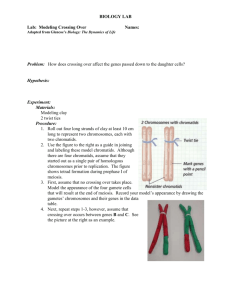
Chapter 6 - Genetic Linkage and mapping in eukaryotes
advertisement

Chapter 6 Genetic Linkage and mapping in eukaryotes Study Outline I. Linkage and crossing over A. Crossing over may produce recombinant genotypes B. Bateson and Punnett discovered two traits that did not assort independently C. Morgan provided evidence for the linkage of X-linked genes and proposed that crossing over between X chromosomes can occur D. The likelihood of crossing over between two genes depends on the distance between them E. A chi square analysis can be used to distinguish between linkage and independent assortment F. Creighton and McClintock showed that crossing over produced new combinations of alleles and resulted in the exchange of segments between homologous chromosomes II. Genetic mapping in plants and animals A. The frequency of recombination between two genes can be correlated with their map distance along a chromosome B. Alfred Sturtevant used the frequency of crossing over in dihybrid crosses to produce the first genetic map C. Trihybrid crosses can be used to determine the order and distance between linked genes D. Interference can influence the number of double crossovers that occur in a short region III. Genetic mapping in haploid eukaryotes A. Ordered tetrad analysis can be used to map the distance between a gene and the centromere B. Unordered tetrad analysis can be used to map genes in dihybrid crosses