Assessment_2studyguide_answerkey[1]
advertisement
![Assessment_2studyguide_answerkey[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007026684_1-c6efcbdf4e41e1f1ada4b1da4c5dcee9-768x994.png)
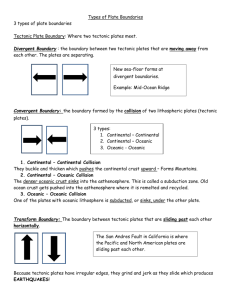
Quarter 1 Assessment #2 Study Guide Assessment on Session 14 Notebook Sessions 5-14 1. What was the scientist’s name who came up with the theory of the moving continents? Alfred Wegenar 2. Explain the theory of Pangaea. The continents were once one big land mass. 3. What is the evidence that supports the theory of continental drift? Fossils, geology, climate and “puzzle pieces” look like continents fit 4. What are the 3 types of boundaries? Divergent Convergent Subduction-special type of convergent Transform 5. Explain what action/direction the plates are moving at a divergent boundary. 6. Explain what is occurring under the surface at a divergent boundary. 7. Explain what is occurring above the surface at a divergent boundary. Divergent Boundaries Pull Apart: plates rift/split ; hot molten rock from the mantle rises, cools and causes the floor to spread causing new rock to form. Ex. Mid-Atlantic Ridge and Iceland 8. Explain what action/direction the plates are moving at a continental convergent boundary. 9. Explain what is occurring under the surface at a continental convergent boundary. 10. Explain what is occurring above the surface at a continental convergent boundary. Convergent Boundaries Collide: plates collide/crash into one another and form mountains over millions of years. Ex. Himilayas 11. Explain what action/direction the plates are moving at an oceanic convergent boundary. 12. Explain what is occurring under the surface at an oceanic convergent boundary. 13. Explain what is occurring above the surface at an oceanic convergent boundary. Subduction: oceanic plates crash/collide with continental plates or oceanic plate, and slide beneath/under them creating trenches. Volcanoes are often formed in this way along oceanic and continental plates Ex. Mount St. Helens 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Hotspots-hot material rises up through the mantle, heats up the lithosphere and forms a volcano. Theses are NOT on plate boundaries Explain what action/direction the plates are moving at a transform boundary. Explain what is occurring under the surface at a transform boundary. Explain what is occurring above the surface at a transform boundary. Transform Boundaries Slide Sideways: continental plates scrape together past each other often causing earthquakes. Ex. San Andreas Fault Compare and contrast the terms lava and magma. Both hot rock, magma is under the crustal surface and lava is above the crustal surface. What type of geological activity can be found along plate boundaries? Mountains forming Earthquakes Volcanoes 19. At which boundary can you find a rift valley? Divergent Boundary 20. What are convection currents in the mantel cause? Movement of the lithosphere/tectonic plates 21. How were the Hawaiian Islands Formed? Hot spots 22. What is a seismograph used for? An instrument that records tectonic plate movement, which includes earthquakes. 23. What do you call smaller vibrations after an earthquake? Aftershocks A good website to review is http://www.platetectonics.com/book/page_5.asp