Crossing Over and Gene Mapping Worksheet
advertisement

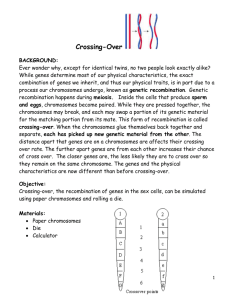
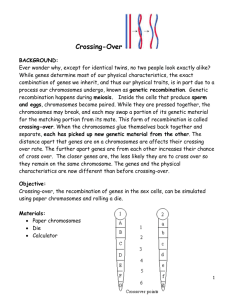
Crossing Over and Gene Mapping WS Ever wonder why, except for identical twins, no two people look exactly alike? While genes determine most of our physical characteristics, the exact combination of genes we inherit, and thus our physical traits, is in part due to a process our chromosomes undergo, known as genetic recombination. Genetic recombination happens during meiosis. Inside the cells that produce sperm and eggs, chromosomes become paired. While they are pressed together during Prophase I, the chromosomes may break, and each may swap a portion of its genetic material for the matching portion from its mate. This form of recombination is called crossing-over. When the chromosomes glue themselves back together and separate, each has picked up new genetic material from the other. The distance apart that genes are on a chromosomes are affects their crossing over rate. The further apart genes are from each other increases their chance of cross over. The closer genes are, the less likely they are to cross over so they remain on the same chromosome. The genes and the physical characteristics are now different than before crossing-over. This process is another major source of genetic diversity. 1. In what kinds of cells does crossing-over take place? _______________________________ 2. During what cell process does crossing-over occur? BE SPECIFIC! ______________________ 3. What happens during crossing-over? ____________________________________________ 4. What is the benefit of crossing-over? ___________________________________________ 5. What determines how often crossing over occurs between any 2 particular genes? What happens to genes on chromosomes during crossing over? 1. Homologous chromosomes pair up 2. Adjacent chromatids cross over. 3. Homologous chromosomes separate. Now you can try it! Use the diagram on the previous page as a guide. What is the genetic significance of crossing over? Gene Mapping: