Meteorology Test 2 Review - Earth Science With Fuller!
advertisement

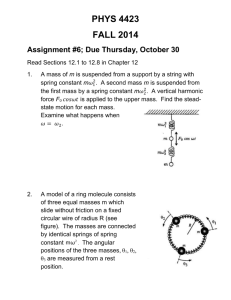
Earth Science Meteorology Test 2 Review: Seasons, Air Masses, Fronts, Pressure, and Wind Seasons Understand how the tilt of the earth and the revolution of the earth around the sun are responsible for the seasons. Know the meaning of Summer Solstice, Autumnal Equinox, Winter Solstice, and Vernal Equinox and what happens to the amount of daylight at each of these. Temperature Controls Know how temperature changes with respect to altitude. Air Masses Know the meaning of isotherm and be able to read the temperatures on an isotherm map as well as identify cold air masses and warm air masses. Identify the four different types of air masses by name and abbreviation and explain the moisture content, temperature, and origin of each. Fronts Identify the four different types of fronts and explain the characteristics of each including the symbols used for each on a weather map. Pressure Differentiate between cyclones (Lows) and anticyclones (Highs) in terms of wind direction, pressure, vertical air movement, etc. Know the meaning of isobar and be able to read the pressures on an isobar map as well as interpret the meaning of closely spaced isobars and identify cyclones (Lows) and anticyclones (Highs). Explain how a barometer works. Wind Understand that wind is the product of pressure gradients and that the greater the difference between the pressures in two locations, the faster the wind will blow. Wind always moves from high pressure to low pressure. When discussing wind, the direction is always where the wind is coming from (e.g., a north wind is coming from the north.) Be able to identify the location of each of the following on a world wind map: southeast trades, northwest trades, westerlies, and polar easterlies. Know the type of ecosystem present at the equator, 30o latitude, 60o latitude, and 90o latitude due to the movement of air in convection cells. Understand how the coriolis effect affects the movement of air in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Earth Science Meteorology Test 2 Review: Seasons, Air Masses, Fronts, Pressure, and Wind Seasons Understand how the tilt of the earth and the revolution of the earth around the sun are responsible for the seasons. Know the meaning of Summer Solstice, Autumnal Equinox, Winter Solstice, and Vernal Equinox and what happens to the amount of daylight at each of these. Temperature Controls Know how temperature changes with respect to altitude. Air Masses Know the meaning of isotherm and be able to read the temperatures on an isotherm map as well as identify cold air masses and warm air masses. Identify the four different types of air masses by name and abbreviation and explain the moisture content, temperature, and origin of each. Fronts Identify the four different types of fronts and explain the characteristics of each including the symbols used for each on a weather map. Pressure Differentiate between cyclones (Lows) and anticyclones (Highs) in terms of wind direction, pressure, vertical air movement, etc. Know the meaning of isobar and be able to read the pressures on an isobar map as well as interpret the meaning of closely spaced isobars and identify cyclones (Lows) and anticyclones (Highs). Explain how a barometer works. Wind Understand that wind is the product of pressure gradients and that the greater the difference between the pressures in two locations, the faster the wind will blow. Wind always moves from high pressure to low pressure. When discussing wind, the direction is always where the wind is coming from (e.g., a north wind is coming from the north.) Be able to identify the location of each of the following on a world wind map: southeast trades, northwest trades, westerlies, and polar easterlies. Know the type of ecosystem present at the equator, 30 o latitude, 60o latitude, and 90o latitude due to the movement of air in convection cells. Understand how the coriolis effect affects the movement of air in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.