The Weather Weather is the state of the atmosphere. To be more
advertisement
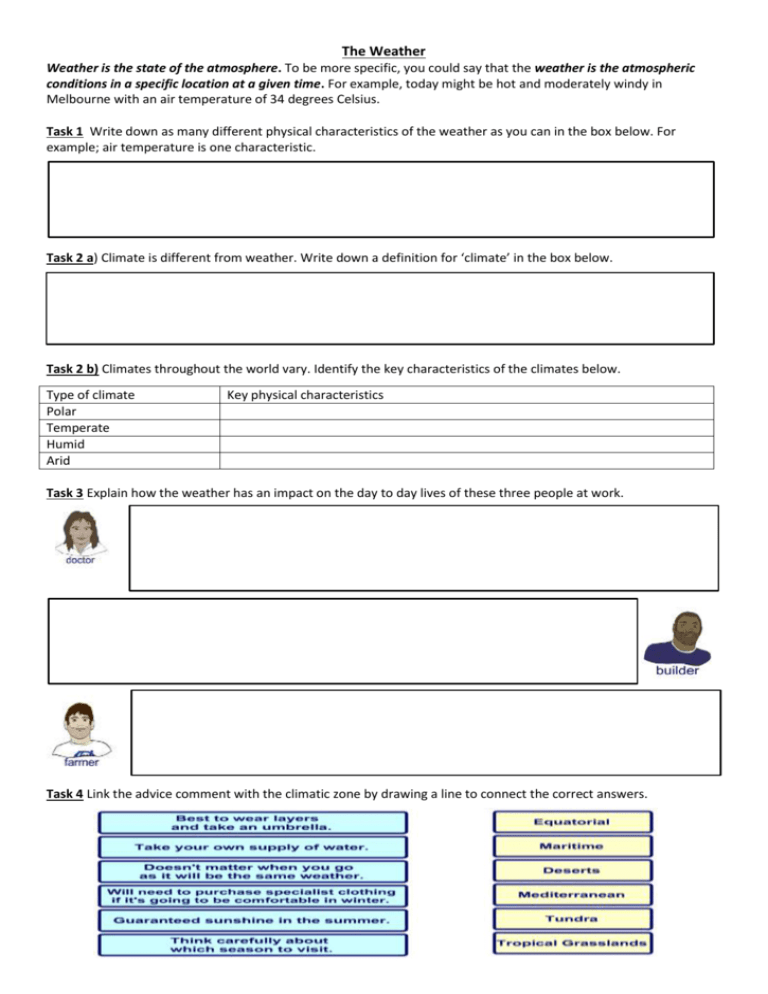
The Weather Weather is the state of the atmosphere. To be more specific, you could say that the weather is the atmospheric conditions in a specific location at a given time. For example, today might be hot and moderately windy in Melbourne with an air temperature of 34 degrees Celsius. Task 1 Write down as many different physical characteristics of the weather as you can in the box below. For example; air temperature is one characteristic. Task 2 a) Climate is different from weather. Write down a definition for ‘climate’ in the box below. Task 2 b) Climates throughout the world vary. Identify the key characteristics of the climates below. Type of climate Polar Temperate Humid Arid Key physical characteristics Task 3 Explain how the weather has an impact on the day to day lives of these three people at work. Task 4 Link the advice comment with the climatic zone by drawing a line to connect the correct answers. Task 5 Identify which climate graph represents the climate for each of the world locations. Task 6 Now it’s time to try and create your own climate graph using the statistics below. You have been given three different sets of data for your climate graph; average maximum temperature, average minimum temperature, and average rainfall (precipitation). Collect graph paper from Mr Jones and get started. Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Average Temp min (°C) 14 14 13 11 8 7 6 6 8 9 11 12 Average Temp -max (°C) 26 26 24 20 17 14 13 15 17 19 22 24 Rainfall (mm) 48 46 56 58 53 53 48 48 58 66 58 58 What is the Water Cycle? The ‘water cycle’ (or hydrological cycle) is the continual movement of water on, above or below the earth’s surface. This cycle of water occurs through various physical processes including evaporation, condensation and precipitation. Task 7 a) How much of the Earth’s surface is covered in water? Task 7 b) What percentage of the Earth’s water storage is held in the atmosphere at any given time? Water Cycle Definitions Task 5 Use these key terms to match the definitions below: surface runoff precipitation condensation transpiration Definition The process where water changes from a liquid to a vapour The process by which cooling vapour turns into a liquid Water that falls on the Earth’s surface The movement of water over the land, possibly as a river Plants giving off water vapour from their leaves Water that has sunk through the soil into the rocks below evaporation groundwater Term Task 8 Label the water cycle diagram below with the terms above as well. Task 9 a) Which type of rainfall is caused by the sun heating the ground? Task 9 b) Which type of rainfall is caused by two air masses meeting? Task 9 c) How does ‘relief rainfall’ occur? Explain below. Summary Once you have completed the tasks above, spend some time navigating the interactive PowerPoint on ‘An Introduction to Weather and Climate’ for yourself. Have a go at each of the animated tasks including the ‘BINGO’ game at the end of the slideshow.