Principles and Methods in Science Final Exam Review Sheet
advertisement

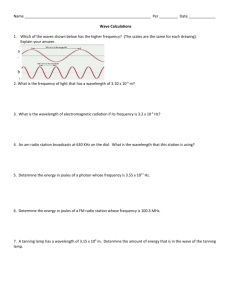
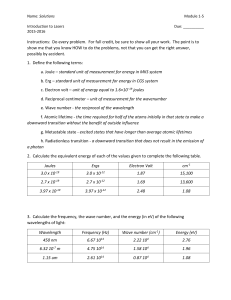
Principles and Methods in Science Final Exam Review Sheet Section 1: Scientific Method 1. What are the basic steps in the scientific method? 2. What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory? 3. What is the difference between qualitative information and quantitative data? 4. What is a control group? How does it differ from an experimental group? 5. What are standard conditions? Why are they necessary in a controlled experiment? 6. What are replicates? Why are they necessary to ensure accurate results in an experiment? 7. What is the difference between an independent and dependent variable? Where should each be placed when graphing data? Section 2: Energy 1. Why is the sun the origin of energy in our universe? 2. What are Newton's laws of motion? Be able to explain them. 3. How can energy be defined? How is it related to work? 4. How is power defined? 5. How do we define kinetic and potential energy? How are they related to each other? Give some examples of each. 6. What is heat? How does it naturally flow? How is it different from temperature? 7. What is absolute zero? 8. What does the specific heat of a substance tell us about it? 9. What are the three ways heat can be transferred? How are they different? What is the only one that can transfer heat without a physical medium? 10. What are the laws of thermodynamics? Be able to explain each and understand how they apply to different situations. Section 3: Chemistry 1. What is matter? How is matter conserved in chemical reactions? 2. Describe the basic structure of an atom. What are the three subatomic particles, what is their charge and where are they found in the atom? 3. What is an element? How is it different from a compound? 4. What does the atomic number tell us about an atom? What does the atomic mass tell us? 5. What is an isotope? What uses have been found for them? 6. What is an ion? How are they formed? What are the specific terms for positive and negative charged ions? 7. What is an atom's valence? What is the octet rule and how does it determine bonding in atoms? 8. Describe and provide examples for both ionic and covalent bonding. 9. What is the difference between catabolic and anabolic reactions? Endergonic and exergonic? 10. Be able to identify the reactants and products in a chemical equation. Why must an equation be balanced? Section 4: The Nucleus 1. Describe protons, neutrons, electrons, quarks and neutrinos. What properties do they have in terms of charge, interactions with other particles, mass, etc.? 2. Describe the structure of the nucleus of an atom. How much of the total mass and total volume of an atom does it account for? What is its charge? 3. List and describe the four fundamental forces in nature. 4. What is the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion? 5. What is the net reaction for nuclear fusion? 6. Explain Einstein’s Relativity Equation. What does this say about the relationship between energy and mass? How does this relate to nuclear fusion? Section 4: Electromagnetism 1. What is a photon? How do atoms emit photons? What happens when an atom absorbs a photon? 2. How do we determine a wave's wavelength, amplitude and frequency? What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency? 3. How is a transverse wave different from a longitudinal wave? 4. What is Planck's constant? How does this relate to the energy of a photon? What is the relationship between frequency and energy? Wavelength and energy? 5. How would a sound wave change if the sound were louder? How would it change if the sound were a higher pitch? 6. What is the electromagnetic spectrum? How does this relate to the energy of photons (and their frequency and wavelength)? How much of the spectrum is visible light? What other kinds of radiation are found on the spectrum? Section 5: Cells 1. What are the main points of the Cell Theory? 2. Describe the organizational hierarchy for multicellular organisms. 3. Describe the structure of an ATP molecule. How is this molecule used for energy? 4. What are the major differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? What kinds of organisms are prokaryotic? What organisms are eukaryotic? 5. Describe the functions of major cell structures (listed on the cell structure handout). Section 7: Energy in Systems 1. Be able to follow energy from the sun through a food chain, identifying each tropic level 2. 3. 4. 5. What is photosynthesis? What organisms can perform photosynthesis? What is cellular respiration? What does it mean to be an autotroph or a heterotroph? How to food chains and food webs account for the flow of energy in natural systems? 6. Describe the organizational hierarchy of ecological levels from population to biosphere. Which one includes abiotic factors? 7. List some major abiotic factors that affect ecosystems. 8. Explain the 10% Rule. Why is so little of the energy from any one level available to the next level? 9. What are fossil fuels? Why are we, as U.S. citizens, so dependent on fossil fuels? 10. Identify some sources of energy that are NOT fossil fuels. Section 8: Conversions 1. Know the prefixes and their equivalence 2. Be able to set up conversions from one metric unit to another. You should be able to do both one step and two step conversions. Section 9: Lab Work 1. Identify basic lab equipment and glassware: beaker, graduated cylinder, Bunsen burner, parts of a microscope, test tube, test tube clamp, test tube holder, forceps, water bath 2. Understand the special equipment used in various labs such as temperature probes; conductivity probe; calorimeter 3. Review the Prelab and Questions for each of your labs 4. Understand proper lab techniques: how to measure volume of a liquid; how to focus a microscope; how to design a controlled experiment; how to tare an electronic balance Section 10: Equations For each, be sure to know: 1. What the variables stand for. 2. What the appropriate units are for each variable. 3. How the equations can be manipulated to solve for each variable. F=ma W=Fxd P = W/t PE = mgh KE = 1/2 m v2 q = mcΔt °F = (1.8 x °C) + 32 c = λν E=hν E = mc2 °C = (°F-32)/1.8 Kelvin = °C + 273