Chapter 7 Regions of the United States Section 1: The Northeast
advertisement

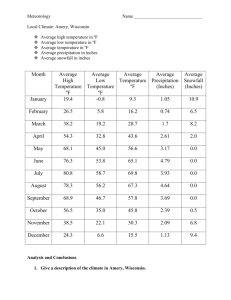
Chapter 7 Regions of the United States Section 1: The Northeast States: Pennsylvania, New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, Vermont, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island and Maine This region includes 9 states that are located in the northeastern part of the United States. The region is known for its beautiful landscape where we see a unique combination of precipitation, soil and a variety of trees. Every years thousands travel to this region for its many tourist attractions. These include: Niagara Falls (NY), rolling farmland (PA), liberty bell (PA) and all that New York City has to offer. Apart from the coal rich mountains of Pennsylvania the region has few mineral resources. But this region does have one very key resource that has turned it into a center of trade and commerce and that is water. Since colonial times people of the northeast have engaged in commerce and fishing. The NE many rivers and lakes include Connecticut River and Hudson River. This region is home to many immigrants who first called this area home in the 1700’s. The cities have grown over the years to form a megalopolis-very large city. This name has been used to describe the region from Boston, Mass to Washington, D.C. About 40 million people now live in this region. Problems facing this area now are overpopulation and pollution. Yet New York remains the business capital of the world and it’s recognized worldwide. Section 2: The South States: Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Tennessee, Alabama, Georgia, Florida, South Carolina, North Carolina, Virginia, Kentucky, West Virginia, Maryland, Delaware The south stands out from the other regions due to its extremely humid, subtropical climate. The region includes great beaches, thick forest, mountain ranges and rolling hills. The south’s location near the equator makes it warmer than other regions. In additions the south’s weather patterns are altered by warm waters in the Gulf of Mexico and Atlantic Ocean. The coastal areas of Miss and Georgia receive over 60 inches of precip annually. One distinct area is the swamplands and bayous of Florida and Louisiana. Bayous are marshy inlets of lakes or rivers. In Florida the Everglades; a vast area of swampland is covered by tall grass and home to a wide variety of wildlife. People have taken advantage of the rich soils dating all the way back to the Native Americans. The traditional image of the south has been with rural and largely dependent on agriculture. But the south has industry as well. Birmingham,AL is known as the “Pittsburgh of the south”. Textile mills have been built in the Appalachian Mountains. In the 1900’s the oil industry in areas like Texas and Oklahoma proved to be very profitable. Not only has business growth led to increase in population for this region but also weather. Many people living in the south have moved there to escape colder climates. Ex: Florida-retired. This region stretching from the Carolina’s to southern California has been called the Sunbelt. Over the years the southern population has become varied. Its proximity to Central and South America bring thousands of immigrants each year. Over ½ of the nation’s African American population live in the south and over ½ of the Hispanic population’s lives in the south. This includes the Latin Americans in Florida and Mexican Americans in Texas. Section 3: The Midwest States: North Dakota, South Dakota, Kansas, Nebraska, Missouri, Iowa, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana, Michigan and Ohio Most of the Midwest is flat with very fertile soil making it America’s richest farmland. The climate also favors farming activities. While the winters do get cold the summers remain mild and the growing season long. The growing season is defined as the time period from the last frost of the spring to the first frost of the fall. The growing season for most of the Midwest is 200 days long while in areas of Canada its only 120 days long. Some example of crops grown in the Midwest include: corn, wheat and grain In smaller Midwest towns the city revolves around the grain elevator-a tall building equipped with machinery that houses the crop. Some of the bigger cities in this region include: Chicago, Omaha, and St. Louis Like the NE region, the MW region relies heavily on water as a valuable resource. Major rivers like the Missouri and Mississippi power industry in cities along these rivers. Section 4: The West States: New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, Idaho, Utah, Nevada, Arizona, California, Oregon and Washington The diverse landscape of this region makes it a popular area for tourist and homeowners. From the towering snow-capped Rocky Mountains to the river-carved canyons the west is home to some of Americans most amazing natural landscapes. The variety of climates is also seen in the West. Some areas receive little to no rainfall while others lead the nation in rainfall per year. Ex: San Diego, California = 9 inches per year / Seattle, Washington = 39 inches per year The physical geography will greatly differ in these areas. In desert area in Arizona cactus will be abundant and in Washington the fir trees and giant redwoods will fill the forest. Hawaii is included in this region and is home to its own special geography. Hawaii is home to tropical forest as well as mountain regions that have been formed from volcanic activity. A world apart in Alaska, the tundra dominates the landscape. The area is rich in natural resources. Ex: California (gold), Nevada (silver), Alaska (oil). This abundance of natural resources has led to rapid population growth in the late 1800’s. Two other resources include forestry and fishing. Major cities in this region include: Phoenix, AZ; Los Angeles, CA; San Francisco, CA; Denver, CO; Seattle, WA; Portland, OR; Anchorage, AK and Honolulu, HI