Agriculture Vocabulary: Key Terms & Definitions
advertisement

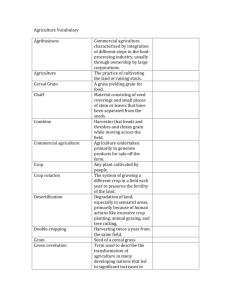
Agriculture Unit Vocabulary 1. Agribusiness 2. Agricultural Revolution 3. Aquaculture (Aquafarming) 4. Cereal grain 5. Commercial Agriculture 6. Desertification 7. Double cropping 8. Green Revolution 9. Intensive subsistence agriculture 10. Milkshed 11. Pastoral Nomadism 12. Shifting cultivation 13. Subsistence agriculture 14. Sustainable agriculture 15. Swidden 16.Truck farming 17. Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) 18. Livestock Ranching 19. Mediterranean Agriculture 20. Organic Farming 21. Pastoralism 22. Monoculture 23. Plantation agriculture Commercial agriculture characterized by the integration of different steps in the food-processing industry, usually through ownership by large corporations The time when human beings first domesticated plants and animals and no longer relied entirely on hunting and gathering The cultivation of seafood under controlled conditions A grass that yields grain for food Agriculture undertaken primarily to generate products for sale off the farm Degradation of land, especially in semiarid areas, primarily because of human actions such as excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting. Harvesting twice a year from the same field Rapid diffusion of new agricultural technology, especially new high-yield seeds and fertilizer A form of subsistence agriculture in which farmers must expend a relatively large amount of effort to produce the maximum feasible yield from a parcel of land The area surrounding a city from which milk is supplied A form of subsistence agriculture based on herding domesticated animals A form of subsistence agriculture in which people shift activity from one field to another; each field is used for crops for a relatively few years and left fallow for a relatively long period Agriculture designed primarily to proved food for direct consumption by the farmer the farmer’s family Farming methods that preserve long-term productivity of land and minimize pollution, typically by rotating soil-restoring crops with cash crops and reducing inputs of fertilizer and pesticides. A patch of land cleared for planting through slashing and burning Commercial gardening and fruit farming Organisms whose genetic material has been modified for increased agricultural output The raising of livestock over an expanse of land for food products from the domesticated animals A form of specialized agriculture in which crops grown in a Mediterranean climate of warm year-round temperatures and sunny summers The process of producing food naturally without the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and other inputs A form of subsistence agriculture in which animals are herded in a seasonal migratory pattern The production of a single crop for commercial markets Monocropping, or planting a single crop for profit, is a specialized form of agriculture and is usually located near the former colonial markets