File
advertisement

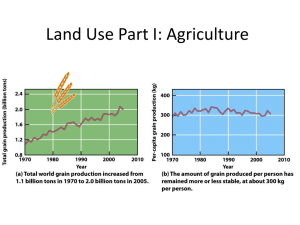
#1 Ch. 18: Food Resources Students should be able to: Name the three most important food crops and explain why having just three plants species to provide almost half of the calories people consume is a potential problem. Contrast industrialized agriculture with subsistence agriculture and describe different kinds of subsistence agriculture. Describe the beneficial and harmful effects of domestication on crop plants and livestock. Describe the benefits and problems associated with the green revolution. Explain the roles of hormones and antibiotics in industrialized agriculture. Identify the potential benefits and problems of genetic engineering. Food since the human population is constantly growing, can we continue to provide enough food for everyone in a sustainable manner? o although there is currently enough food per person right now, many people (~ 1 billion) are undernourished, malnourished, or both, while people in developed countries are often overnourished o when our food security (world grain stocks) is threatened, food prices increase, causing the poor to be more at risk (don’t have money to buy food or land to grow it) and political unrest to increase heat waves and droughts reduce grain yields more corn is being converted into ethanol increased meat consumption in countries such as China has caused a surge in grain used to feed livestock rather than people o getting food to the people who need it most is often a political battle (red tape, dishonest government officials, etc.) What are We Eating? 330,000 species of plants 100 plants provide 90% of our food 15 of those 100 species provide the bulk of the 90% 3 species (rice, wheat, and corn) provide about half of all the calories we consume #1 o what if one of these crops is wiped out? about 80 important livestock species (cows, sheep, pigs, chickens, turkeys, geese, ducks, goats, and water buffalo are the most eaten) o important sources of protein o expensive inefficient converters of plant material about half of all the grains grown in developed countries goes to feeding livestock Types of Agriculture Industrialized (Developed) Subsistence (Developing) relies on large inputs of capital and E (fossil fuels) produce enough food to feed your family, with little left over to sell or store E used to produce/run machinery, irrigate, and produce agrochemicals input of E is from humans and draft animals, not fossil fuels produces high yields (less land has to be converted) types include slashand-burn, nomadic herding, and intercropping can cause soil degradation and pesticide resistance #1 Challenges domestication causes a loss of genetic diversity can negatively affect longterm survival of crops/livestock because they are less able to adapt to changing environmental conditions o bred for uniformity and maximum production more susceptible to disease and pests, less able to adapt o local varieties (domesticated versions of species that represent adaptations to specific places) are becoming extinct we can cross-breed local varieties with modern varieties to increase genetic diversity and resistance *read excerpt from Animal, Vegetable, Miracle with pictures increasing crop yields o research of plant nutrition and pests has resulted in better fertilizers and pesticides o the Green Revolution (1960s) using modern cultivation methods (use of commercial inorganic fertilizers, pesticides, and machinery) and highyielding varieties of certain staple crops to produce more food per acre of cropland developed countries shared their seeds, supplies, and knowledge with less developed countries in Asia and Latin America can help the economy of some developing countries, but in some cases, makes them dependent serious environmental implications (soil degradation, more E use, loss of traditional know-how) what about Africa? o as we gain more people, we cannot dedicate more arable land … because there isn’t any more water shortage is also a major issue have to convert to waterefficient irrigation law of diminishing returns GMOs? increasing livestock yields o hormones to promote faster growth some concern that these can promote cancer or affect growth of children (although typically the amounts found in meat are quite low) #1 EU bans meat from U.S. and Canada health or economics? o antibiotics (40% of all produced in the U.S.) are routinely added to animal feed, even for healthy animals increased bacterial resistance to antibiotics (TB, MRSA, etc.) reduces medical effectiveness in humans many European countries have stopped at the urging of the WHO o * show The Meatrix and discuss the gene revolution (making genetically modified foods/Frankenfoods) o can alter traits of crops and livestock quicker than by using traditional breeding methods can produce food that is more nutritious, resistant to disease, able to grow in a variety of environmental conditions, grows faster o regulated by the FDA in the U.S. seem to be safe, although there is some concern that introducing GM crops might spread foreign genes into non-GM plants (like weeds) food allergies are potentially possible