Homework Questions
advertisement

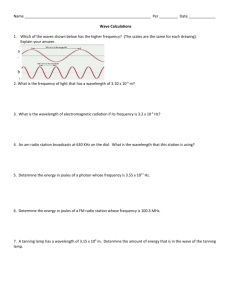
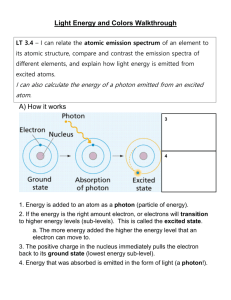
P. 149 – Q – 22 What was inadequate about Rutherford’s model of the atom? Which subatomic particles did Thomson include in the plum-pudding model of the atom. P. 149 – Q – 41 What is meant by the frequency of a wave? What are the units of frequency? Describe the relationship between frequency and wavelength? P. 149 – Q – 42 Use a diagram to illustrate each term for a wave: a. wavelength b. amplitude c. cycle P. 149 – Q – 45 Consider the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum: ultraviolet, X-ray, visible, infrared, radiowave, microwave a. Use Figure 5.10 to arrange them in order of decreasing wave length. b. How does this order differ from that of decreasing frequency? P. 150 – Q – 55 A mercury lamp emits radiation with a wavelength of 4.36 x 10-7 m. a. What is the wavelength of this radiation in cm? b. In what region of the electromagnetic spectrum is this radiation? c . Calculate the frequency of this radiation. P. 150 – Q – 56 Sodium vapor lamps are used to illuminate streets and highways. The very bright light emmited by these lamps is actually due to two closely spaced emission lines in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. One of these lines has a wavelength of 5.890 x 10-7 m, and the other line has a wavelength of 5.896 x 10-7 m. a. What are the wavelengths of these radiations in centimeters? b. Calculate the frequencies of these radiations . c. In what region of the visible spectrum do these lines appear? P. 151 – Q – 74 The average distance between Earth and Mars is about 2.08 x 10 km. How long does it take to transmit television pictures from the Mariner spacecraft to Earth and Mars? P. 151 – Q – 73 The energy of a photon is related to its wavelength and its frequency. Energy of Photon (J) Frequency (s-1) Wavelength (cm) 3.45 x 10 -21 a) 5.77 x 10-3 2.92 x 10 -21 b) 6.82 x 10-4 6.29 x 10 -21 c) 3.16 x 10-4 1.13 x 10 -21 d) 1.76 x 10-4 1.46 x 10 -21 e) 1.36 x 10-4 3.11 x 10 -21 f) 6.38 x 10-5 a. Complete the table above. b. Plot the energy of the photon (y axis) versus the frequency (x axis) c. What is the significance of this slope? P – 151 – Q 76 The energy (E) of a photon absorbed or emitted by a body is proportional to its frequency (v). E=hxv The constant h equals 6.63 x 10-34 J∙s. What is the energy of a photon of microwave radiation with a frequency of 3.20 x 1011 s-1? P. 149 – Q 23 – What did Bohr assume about the motion of electrons? P. 149 – Q 24 – Describe Rutherford’s model of the atom and compare it with the model proposed by his student Neils Bohr. P. 149 – Q 47 - What happens when a hydrogen atom absorbs a quantum of energy? P. 149 – Q 25 – What is the significance of the boundary of an electron cloud? P. 149 – Q 26 – What is an atomic orbital? P. 149 – Q 27 – How many orbitals are in the 2p sublevel? P. 149 – Q 29 – How many sublevels are contained in each of these principal energy levels? a. n = 1 b. n = 2 c. n = 3 d. n = 4 P. 149 – Q 35 – Which of these orbital designations are invalid? a. 4s b. 3f c. 2d d. 3d P. 149 – Q 36 – What is the maximum number of electrons that can go into each of the following sublevels. a. 2s b. 3p c. 4s d. 3d e. 4p f. 5s g. 4f h. 5p P. 149 – Q 37 – Arrange the following sublevels in order of increasing energy: 3d, 2s, 4s, 3p P. 149 – Q 32 – Write electron configurations for the elements that are identified only by these atomic numbers. a. 15 b. 12 c. 9 d. 18 P. 149 – Q 34 – Write electron configurations for atoms of these elements: a. Na b. S c. Mg d. Ne P. 149 – Q 38 – How many electrons are in the second energy level of an atom of each element? a. chlorine b. phosphorus c. potassium P. 207 – Q 35 - Write electron dot structures for each of the following elements. a. Cl b. S c. Al d. Li