sodium carbonate
advertisement

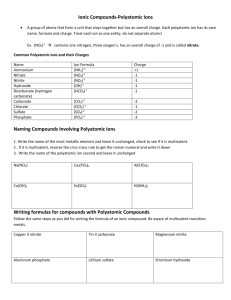
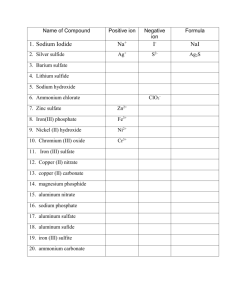
USING POLYATOMIC IONS Name __________________________________ When writing the formulas for compounds with polyatomic ions from the names, you need to balance the charges just like you did before with binary (only two elements) ionic compounds. (That’s what we were doing yesterday!) ******When a polyatomic ion must be multiplied to make the compound neutral, parentheses must be used so that any subscripts added will apply to the entire polyatomic ion.****** examples: sodium carbonate sodium in compounds = Na + carbonate = CO32- drop the sign and switch the charge number to be a subscript for the opposite ion: Na 2 (CO3) parentheses around CO3 not needed since there is just one, we do not write the subscript “1”. Na2CO3 Barium phosphite = final answer barium = Ba + phosphite = PO33- Ba3 (PO3) distinguish between subscripts used for balancing charge and those that are part of the formula of the polyatomic ion Ba3(PO3)2 final answer Please write correct formulas for the ionic compounds listed below. 1. Potassium nitrate – an ingredient in gunpowder (also known as “saltpeter”) 2. Calcium sulfate – a component of plaster and chalk 3. Calcium phosphate – a component of fertilizer as well as bones and teeth 4. Aluminum sulfate – also known as “alum,” used in water purification 5. Sodium hydrogen carbonate – baking soda (also known as sodium bicarbonate) 6. Magnesium hydroxide – relieves upset stomach and heartburn (milk of magnesia) 7. Calcium carbonate – the chemical name for marble and limestone 8. Ammonium Hydroxide – otherwise known as household ammonia. 9. Calcium Hydroxide – also known as “slaked lime,” is a component of cement. 10. Copper (II) Sulfate – a bright blue salt used as an algaecide and a disinfectant. 11. Ammonium Nitrate – used in fertilizers and instant cold-packs 12. Sodium Nitrite – a preservative found in processed meats Naming ionics with polyatomic ions. Identify the compound as an ionic compound first [begins with a metal and ends with nonmetal(s)]. You have to recognize the polyatomic ions within the formula. At first you may incorrectly attempt to name every element in the formula. If the formula begins with a metal and ends with two or three nonmetals then it must be a polyatomic ion in the formula. steps for naming: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. name the metal with its full name. (may need a roman #, but you determine that later) Identify the polyatomic ion at the end of the formula, use its name. Use charge of polyatomic ion to determine charge of ‘transition’ metal Write charge for ‘transition’ metal as roman number in parentheses No prefixes used. naming examples: Ca(NO3)2 Ca ( NO3 ) 2 calcium nitrate KNO3 K NO3 potassium nitrate Ba(OH)2 Ba ( OH ) 2 barium hydroxide NiCO3 Ni CO3 nickel (II) carbonate Fe2(SO4)3 Fe2 ( SO4 ) 3 iron (III) sulfate NH4ClO3 NH4 ClO3 ammonium chlorate The following contain polyatomic ions. Don’t forget about the metals with multiple charges as they require a roman number in the name. Name the ionic compounds below. 13.FeCrO4 14.Cu(OH)2 15. Cu2CO3 16. Cr(C2H3O2)3 17. Ca(ClO3)2 18. (NH4)2O 19. Al(ClO4)3 20. Zn(HCO3)2 21. Na3PO4 22. AgClO 23. (NH4)3PO4 24. Fe(ClO2)2 25. Mg(HCO3)2 This last page practices naming and formula writing of ionic compounds – AGAIN – and uses the metals with multiple charges or single charged metals AND polyatomic ions. Name or write the formula of the information provided. 1. K2CO3 _______________________________________________ 2. Na2SO4 ______________________________________________ 3. KC2H3O2 _________________________________________________________________________ 4. Potassium hydrogen carbonate _______________________________ 5. Ammonium fluoride _______________________________________ 6. NaHCO3 _______________________________________________ 7. Ca(NO3)2 _______________________________________________ 8. BaSO4 _______________________________________________ 9. Potassium chlorate _________________________________________ 10. Sodium acetate ____________________________________________ 11. MgSO4 ________________________________________________ 12. AgNO3 _______________________________________________ 13. Calcium chlorate ___________________________________________ 14. Strontium nitrate ___________________________________________ 15. Barium hydroxide __________________________________________ 16. Lithium hydroxide __________________________________________ 17. Beryllium hydroxide ________________________________________ 18. Lithium sulfite _____________________________________________ 19. NH4Cl ________________________________________________ 20. Copper (II) phosphate ________________________________________ 21. Zn(NO3)2 _________________________________________________ 22. Nickel (I) hydroxide _________________________________________ 23. Zinc sulfate ________________________________________________ 24. Manganese (II) carbonate _____________________________________ 25. KOH ________________________________________________