imbalance in O2 supply and demand Types of Angina • Angina occurs in three overlapping patterns: – Stable angina – Unstable angina – Prinzmetal (variant) angina Nitrat • Nitrogliserin (gliseril trinitrat) very fast onset sublingually acute condition • Isosorbide dinitrate fast onset sublingually (substitute of gliseril trinitrat) • Isosorbide mononitrate slow onset used in preventing angina Nitrates Tolerance " Decrease in the effect of a drug when administered in a long-acting form" • Develops with all nitrates • Is dose-dependent • Disappears in 24 h. after stopping the drug • Tolerance can be avoided – Using the least effective dose – Creating discontinuous plasma levels Nitrates Contraindications • • • • Previous hypersensitivity Hypotension ( < 80 mmHg) AMI with low ventricular filling pressure 1st trimester of pregnancy WITH CAUTION: ž ž ž Constrictive pericarditis Intracranial hypertension Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Contraindication B-Blocker • Hypotension: BP < 100 mmHg • Bradycardia: HR < 50 bpm • Chronic bronchitis, ASTHMA • Severe chronic renal insufficiency Reasons for Using Nitrates and Beta Blockers in Combination in Angina • Beta Blockers prevent reflex tachycardia and contractility produced by nitrate-induced hypotension. • Nitrates prevent any coronary vasospasm produced by Beta Blockers. • Nitrates prevent increases in left ventricular filling pressure or preload resulting from the negative inotropic effects produced by Beta Blockers. • Nitrates and Beta Blockers both reduce myocardial oxygen consumption by different mechanisms. • Nitrates and Beta Blockers both increase subendocardial blood flow by different mechanisms Anti Anginal Effect Endocardial blood flow Collateral Wall tension Heart rate Contractility Cardiac work Nitrate B-Blocker CCB ↑↑ ↑ ↑ ↑↑ → ↑↑ ↓ →↑ ↓ ↑ (reflex) ↓↓ ↑↓ ↑ (reflex) ↓↓ ↓→↑ ↓↓ ↓↓ ↓↓ Take Home Messages • Angina pectoris imbalance of O2 in supply & demand of the myocardium • Nitrogliserin: very fast onset of nitrate in angina pectoris THANK YOU...