Genetics 101 Worksheet: Genes, DNA, and Phenotypes
advertisement

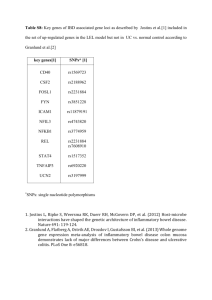
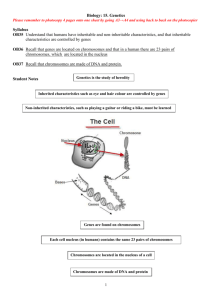
Class # ______: Genetics 101 Name _______________________________________ 1 2 3 Lesson 1: Watch the What are genes?” (Video 4:24) http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=eOvMNOMRRm8#t=44 1. Your body is made up of 50 t______________________________ cells. 2. 99.9% of your g____________________ are contained in the n________________________, but a few are also found in your m____________________________. 3. All told you have about _______________________ genes. 4. Your genes are small parts of a larger chemical called D_____________ or deoxyribonucleic acid. 5. DNA is made up of 4 b_____________________. 6. The 4 base nucleotides are: o Adenine o T________________________ o Cytosine o G________________________ 7. The number and order of the genetic c______________ determines what the living organism is such as a ______________________________ or a ____________________________. 8. The “recipes” are passed down from one g___________________________ to the next generation. 9. When someone says, “You have your father’s hair,” they mean: You have i_________________ a gene or genes from your father that makes a protein that instructs your hair follicle cells to produce hair that curls like your father’s. 10. Genes tell a cell how to f____________________ and what t________________ to express. 11. Genes are organized into c________________________________. 12. Different species have different numbers of chromosomes. Humans have ________ pairs of chromosomes. 13. What percentage of the DNA in your chromosomes do you share with other species? 93% with rhesus monkeys _______ with chimpanzees _______ with other humans Lesson 2: Watch the What are SNPs? video (Video 2:00) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8GUJx2NQPDg 14. An entire set of 23 chromosomes is called a human g_________________________. 15. A variation at a single base pair is called a s________________. Or a: _____ingle _____ucleotide _____olymorphism 16. Sometimes cells make mistakes when DNA c________________ are made. 17. Single base substitutions create ______________. 18. There are about ______ million SNPS in the human genome. 19. These SNPS account for most of the d____________________ between you and everyone else. 20. Some SNPS cause differences in a____________________ and others can cause certain d____________________ or how we respond to d___________________. (Like how some people are allergic to certain drugs.) 21. Since variants are passed down through g_____________________, the number of variants can tell you how related you are to your neighbor. Lesson 3: Watch the Where do genes come from? (Video 4:20) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Yg89GY61DE 22. Your g________________ come from your p_________________________. 23. You have 2 sets of ___________ chromosomes. 24. One set from each p__________________. 25. One set comes from your m___________________, and the other from your f_____________________. 26. 22 pairs are h____________________________ (or the same kind) of chromosomes. 27. The 23rd pair is special. The X and Y c_______________________________ are special: 28. Females have 2 ______ chromosomes or ______ _______ 29. Males have an X and a ________ chromosome or ________ ________ 30. Eggs and sperm cells have only ______ set of 23 chromosomes each. 31. You receive h___________ of your chromosome pairs from your m_____________ with the egg cell and half from your f__________________ with the sperm cell. 32. The Y cell is passed down directly from f_______________ to s_______________. 33. Mitochondrial DNA is passed down directly from mother to c____________________. 34. F___________________________ occurs when the egg and sperm unite. 35. This single cell divides over and over until a c_____________________ is created. Lesson 4: Watch the What are Phenotypes? (Video 2:03) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kLpr6t4-eLI 36. Your o_______________________ t__________________ are known as your p____________________________. 37. Your phenotype is determined by interactions of your g________________ and the e___________________________. 38. An example might be how long you live (your longevity) if you s__________________ or e__________________________. 39. Many phenotypes are determined mostly by g_____________________. H_______________ is one example; though, n_______________________ can play a role. 40. How genes affect traits like your p__________________________ are less well understood.