A Whistle stop tour * Grammar! - Brookmans Park Primary School
advertisement

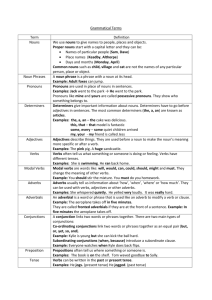
A Whistle stop tour – Grammar! Word Types nouns adjectives verbs adverbs pronouns determiners conjunctions Types of noun Concrete nouns (ones you can see, touch, smell, hear) Abstract nouns ( eg happiness, power, success) Collective nouns ( a pack of wolves) Noun phrases: group of words doing the job of a noun The old yak walked slowly to the field. Pronouns Pronouns stand in place of nouns to avoid repetition. Jane went to school. She went to school. Pronouns such as mine and yours are known as possessive pronouns. Determiners Determiners give important information about noun introduces a noun phrase Examples: the, a, an (also called articles) the picture was amazing this, your that book is fantastic some, every some noisy people arrived my, your my name is Sam Adjectives Adjectives describe nouns/pronouns Adjectival phrases are a group of words that describe nouns/pronouns This pie is very delicious and extremely expensive. Everyone was really delighted when the winner was announced. The new outfit was very pricey but incredibly smart. beautiful. Verbs Verbs are doing words. A verb can express a physical action, a mental action, or a state of being. Verbs have different tenses different genres of writing often require a specific verb tense. Regular and irregular tenses. Modal verbs verbs of possibility Modal verbs are words like will would can could should might must We must follow directions. Verbs Subject verb agreement The children wasn’t very happy. The children weren’t very happy. Prepositions A word that shows position and how things relate in time and space. Position The cat sat by the window. Time The match is on Friday. How We had to go without them Conjunctions Conjunctions usually connect words or ideas together inside a sentence. (Have been referred to as connectives) Co-ordinating conjunctions (FANBOYS) for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so, Subordinating conjunctions: if, because, although, that, while, even though, unless, since, when, whenever, before, after Many subordinating conjunctions can be other parts of speech Adverb: Jill came tumbling after. Preposition: Jill came tumbling after Jack. Subordinating Conjunction: after Jack had fallen. Jill came tumbling Adverbs Usually tell us information about ‘how’ ‘when’ ‘where’. They can be used with verbs, adjectives or other adverbs. He shouted loudly. The game was really exciting. She ran very quickly. The film will start soon. We can sit over there. Connecting adverbs Can be used to link ideas in one sentence to ideas in another. Addition: furthermore, moreover Opposition: however, nevertheless Reinforcing: besides, after all Explaining: for example, in other words Listing: first of all, finally Indicating result: consequently, therefore, Indicating time: meanwhile, just then These words create cohesion within their writing. Sentence Parts Phrase: a small group of words that do not make sense on their own. Clause: a group of words that includes a verb and can stand on its own. Simple sentence: A simple sentence has one subject and one verb. Compound sentence: Two or main clauses that are joined by a conjunction. Complex sentence: A main clause joined to one or more subordinate clauses.