Science K-12 Vocabulary 2012
advertisement
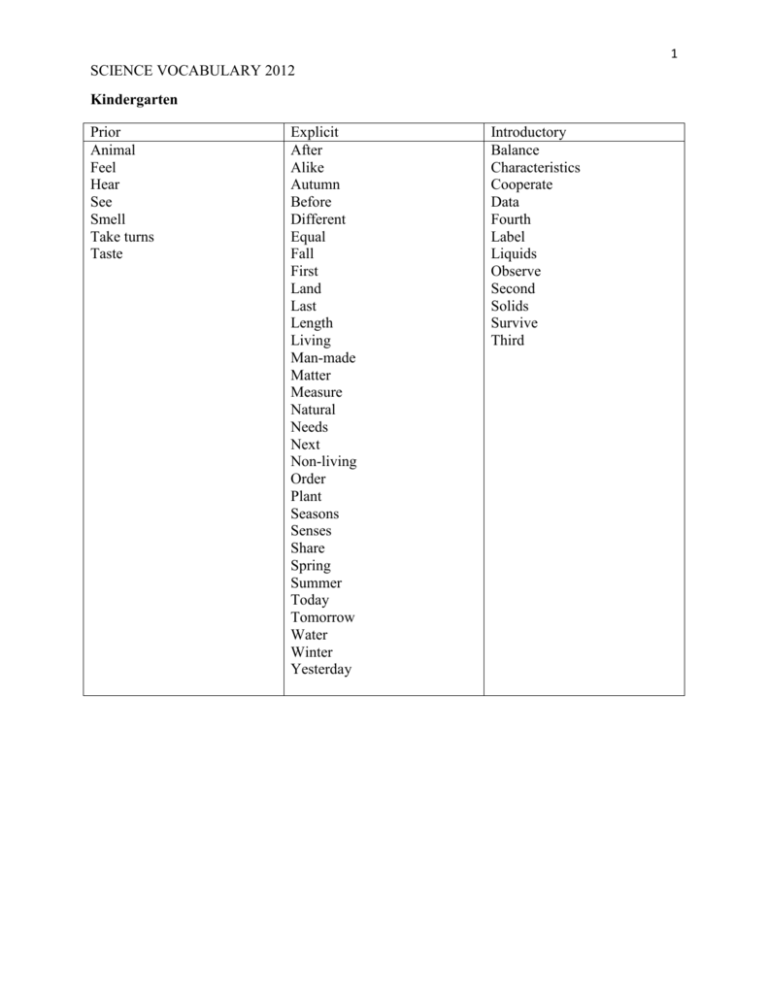
1 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Kindergarten Prior Animal Feel Hear See Smell Take turns Taste Explicit After Alike Autumn Before Different Equal Fall First Land Last Length Living Man-made Matter Measure Natural Needs Next Non-living Order Plant Seasons Senses Share Spring Summer Today Tomorrow Water Winter Yesterday Introductory Balance Characteristics Cooperate Data Fourth Label Liquids Observe Second Solids Survive Third 2 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Grade 1 Prior After Alike Animal Babies Before Calendar Color Different Direction Egg Fall Food Growth Now Plants Playground Seeds Shape Spring Summer Today Tomorrow Winter Yesterday Explicit Backyard Cloudy Cold Collect Describe First Future Graph/table Hot Label Life cycles Living Measure Measurement Need Next Non-living Non-standard units (hands, your feet) Observation Observe Past Present Rainy Season Size Sprout Standard Units (length, capacity, weight) Sunny Then Windy Introductory At rest Attribute Birth Celsius Change Characteristics Communication Cooperation Data Death Development Environments Evidence Fall Fahrenheit Features Float Germinate Group Life Local Man-made Motion Movement Multi-step Ordinal numbers Natural Position Properties Record Findings Revolve Rotate Similar Size Social norms (taking turns, listening with respect, personal space) Survive Temperature Texture Time Weather Weight 3 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Grade 2 Prior Change Collect Color Cooperation Float Food Future Liquid Living Measurement Non-living Observation Past Present Pull Push Season Shape Shelter Size Solid Speed Temperature Twist Water Weight Explicit Adaptations Change Classify Compare/ Contrast Data Examine Experiment Food chain Force Function Gas Habitat Identify Life cycle Man-made Matter Molecules Motion Natural resource Organize Predict Properties Record Record Space Survive Temperature Tools Introductory Analyze Atmosphere Attribute Characteristics Communicate Condensation Distance Energy Environment Evaporation Evidence Extinct Friction Gravity Infer Interaction Interpret Precipitation Predator/ Prey Revolve Rotate Scientific method Sensory Texture Water cycle Weather 4 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Grade 3 Prior Celsius Change Charts Cool Data Experiment Fahrenheit Freeze Graphs Habitat Heat Liquid Measurement Melt Pollution Predict Recycle Reduce Reuse Shape Soil Standard units Temperature Thermometer Tools Use Weight Explicit Adaptations Aquifer Community Conclusion Conservation Constant Cups Diagrams Ecosystem Energy Environment Evaluate Food chain Food web Function Hypothesis Metric units Models Observation Physical properties Predator Prey Record Resource Results Sequence Variable Introductory Acid rain Atom Behavior Camouflage Carnivore Competition Condense Constancy Consumer Contract Cooperation Decomposer Dormant Ecosystem Energy Energy in motion Erosion Evaporate Evidence Exhaustible Expand Force Form Gas Gravity Herbivore Hibernation Host Inexhaustible resource Insulation International System of Measurement Kinetic energy Length Logical Mass Meter stick Migrate Mineral Molecules Niche Nocturnal Nonrenewable 5 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Omnivore Parasite Photosynthesis Potential energy Producer Property Renewable Rule Scales Scientific inquiry Scientific law Solid States of matter Stored energy Survival Symbiosis System Theory U.S. Customary System of Measurement Volume Watershed Weathering Yardstick 6 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Grade 4 Prior Adaptations Backbone Balance Behavior Birds Boiling point Camouflage Celsius Cold-blooded Compare Computers Constant Contrast Data Distance Environments Evaluate Experiment Fahrenheit Fish Freezing point Graphs Hibernation Hypothesis Length Liquid Measurable Measurements Meter stick Migration Moons Observations Orbit Planets Question Rockets Rulers Scale Sequence Shape Solar system Solid Space Explicit Amphibians Asteroids Axis Comets Conclusion Condensation Data Dissolve Elliptical orbits Evaporation Experiment Fibrous root Gas Gravity Hypothesis Infer Invertebrate Mammals Metamorphosis Meteors Models Molecules Predict Reptiles Results Revolution Rotation Satellites Scientific method Sir Isaac Newton’s Laws of Motion Solubility Solution Taproot Telescopes Transpiration Valid Variable Vertebrate Volume Introductory Arthropod Atmosphere Beakers Bulge Chemical change Chemical reaction Defend Density Dormancy Endoskeleton Exoskeleton Explanations Form Friction Gas giants Inference Inner planets Instinct International System of Measurement (metric) Lunar Mass Mean Mimicry NASA Outcomes Outer planets Phases Phases of moon (waxes, wanes) Physical change Probe Protective coloration Reject Robotics Rovers Space shuttle Space station Specifics Tidal Tides US Customary Volume 7 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Sun Tables Temperature Thermometer Use Warm-blooded Weight Yard stick 8 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Grade 5 Prior Characteristics Compare Condensation Conservation Contrast Data table DecaDeciDefend Energy Evaporation Explanation Gas Gram Graph Hypothesis KiloLiquid Liter Measurable Meter Metric system (International System of Measurement) MiliModel Observation Physical changes Precipitation Prediction Recycle Reduce Reject Reuse Scientific procedure Shape Solid Standard system (U.S. Customary System) System Tools Valid Variable Volume Explicit Adaptation Carbon dioxide Cell Cell membrane Cell wall Chlorophyll Chloroplast Compounds Conclusion Control Elements Evidence Form Grams Hypothesis Igneous Inference Liters Metamorphic Meters Mixtures Model Molecule Nonrenewable Offspring Oxygen Photosynthesis Physical properties Punnett square Renewable Resources Scientific procedure Sedimentary Technology Traits Variable Introductory Atom Atomic weight Balance scale Chromosomes Concept (conceptual) Conservation Crust Cycle Cyclic Density Dependent Dominant Epicenter Fossils Function Genes Human impact Independent Inherited traits Inner core Lithosphere Magma Mantle Mass Matter Minerals Mitochondria Molecular Molecule Natural resources Nucleus Organelle Organization Outer core Periodic table Recessive Rock cycle Sample Scale Scale (interval appropriateness) Theory Vacuole 9 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Weathering Volume 10 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Grade 6 Prior Atmosphere Cell Characteristics Climate Community Conclusion Condensation Conservation Continental drift Data Describe Earthquake Environment Erosion Erosion Evaporation Evidence Explain Fahrenheit Gas Habitat Human impact Hypothesis Infer Inference Lava Liquid Magma Matter Meter stick Metric and customary measurements Metric ruler Model Objective Observation Offspring Physical change Plant and animal cell Plate tectonics Pollution Population Precipitation Explicit Air masses Atom Balance Celsius Chromosomes Cirrus Compound Control group Crust Cumulus Cycle (cyclic) Density Dominant Element Force Friction Fronts Function Gene Genetic traits Gravity Inner core Mantle Mass Mixture Molecule Nonrenewable Nucleus Order Organelles Organization Outer core Periodic table Physical property Recessive Renewable Sample Scales (intervals) Speed Weight Stratus Theory Variables (dependent and independent) Introductory Abiotic Acceleration Aphotic Aquifer Asthenosphere Average atomic mass Biome Biotic Buoyancy Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Climate Controlled variable Convection currents Cumulonimbus Deforestation Diffusion Displacement DNA Ductility Experimental variable Geothermal Global warming Hierarchy Hydroelectric power Interrelated Invasive species Isaac Newton Lithosphere Malleability Meiosis Mesosphere Mitochondria Mitosis Newton Noxious weeds Nuclear energy Organ Organ systems Photic Plasma Replication 11 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Predict Punnett square Recycle Resources Shape Solid Structure System Technology Temperature Thermometer Traits Volcano Weather Volume Water cycle Solar Stratosphere Subjective Thermosphere Tissue Transpiration Vacuole Wind power 12 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Grade 7 Life Science Prior Analyze Atoms Bar graph Base unit Cell membrane Cell wall Cells Characteristic Chart Chloroplast Classify Concept Conclusion Condensation Control group Conversion Cycle Data Demonstrate Dominant and recessive traits Element Evaporation Evidence Food chain Food web Graph Hypothesis Inference Interpret Line graph Measurement Model Molecules Natural resource Nonrenewable resource Nucleus Observation Organ systems Organisms Organs Part to whole Photosynthesis Pie chart Explicit Abiotic factors (nonliving) Active transport Adaption Alleles Alternative resource Beaker Biomass Biome Biosphere Biotic factor (living) Carbohydrates Carbon cycle Carnivore Carrying capacity Cellular respiration Cellular respiration Chemical reaction Chlorophyll Chloroplast Chromosome Commensalism Community Competition Consumer (heterotroph) Controlled variable Cytoplasm Decomposer Decomposition Defendable inference Dependent variable Diffusion Digital balance DNA Ecosystem Endoplasmic reticulum Energy pyramid Eukaryotic Evolution Flask Fossil Fossil fuels Gene Genotype Introductory Aerobic respiration Alcohol fermentation Anaerobic respiration ATP Binomial Cell cycle Decomposition Development Dichotomous key Domain Endocytosis Exocytosis Fermentation Growth Homologous structures Lactic acid Levels of Classification Manipulated Nitrogen fixation Nomenclature Pedigree chart Permeable Primary consumer Reliability Reproduction Responding Scientific name Secondary consumer Semipermeable Taxonomy Tertiary consumer Validity Vestigial organ 13 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Precipitation Predator Prediction Prey Probability Ratio Renewable resource SI units States of matter System Table Theory Tissue Tool Variable Water cycle Glucose Golgi bodies Habitat Herbivore Heredity Heterozygous Homozygous Limiting factor Lipids Mitochondria Multicellular Natural selection Neurons Nitrogen cycle Nucleic acids Omnivore Organ systems Organelles Organism Organisms Osmosis Overproduction Parasitism Passive transport Phenotype Photosynthesis Population Prediction Procedure Producer Producer (autotroph) Prokaryotic Protein Punnett square Qualitative observation Quantitative observation Respiration Ribosome Scientific law Specialized cells Species Sustainable practice Technology Testable hypothesis Theory Tissues 14 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Transpiration Triple beam balance Unicellular Vacuole Variation 15 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Biology Prior Agriculture Analysis Analyze Carbon dioxide Celsius CentiChart Chemical Compare Conclusion Cons Contrast Control group Controlled experiment Data Debate DecaDeciDegree Dependent variable DNA Energy Energy sources Evidence Explanation Fossil record Glucose Gram Graph Graphing Habitat Hecto Hypothesis Independent variable Interactions Interpret KiloKinetic Law Legend Length Liter Mass Explicit Active transport Allele Amino acids ATP Autotrophs Biosphere Carbohydrates Carrying capacity Cellular respiration Chromosome Community Diffusion DNA Ecosystem Enzyme Gametes Gene Genotype Glucose Heterotrophs Heterozygous Homeostasis Homozygous Lipids Mutation Niche Nucleic acids Nucleus Osmosis Phenotype Photosynthesis Proteins Replication RNA Transcription Translation Introductory Adenine Air quality Anaphase Anticodon Artificial selection Base pair Biogeochemical cycles Cell cycle Cell wall Chlorophyll Chloroplasts Cilia Codon Conservation Crossing over Cytokinesis Cytoplasm Cytosine Cytoskeleton Darwin Decomposition Deforestation Deoxyribose Differentiation Diploid Dominant Double helix Endoplasmic reticulum Energy pyramids Entropy Facilitated diffusion Fertilizer Flagella Food webs Genetic disease Genetic fitness Genetic recombination Genetic variability Golgi apparatus Guanine Haploid Hazardous waste Herbicides 16 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Matter Meter Micro MilliModel Modeling Nano Nonrenewable Nucleus Observation Order Organization Oxygen Oxygen Pollution Potential Prediction Pros Recycling Renewable Research Scientific method Solar System Table Technology Technology science Temperature Theory Thermal Title Volume Water X and Y axis Hypertonic Hypotonic Inferring Inheritance patterns Interdependence Interphase Intradependence Isotonic Limiting factors Lysosomes Macromolecules Metaphase Mitochondria mRNA Nucleic acid Nucleolus Nucleotide Organelle Organelle Passive transport Pedigree Pesticides Phosphate Plasma membrane Population density Preservation Prophase Punnett square Qualitative Quantitative Recessive Resource Resources selection Ribosomes Segregation Sex linked trait Specialization Succession Sustainable development Telophase Thymine Trait tRNA Trophic levels Vacuole Variation 17 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Water quality 18 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Physical Science Prior Atom Balance Celsius Constant Control group Data Distance Experiment External Force Friction Graduated cylinder Grams Gravity Half-life Hypothesis Internal Law Length Liters Mass Mass Volume Meters Metric ruler Metric system Model Molecule Motion Observation Order Organization Periodic table Physical change Physical property Qualitative Quantitative Science Scientific method Seconds Speed System Technology Theory Explicit Acceleration Atomic number Average atomic mass Balanced force Chemical change Chemical property Chemical reaction cm3 Conductor Covalent bond Dependent variable Electric charge Electric current Electric field Electron Electron cloud Endothermic Energy Exothermic Fission Frame of reference Fusion Independent variable Inertia Insulator Ion Ionic bond Isotopes Kelvin Kinetic energy Law of conservation of energy Law of conservation of mass Magnetic field Mass number Neutron Nucleus Potential energy Proton Standard Unbalanced force Valence electrons Velocity Introductory Acids Atomic mass unit Bases Chemical energy Chemical equation Combustion Conduction Decomposition Double-replacement Electromagnetic energy Energy levels Generator Induction Light energy Mechanical energy Momentum Motor Neutralization pH Radioactive decay Semiconductor Single-replacement Sound energy Synthesis Thermal energy 19 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Thermometer Time Timer Weight 20 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Earth Science Prior Acid rain Air mass Air pressure Aquifer Atmosphere Axis Bar graphs Beaker Biosphere Celsius CentiChart Circle graphs Cirrus Climate Cloud Compass Conclusion Condensation Conservation Constellation Continental Drift Hypothesis Convection Crust Cumulonimbus Cumulus Data DecaDeciDegree Density Diagram Digital balance Earthquake Epicenter Erosion Evaporation Evidence Experiment Flask Focus Fossil Fossil fuels Explicit Absolute dating Alternative energy resource Asthenosphere Axial tilt Barometer Conduction Controlled variable Convection Convergent boundary Coriolis effect Crescent Dependent variable Divergent boundary Eclipse Electromagnetic radiation Equinox Fault Geologic time scale Geosphere Gibbous Global climate change Global warming Greenhouse effect Half life Heat transfer High pressure system Hydrosphere Independent variable Intensity Lithosphere Low pressure system Lunar Phase Magnitude Mesosphere Natural resource Nebula Nonrenewable resource Ozone Plate tectonics Radiation Radioactive dating Rain shadow Relative dating Introductory Aphelion Apogee Astronomical unit Biomass Blue shift Deforestation Doppler effect Eutrophication Exosphere Fault block mountain Folded mountain Fossil types (cast, mold, trace) Geothermal energy Hydroelectric energy Ice core Index fossil Ionosphere Isotopes Joule Light year Manipulated variable Measurable Mid-ocean ridge (spreading center) Nonpermeable Normal fault Nuclear energy Nuclear fusion Observable Parallax Percolate Perigee Perihelion Permeable Plasma Precession Predicative Primary wave Radioactive decay Radioisotopes Red shift Repeatable Responding variable 21 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Front Galaxy Graduated cylinder Gram Graph Gravity HectoHurricane Hypothesis Igneous Inner core KiloLava Line graphs Liter Magma Mantle Mass Metamorphic Meter Meter stick Metric ruler Metric system MilliModel Orbit Order Organization Outer core Pangaea Pollution Precipitation Prediction Protractor Qualitative observation Quantitative observation Recycling Revolution Rock cycle Rotation Satellite Scientific data Scientific investigation Scientific method Scientific question Season Renewable resource Seismic wave Solstice Stratosphere Subduction Superposition Thermosphere Timer Transform boundary Troposphere Waning Waxing Reverse fault Science Scientific method Secondary wave Spectrum Strike slip fault Submersible Surface wave Technical writing Technology Tentative Testable Tree ring Trench Water table Wavelength 22 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Sedimentary Solar energy Solar system Space Star Stratus System Table Technology Telescope Theory Thermometer Tornado Transpiration Triple beam balance Universe Variable Volcano Volume Water cycle Weather Wind Wind energy 23 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Chemistry Prior Acid Alpha particle Apron Atom Atomic mass Atomic number Balance Bar graph Base Beaker Centi Chemical Chemical equation Chemical formula Chemical reaction Chemical symbol Coal Coefficient Compound Conclusion Condensation Constant Control data Conversion factor Conversion factors Covalent bonding Deci Dependent variable Electron Element Energy Energy levels Experiment Exponent Fire extinguisher Freezing Gas Gloves Goggles Graduated cylinder Gram Heterogeneous mixture Homogeneous mixture Explicit Absolute temperature Absorption Accuracy Amu Anion Arrhenius acids and bases Atomic radii Aufbau principle Avogadro’s number Binary compound Bohr Boiling point Bunsen burner Capillary action Catalyst Cathode ray tube Cation Chemical change Colligative properties Combustion Concentration Conservation of matter Dalton Decomposition Democritus Deposition Diatomic Dimensional analysis Dipole Dispersion Dissociation Double displacement/ replacement Electrolyte Electromagnetic-radiation Electronegativity Electronegativity difference Elevation Emission Endothermic Energy Energy levels Excited state Introductory Abstract Acid Activation energy Angular momentum Anhydrous Atom economy Balmer series Bronsted-Lowry Colloid Effective nuclear charge Electron affinity Extensive Extrapolate Formal charge Formula unit Hydrate Hydrogen fuel cells Hydronium ion Ideal gas constant Intensive Interpolate Ionization energy Lewis Acid Lyman series Magnitude Molality Orientation Paschan series Percent by mass Suspension Titration Vector Wave function 24 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Hot plate Hydroelectric Hypothesis Independent variable Ion Ionic bonding Kelvin Kilo Kinetic energy Lewis dot diagram Line graph Liquid Mass Mass number Material Melting Metric ruler Milli Model Molecule Neutron Nuclear Nucleus Observation Periodic table Petroleum pH Physical Physical properties Pie graphs Product Products Property Proportion Proton Protons Pure substance Reactants Scientific notation Slope Solid States of matter Subscript Temperature Theory Thermometer Exothermic Eye wash Freezing point depression Fume hood Ground state Heat Heat energy Hund’s rule Hydrogen bonding Hydronium ion Hydroxide Hydroxide ion Indicator Ion Ionization Isotope Lab report Latent heat Lone pair Micro Molality Molar mass Molarity Mole Molecule Neutralization Nonelectrolyte Octet rule Orbitals Pauli Exclusion Principle Percent by mass Physical change Pipette Polarity Polyatomic ion Precision Pressure Quantum numbers Quantum theory Reaction rates Resonance Ring stand Rutherford Safety shower Salt Schodiner 25 SCIENCE VOCABULARY 2012 Valence electrons Variable Volume Wavelength x-axis y-axis Shared pair SI base units Significant digits Single displacement/ replacement Solute Solution Solvent Specific heat Spectrum Spin Stoichiometry STP Strong electrolyte Sublevels Sublimation Surface area Surface tension Surroundings Synthesis System Thomson Titration Uncertainty Vaporization Weak electrolyte









