Agriculture Vocabulary Agribusiness Commercial agriculture
advertisement
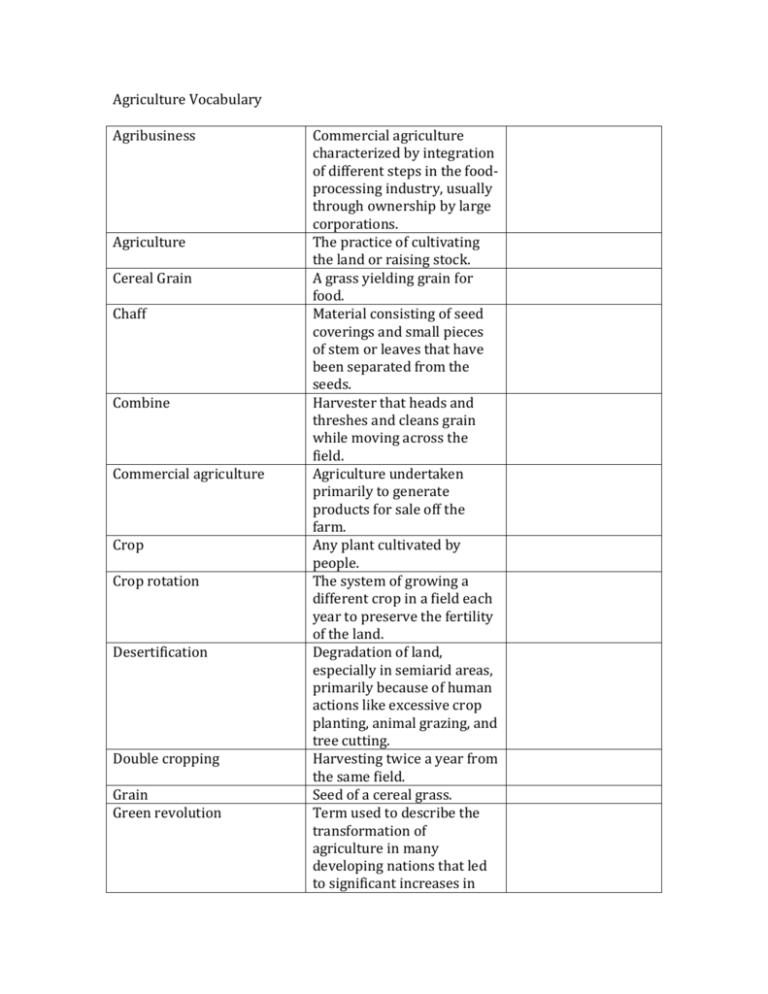
Agriculture Vocabulary Agribusiness Agriculture Cereal Grain Chaff Combine Commercial agriculture Crop Crop rotation Desertification Double cropping Grain Green revolution Commercial agriculture characterized by integration of different steps in the foodprocessing industry, usually through ownership by large corporations. The practice of cultivating the land or raising stock. A grass yielding grain for food. Material consisting of seed coverings and small pieces of stem or leaves that have been separated from the seeds. Harvester that heads and threshes and cleans grain while moving across the field. Agriculture undertaken primarily to generate products for sale off the farm. Any plant cultivated by people. The system of growing a different crop in a field each year to preserve the fertility of the land. Degradation of land, especially in semiarid areas, primarily because of human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting. Harvesting twice a year from the same field. Seed of a cereal grass. Term used to describe the transformation of agriculture in many developing nations that led to significant increases in Horticulture Hull Intensive subsistence agriculture Milkshed Paddy Pastoral nomadism Pasture Plantation Prime agricultural land Ranching Reaper Ridge tillage agricultural production between the 1940s and 1960s. Cultivation of crops carried out with simple hand tools such as digging sticks or hoes. Husk; dry outer covering of a seed; frame or body of a ship. A form of subsistence agriculture in which farmers must expend a relatively large amount of effort to produce the maximum feasible yield from a parcel of land. The area surrounding a city from which milk is supplied. Rice in the husk either gathered or still in the field. A traditional subsistence agricultural system in which practitioners depend on the seasonal movements of livestock within marginal natural environments. A field covered with grass or herbage and suitable for grazing by livestock. An estate where cash crops are grown on a large scale (especially in tropical areas). The most productive farmland. Farming for the raising of livestock (particularly cattle). Farm machine that gathers a food crop from the fields. System of planting crops on ridge tops, in order to reduce farm production costs and promote greater soil conservation. Sawah Seed agriculture Shifting cultivation Slash-and-burn agriculture Spring wheat Subsistence agriculture Sustainable agriculture Swidden Thresh Transhumance A flooded field for growing rice Reproduction of plants through annual introduction of seeds, which result from sexual fertilization. Cultivation of crops in tropical forest clearings in which the forest vegetation has been removed by cutting and burning. These clearings are usually abandoned after a few years in favor of newly cleared forestland. Also known as slash-and-burn agriculture. Another name for shifting cultivation, so named because fields are cleared by slashing the vegetation and burning the debris. Wheat planted in the spring and harvested in the late summer. Agriculture designed primarily to provide food for direct consumption by the farmer and the farmer's family. Farming methods that preserve long-term productivity of land and minimize pollution, typically by rotating soil- restoring crops with cash crops and reducing in-puts of fertilizer and pesticides. A patch of land cleared for planting through slashing and burning. To separate the grain from the stalk and the hull. The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland Truck farming Vegetative planting Wet rice Winnow Winter wheat pastures. Commercial gardening and fruit farming, so named because truck was a Middle English word meaning battering or the exchange of commodities. Reproduction of plants by direct cloning from existing plants, such as cutting stems and dividing roots. Rice planted on dryland in a nursery, then moved to a deliberately flooded field to promote growth. Treat by exposure to a current of air so that waste matter is eliminated. Wheat planted in the fall and harvested in the summer.