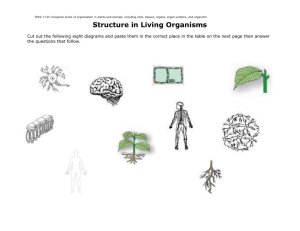
Human vs. Plant Organ Systems Worksheet
advertisement

Comparing Human and Plant Organ Systems: Basic Functions of Living Things Name: ____________________ Date:___________ Period:____ Question: How are human and plant organ systems similar Procedure: By comparing the functions of both human and plant organ systems we will build a list of functions that they have in common. Structure: Function: Basic Functions of Living Things Levels of Organization Questions: 1. Why are cells considered the basic units of life? 2. Can an organ system function correctly when one of its organs does not? Explain. 3. Can an organism function correctly when one of its organ systems does not? Explain. Name: _________________________________ Date:_____________ Period:______ Systems Comparisons Needs and Functions Human Organ System Plant Organ System Support the body Skeletal system Stem system Transport nutrients Circulatory system Stem system (vascular) Reproduce Reproductive System Flower system (sexual) Remove wastes Excretory system Root and Leaf systems Use or make energy All systems All systems Provide a barrier to the outside environment Skin system Epidermal system Takes in water and nutrients Digestive system Root and Leaf systems Cell Organelle Write two more comparison statements (#1 and #2 are examples): 1. The cell membrane, cell wall, and cytoplasm all help to support the body of the cell like the skeletal system supports in humans. 2. The cell membrane is similar to the skin system in humans because they both provide a barrier to the outside environment. 3. 4. Comparing Human and Plant Organ Systems: Basic Functions of Living Things Name: KEY Date:___________ Period:____ Question: How are human and plant organ systems similar Procedure: By comparing the functions of both human and plant organ systems we will build a list of functions that they have in common. Structure: how something is built, parts Function: how something works, what it does Types of Unicellular Organisms: 1-celled Multicellular Basic Functions of Living Things: Levels of Cell = Organization Organism Organism Many cells Organ Systems Organs Tissues Cells Support the body Transport nutrients Reproduce Remove wastes Use energy Provide a barrier to the outside environment Takes in water and nutrients Questions: 1. Why are cells considered the basic units of life? Cells are considered the basic units of life because they are the smallest structures that can perform all the functions necessary for life: support, transport nutrients, reproduce, remove wastes, and use energy. 2. Can an organ system function correctly when one of its organs does not? Explain. No, if an organ system does not function correctly then one of the functions necessary for life does not get completed and the organ system would not work, this in turn will affect the survival of the organism as a whole. 3. Can an organism function correctly when one of its organ systems does not? Explain. No, multicellular organisms split up the necessary functions of life into the organ systems: therefore, when one doesn’t function correctly the organism can die. Name: _________________________________ KEY Date:_____________ Period:______ Systems Comparisons Needs and Functions Human Organ System Plant Organ System Cell Organelle Support the body Skeletal system Stem system Cell membrane, cell wall, and cytoplasm Transport nutrients Circulatory system Stem system (vascular) Endoplasmic reticulum Reproduce Reproductive System Flower system (sexual) Centrioles Remove wastes Excretory system Root and Leaf systems Golgi complex Use or make energy All systems All systems Provide a barrier to the outside environment Skin system Epidermal system Cell membrane Takes in water and nutrients Digestive system Root and Leaf systems Cell membrane Mitochondria, chloroplasts Write two more comparison statements (#1 and #2 are examples): 1. The cell membrane, cell wall, and cytoplasm all help to support the body of the cell like the skeletal system supports in humans. 2. The cell membrane is similar to the skin system in humans because they both provide a barrier to the outside environment. 3. 4.