4-8-15 Biomes & Levels of Organization Handout
advertisement

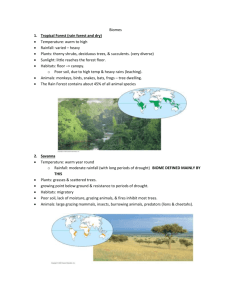
Levels of Life’s Hierarchy (Levels of Organization) Least specific Biosphere – All environments on earth that support life (Basically, the Earth and the sky above it that has living things occupying it.) Biome – Major types of ecological associations that occupy broad geographic regions of land or water and are characterized by organisms adapted to the particular environments Ecosystem – all living organisms in a particular area as well as the nonliving, physical components they interact with (ex. Sunlight, water, etc.) Community – All living things in an area Population – Single species living in a single area Organism – Single individual Organ System – group of organs working together for a certain function Organ – 1 part of an organ system Tissue – group of similar cells that do a particular function for an organ Cell – Smallest unit of life (All living things are made of up one or more cells) Organelle – “organ” of a cell Molecule – cluster of atoms held together by chemical bonds Atom - basic unit of matter made of dense nucleus (protons and neutrons) with electron cloud around it Most specific Biomes 1. Tropical Forest (rain forest and dry) Temperature: warm to high Rainfall: varied – heavy Plants: thorny shrubs, deciduous trees, & succulents. (very diverse) Sunlight: little reaches the forest floor. Habitats: floor –> canopy. o Poor soil, due to high temp & heavy rains (leaching). Animals: monkeys, birds, snakes, bats, frogs – tree dwelling. The Rain Forest contains about 45% of all animal species 2. Savanna Temperature: warm year round o Rainfall: moderate rainfall (with long periods of drought) BIOME DEFINED MAINLY BY THIS Plants: grasses & scattered trees. o growing point below ground & resistance to periods of drought. Habitats: migratory Poor soil, lack of moisture, grazing animals, & fires inhibit most trees. o Biome is dependent upon fires to keep nutrient rich enough to support life Animals: large grazing mammals, insects, burrowing animals, predators (lions & cheetahs). 3. Deserts • Temperature: very hot, and cold (Antarctica) • Rainfall: dry • Plants: none, deep rooted shrubs, succulents. – waxy coating to prevent water loss – many seeds that remain dormant until it rains • Sunlight: extreme • Habitats: burrows, active at night • Animals: ants, birds, rodents, lizards, snakes, & hawks. 4. • • • • Chaparral Temperature: mild winter, hot summer Rainfall: rain in winter, dry in summer Plants: dense shrubs with tough evergreen leaves. Seasonal plants. – Food reserves in roots allow for rapid growth after frequent fires. – Seeds only germinate after hot fire. Animals: deer, birds, rodents, lizards & snakes 5. Temperate grasslands (Prairies) Temperature: relatively cold Rainfall: rain, but periodic severe droughts Plants: grass, mostly treeless o fire & grazing prevents tree growth Habitats: bird nests on ground, burrows. Animals: large grazing mammals (bison, wild horses). Soil supports diverse microorganisms & small animals. One of the most productive agricultural regions in the world 6. Temperate (deciduous) Forest Temperature: cold winter, hot summer Rainfall: high precipitation Plants: deciduous trees (oak, hickory, maple) Habitats: rich soil, leaf litter, burrow Animals: invertebrates, mice, shrew, squirrels, birds, bobcats, foxes, bears, & mountain lions. Most destroyed by loggers & urban development. 7. • • • • • • • 8. • • • • • • • Taiga (Coniferous) ForestTemperature: long cold winters, short wet summers Rainfall: considerable precipitation (snow) Plants: cone bearing evergreens – (spruce, pine, fur) Habitats: soil thin & acidic Animals: moose, elk, bears, wolves, hares, migratory birds. Heavily logged. Largest terrestrial biome Tundra Temperature: extremely cold Rainfall: little Plants: no trees, shrubs, grasses, mosses, and lichens. – Permafrost prevents deep root penetration Sunlight: little light for much of the winter, constant daylight in summer Habitats: migratory (summer is a breeding ground), high altitude, permafrost, soil continually saturated due to poor drainage and slow evaporation. Animals: well insulated (oxen & caribou), lemmings, fox, snowy owl. During the summer, clouds of mosquitoes fill the air due to the marshy ground.