Agriculture Powerpoint
advertisement

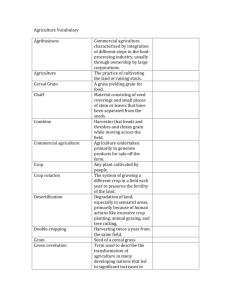
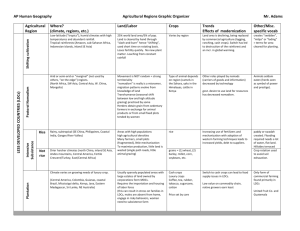
Agriculture- Key Issue 2 & 3 Principle Practices of Subsistence Agriculture • sensitive land management. • limited use of chemicals. • better integration of crops and livestock. Forms of subsistence agriculture • Shifting Cultivation • Pastoral Nomadism • Intensive Characteristics ofshifting cultivation • • • • • • Land is cleared by slashing the vegetation. Debris is burned to provide the soil with nutrients. A new site is designated every few years. Swiddens not under cultivation are used for fruit trees. Most commonly found in humid low-latitude climates Occupies the largest percentage of the world's land area Defenders of shifting cultivation say that it is the best approach for the tropics because… • Permanently clearing fields and using fertilizers will destroy tropical soils. • It destroys less tropical rain forest than permanently clearing the land. • It is part of the cultural diversity of folk customs in the tropics. Pastoral Nomadism • Only about 15 million people are nomads, but they sparsely occupy 20 percent of the earth's land area. • Most commonly found in a dry climate • Pastoral Nomads occupy only their own territory, moving with the seasons to find food and water. Intensive Subsistence • Practiced by the largest percentage of the world's people • The largest proportion of farmers in Asia practice it • Greater use of animal power, compared to shifting cultivation • involves large amounts of efforts used to produce the maximum feasible yield from a given piece of land. Asian agriculture is characterized by shortages of… • equipment • funds • Land • To increase crop yields, farmers in southeastern China commonly practice double cropping • To separate husks from seeds, Asian farmers beat the heads on the ground, a practice known as threshing. Practices for growing rice in Asia • • • • preparing fields with a plow drawn by oxen flooding the plowed field with water growing seedlings in a nursery transplanting seedlings into the flooded field The reason why most people in North China grow crops other than wet rice is our CLIMATE! Transhumance • The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pastures Commercial agriculture is distinguished from subsistence agriculture by • • • • low percentage of farmers in the labor force farm size heavy use of machinery surplus production Types of Commercial Agriculture in the US • • • • • • Mixed crops and livestock Dairying Grain farming Livestock Ranching Mediterranean agriculture Gardening and Fruit Farming *don’t usually sell their products directly to consumers, but to wholesalers who distribute them to retailers LDCS: • Unlike other forms of commercial agriculture, plantations are found primarily in less developed countries. Commercial Agriculture- Mixed Crop and Livestock Farming • The most common form of commercial agriculture in Europe and the US (west of the Appalachian mountains) is mixed crop and livestock farming. • This method is good because it permits farmers to spread the workload and income throughout the year. Usually involves Crop Rotation to maintain the fertility of the fields. • The U.S. Midwest, from Ohio to the Dakotas with it’s center in Iowa, is the mixed crop and livestock region in the Us and is known for corn followed by soybeans. Known as the .”Corn Belt” • Crops grown in the mixed crop and livestock region are used primarily to feed animals. Commercial Agriculture- Dairy Farming • Most important in Northeast US, Southeast Canada, and Northwest Europe • Huge spike in Dairy Farming in LDCs (increased 20% in 25 years) • India just surpassed the US as the world’s largest milk producer. • *** MILK IS A PERISHABLE GOOD SO FARMS MUST BE CLOSE TO THEIR MARKET FOR TRANSPORTATION FACTORS*** • The ring surrounding the city from which milk can be supplied without spoiling is called the Milkshed. If outside the milkshed dairy farms may specialize in butter, cheese, etc. • Many US dairy farmers left the profession because it is not very profitable and extremely labor intensive Commercial Agriculture- Grain Farming • Grain is the seed from various grasses, like wheat corn, oats, and barley • Crops on grain farms are grown for consumption by humans not livestock • Wheat is the most important crop- used to make bread flour. It is stored easily without spoiling, transported long distances, and has a high value per unit weight. It is the world’s leading export crop. US/Canada=“breadbasket”. Located in regions that are too dry for mixed crop and livestock agriculture. • The U.S. is the largest commercial producer of grain. 3 areas of grain production in North America 1. “Winter-wheat Belt”- Kansas, Colorado, Oklahoma. In the winter wheat area, the crop is planted in autumn and develops a strong root system before it stops in the winter. The wheat survives the winter under a snow blanket and is harvested in summer. 2. “Spring-wheat Belt”- Dakotas, Montana, and Southern CanadaWinters are too severe for winter wheat so they plant in the spring and harvest in the late summer 3. Washington State The McCormick Reaper is a machine that cuts grain standing the field and first permitted large scale wheat production in 1830 Today the combine machine combines reaping, threshing, and cleaning in one task • The predominant form of agriculture in the U.S. Southeast is commercial gardening Commercial Agriculture- Livestock Ranching • Livestock Ranching is the commercial grazing of livestock over and extensive area. It practiced in the dry (arid) lands of the southwestern U.S. where the soil is too poor to support crops • Has declined in the southwestern United States primarily because crops yield more income per area now that we have better irrigation techniques. • Ranching is practiced in dry climate regions • Hollywood has romanticized the cowboy. Cattle were driven on hoof to the nearest railroad in Kansas where they were put into cattle cars • In the United States many farms are integrated into a large food production industry. This is known as agribusiness. Leading producers of commercial grain… • • • • China United States Russia India • Northwest Europe= Dairying • South Europe= Mediterranean • East Europe= Grain Von Thünen's model, 1826, Germany • Explains how important it is to be close to a market for certain commercial farms • The primary factor for choosing commercial farm products is market location • Takes into consideration: 1. the value of the yield 2. The cost of transporting the yield • can best be used to explain the location of dairying in the Northeast United States • The farther a dairy farm is from a large urban area the lower the percentage of output devoted to fresh milk. This occurs primarily because processed milk is less perishable. • timber production was located in the second ring from the city because of product weight • Strategies for increasing food supply • • • • expanding arable land area increasing land productivity identifying new food sources increasing exports of surplus production Mediterranean agriculture • Practiced in different areas of the world, but they all have similar climate (all boarder a sea) • Produces fruits, grapes, olives, and cereals Problems in BOTH LDCs and MDCS • Farmers have inadequate incomes • • LDCs generate funds to promote development through selling export crops • To raise money for development, farmers inLDCs are encouraged to growluxury crops for export, cash crops, and items for consumption abroad Warm-Up • How do you behave differently in groups than you do on your own?