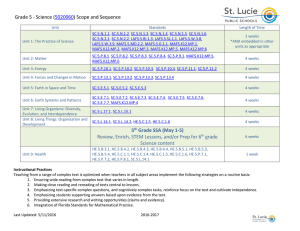
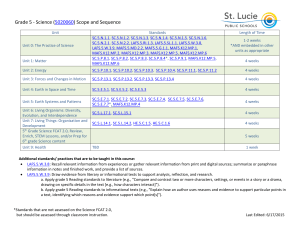
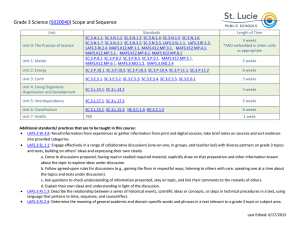
math-7-leq-5

Comparing Populations
Unit 5 – Lesson 4
5 days
Learning Goals for this Lesson: Standards:
MAFS.7.SP.2.3., MAFS.7.SP.2.4
MAFS.K12.MP.1.1, MAFS.K12.MP.3.1, MAFS.K12.MP.4.1,
MAFS.K12.MP.5.1
LAFS.68.WHST.1.1, LAFS.7.SL.1.1, LAFS.7.SL.1.2, LAFS.68.
RST.3.7
Students Will Be Able To:
Informally assess the degree of visual overlap of
Students Will Know:
The most appropriate measure for comparing data sets depends on the symmetry of the data sets. two numerical data distributions with similar variabilities. Use measures of center and measures of variability for numerical data from random samples to draw informal comparative inferences about two populations.
Lesson Essential Question:
How are informal comparative inferences about two populations drawn?
Activating Strategy:
Real-World Link p. 827 - Exercise – Students will identify the components of a box plot
Key Vocabulary to Preview and Vocabulary Strategy:
Double Box Plot Double Dot Plot
Lesson Instruction:
Learning Activity 1:
Use the Cornell Note format to take notes on the key vocabulary.
(Preview of the vocabulary.)
Assessment Prompt for LA 1:
Question: “What is the relationship between Pi, Circumference, and Diameter? Explain.” A reasoning. B s to? Call on B s s tell the B s their answer and give their
follow up – do you agree, disagree, or need to add
to answer aloud for the class.
Differentiation for LA 1:
Ability Levels: Paired Groupings (stronger/slightly weaker students)
Learning Styles: Visual, Auditory, Interpersonal, Intrapersonal,
Kinetic
Graphic Organizer:
Frayer
Cornell Notes
Varied Interest: Students will be allowed to choose 2 of the new vocabulary
words to create a Frayer Model.
*** See the document at the end of the unit for more information.
Learning Activity 2:
Discuss the error points and model problems involving angle relationships. After each example, students complete the “Got It?” questions with their partners. (Ink-Pair-Share.)
R 2 is NOT r x 2
Circumference answers are NOT squared.
Assessment Prompt for LA 2:
Text p. 832 Q 3
Differentiation for LA 2:
Ability Levels: Paired Groupings (stronger/slightly weaker students)
Learning Styles: Visual, Auditory, Interpersonal, Intrapersonal,
Kinetic
*** See the document at the end of the unit for more information.
Learning Activity 3:
Review how to use Marking the Text with students using a problem involving circumference and area. Provide students with an additional word problem to solve. (Ink-Pair-Share)
Assessment Prompt for LA 3:
Complete word problems pertaining to the LEQ using the Marking the Text
Strategy with their partners.
Differentiation for LA 3:
Ability Levels: Paired Groupings (stronger/slightly weaker students)
Learning Styles: Interpersonal, Intrapersonal, and Kinetic
Varied Interest: Create and solve their own word problem.
*** See the document at the end of the unit for more information.
Learning Activity 4:
Review how to solve word problem involving a H.O.T. skill that involve angle relationships. Remind students to use the Marking the
Text strategy. Provide students with an additional H.O.T. problem to solve. (Ink-Pair-Share)
Assessment Prompt for LA 4:
Assignment:
Textbook p. 851
Performance Task – Class
Evaluation
Students are asked to analyze the data from a random sampling of 3 years worth of student grades.
Rubric – PT6
Complete H.O.T problems pertaining to the LEQ using the Marking the Text
Strategy with their partners.
Differentiation for LA 4:
Ability Levels: Paired Groupings (stronger/slightly weaker students)
Learning Styles: Visual, Auditory, Interpersonal, Intrapersonal,
Kinetic
Varied Interest: Choose two of the H.O.T questions from the textbook related
content.
*** See the document at the end of the unit for more information.
Summarizing Strategy:
Students will review their Cornell Notes to answer the LEQ in the Summary section.
Students: Modifications/Accomodations:
1. Seat student near teacher.
2. Stand near student when giving directions/presenting.
3.
Provide visual aids/graphic organizers.
4.
Ensure oral directions are understood.
5.
Allow extra time to complete tasks.
6.
Simplify complex written directions.
7.
Give test items orally.
8.
Provide peer assistance/study groups.