BIOMES CHAPTER 2 PowerPoint guided rdg
advertisement
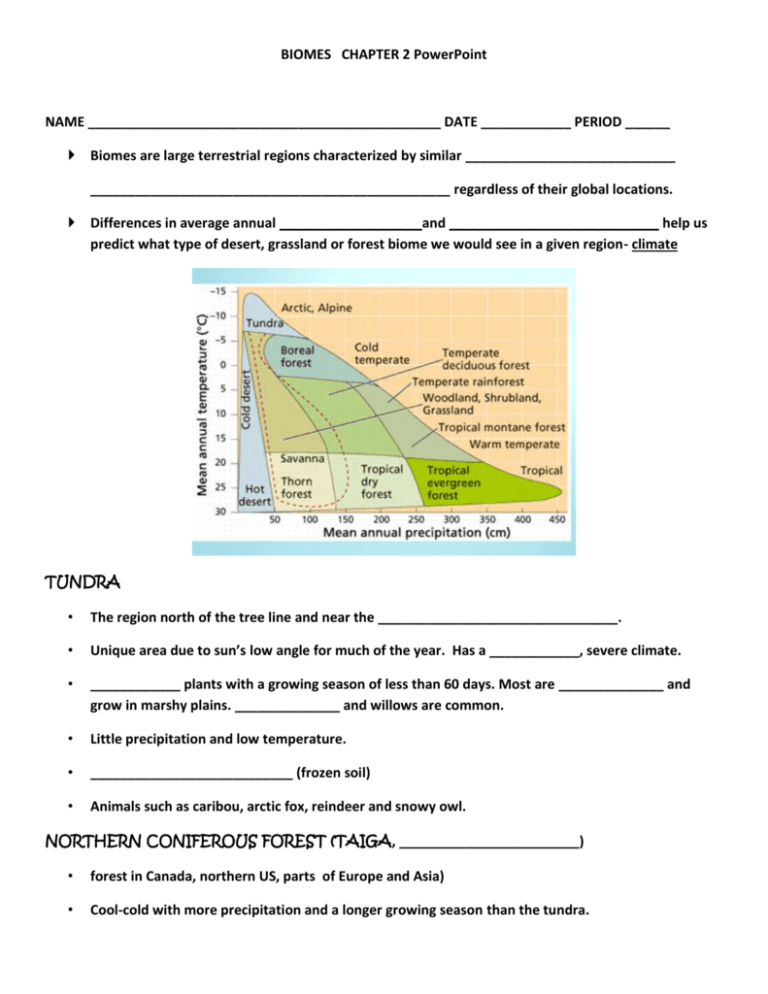
BIOMES CHAPTER 2 PowerPoint NAME _______________________________________________ DATE ____________ PERIOD ______ Biomes are large terrestrial regions characterized by similar ____________________________ ________________________________________________ regardless of their global locations. Differences in average annual ___________________and ____________________________ help us predict what type of desert, grassland or forest biome we would see in a given region- climate TUNDRA • The region north of the tree line and near the ________________________________. • Unique area due to sun’s low angle for much of the year. Has a ____________, severe climate. • ____________ plants with a growing season of less than 60 days. Most are ______________ and grow in marshy plains. ______________ and willows are common. • Little precipitation and low temperature. • ___________________________ (frozen soil) • Animals such as caribou, arctic fox, reindeer and snowy owl. NORTHERN CONIFEROUS FOREST (TAIGA, ________________________) • forest in Canada, northern US, parts of Europe and Asia) • Cool-cold with more precipitation and a longer growing season than the tundra. • Lots of _______________________________ trees such as pine, spruce and fir. • Dense forests allow little ________________________to reach the ground. Little _________________________ on the shady forest floor. • Big mammals such as elk, deer, moose, bear, and smaller animals such as weasels, snowshoe hares and lots of birds. DECIDUOUS FOREST This is the biome we live in! • Temperature is moderate, climate has warm, humid summers and cold winters. Rainfall is from 3060 inches/year. • Dominated by broadleaf, ________________________ trees and soil is rich with ___________. • High productivity and diversity of organisms GRASSLANDS • Also called _____________, ___________________ (S. America), steppes (Russia, Asia, and Europe). • Are usually located in the ________________________ of continents. • Not enough precipitation to support tree growth, but enough for lots of grasses. Often used as farmlands. • Animals found are bison, antelope, coyote, badgers, prairie dogs, rattlesnakes. Have lots of insects. DESERTS • Receive less than 10 inches of rainfall/year. • Plants and animals are adapted to __________________ water. • Largest are the Sahara and ________________. Sahara is getting larger due to drought, __________ _________________ and _______________________________ for fuel. • Occur in the _____________________ of continents and on the leeward side of mountains. • Ecosystems are easily damaged and are severely affected by human activities such as _________________, city growth, _________________________________, and ______________________. TROPICAL FORESTS • Located near the _________________________. • Contain the greatest plant and animal ___________________________ of all ecosystems. • Soils are thin and ________________________. No freezing and lots of moisture. • Largest rain forests occur in the _______________________________ of South America. • Major reservoirs for the production of atmospheric _______ and the consumption of CO2. • Many forests are being cleared for ________________________, ____________________ and lumber. SHRUBLANDS • Covered by shrubby vegetation with hard, thick, waxy leaves that are _______________________ resistant. • Climate is hot and dry in the summer and cool/cold, and wet in the winter. • Coast of California-______________________ • Subject to fire. AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS FRESHWATER – inland waters with few salts. Can be flowing (river) or standing (lake) FLOWING WATERS • Springs → Brooks → Streams → Creeks → Rivers • Rivers ◦ Erode banks ◦ Carry sediment which get deposited and forms fertile soils. STANDING WATERS • The water is _________________________________. • Puddles, ponds, bogs and ______________________. • Salt concentrations may vary. • All are temporary because they will eventually fill with sediment (____________________________). WETLAND AREAS • Swamps- shallow with trees and shrubs (Okefenokee Swamp) • Bogs- shallow with trees and shrubs. Accumulates a deposit of peat (dead plants) such as Sphagnum moss. Water is acidic and low in _________________________. • Marshes – ____________________________________ (Florida Everglades) • Swamps and Marshes are areas of breeding and rearing habitats for insects, birds, amphibians, reptiles, shrimp MARINE WATERS • All the oceans are connected and form one large ecosystem. • Moderates earth’s _____________________ by absorbing the sun’s energy in the summer and releasing it in the winters. • Dissolved salts/minerals increase with ___________ and nearness to the equator. Salinity is less near the shoreline. • Most productivity is along the continental shelf, shorelines and in the ___________________________. • Small phytoplankton called ______________________produce a large part of earth’s oxygen. ESTUARIES • Transitional zones between freshwater and open ocean. • Also called bays, coves, sounds, and are sheltered from direct wind and ocean waves. • Are very productive regions and are considered a _________________________for many sea animals. • Chesapeake Bay in Virginia is the largest in the world. MANGROVES • Trees and shrubs that grow in___________________ coastal sediment habitats in the tropics and subtropics • Plants have physiological adaptations to overcome the problems of anoxia (low oxygen), high salinity and frequent _____________________________________________. CORAL REEFS - the marine equivalent of _______________________________________ forests. • habitat for _______ of all marine species. • are underwater structures made from ____________________________________ secreted by _________________ which are tiny, living animals. • grow best in _____________, ___________________, clear, sunny and agitated waters.