Genetics Study Guide: Vocabulary, Concepts, and Standards
advertisement

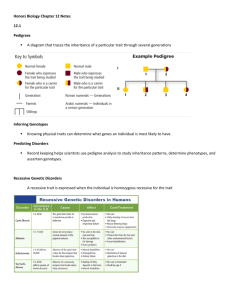
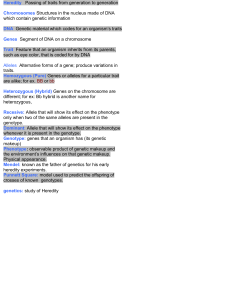
Science Chapter 5 Study Guide Genetics Vocabulary: Heredity dominant allele recessive allele sexual reproduction mutation genetics hybrid genotype diploid trait fertilization probability homozygous meiosis alleles purebred punnett square heterozygous messenger RNA gene phenotype codominance transfer RNA Concepts: Big Idea: How are traits passed from parents to offspring? Know where DNA is located in the cell Know different types of mutations Process and stages of meiosis; know what happens at each stage Process of protein synthesis Know what Gregor Mendel’s experiment was and what results he obtained Why was Gregor Mendel’s work important? It created the foundation for what understanding? Know how organism’s traits are determined by its alleles Know how dominant and recessive genes are written Know how probability helps to explain the results of genetic outcomes Know what the chromosome theory of inheritance is Know the role chromosomes play in inheritance Know the relationship between chromosomes and genes Know how genetic code is formed Know how cells make proteins Know where protein synthesis takes place Know the process of protein synthesis and what occurs during this process Know the function of transfer RNA and messenger RNA Know how RNA is different from DNA Know what a mutation causes Know what phenotype codominant traits show Know how to read information off of a punnett square What determines the genetic code? Know the effects of harmful mutations and helpful mutations California State Standards: Genetics 2. A typical cell of any organism contains genetic instructions that specify its traits. Those traits may be modified by environmental influences. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know the differences between the life cycles and reproduction methods of sexual and asexual organisms. b. Students know sexual reproduction produces offspring that inherit half their genes from each parent. c. Students know an inherited trait can be determined by one or more genes. d. Students know plant and animal cells contain many thousands of different genes and typically have two copies of every gene. The two copies (or alleles) of the gene may or may not be identical, and one may be dominant in determining the phenotype while the other is recessive. e. Students know DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material of living organisms and is located in the chromosomes of each cell.