Modeling an Enzyme Lab - Manhasset Public Schools
advertisement
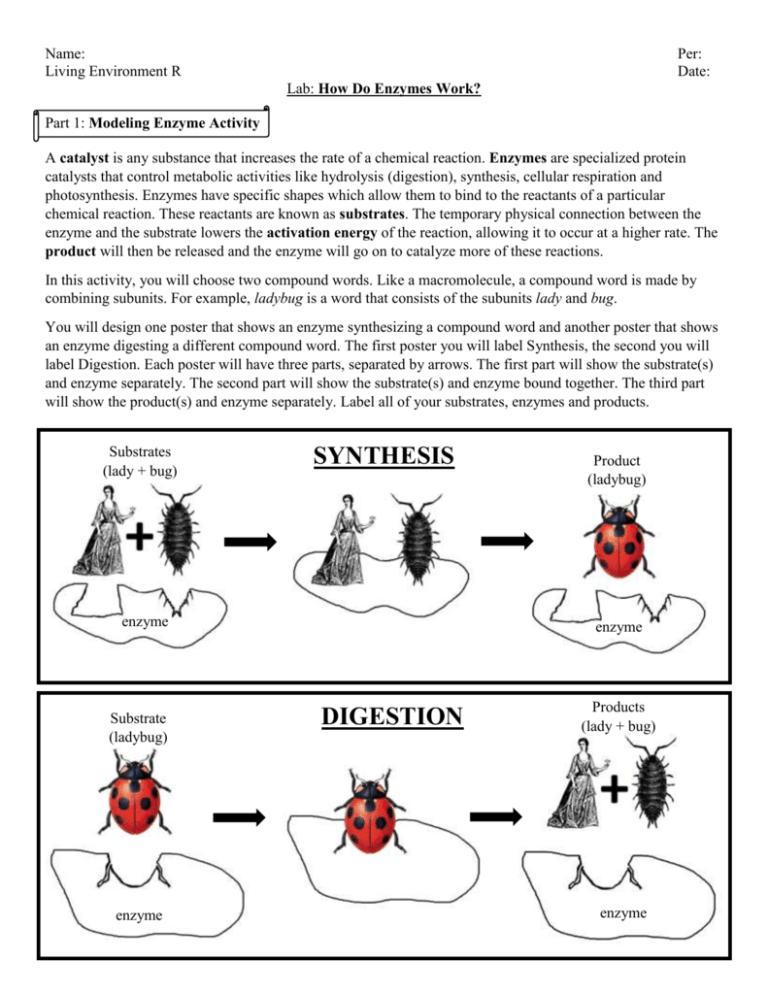
Name: Living Environment R Per: Date: Lab: How Do Enzymes Work? Part 1: Modeling Enzyme Activity A catalyst is any substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction. Enzymes are specialized protein catalysts that control metabolic activities like hydrolysis (digestion), synthesis, cellular respiration and photosynthesis. Enzymes have specific shapes which allow them to bind to the reactants of a particular chemical reaction. These reactants are known as substrates. The temporary physical connection between the enzyme and the substrate lowers the activation energy of the reaction, allowing it to occur at a higher rate. The product will then be released and the enzyme will go on to catalyze more of these reactions. In this activity, you will choose two compound words. Like a macromolecule, a compound word is made by combining subunits. For example, ladybug is a word that consists of the subunits lady and bug. You will design one poster that shows an enzyme synthesizing a compound word and another poster that shows an enzyme digesting a different compound word. The first poster you will label Synthesis, the second you will label Digestion. Each poster will have three parts, separated by arrows. The first part will show the substrate(s) and enzyme separately. The second part will show the substrate(s) and enzyme bound together. The third part will show the product(s) and enzyme separately. Label all of your substrates, enzymes and products. Substrates (lady + bug) SYNTHESIS enzyme Substrate (ladybug) enzyme Product (ladybug) enzyme DIGESTION Products (lady + bug) enzyme Record your poster design below: a. Name the compound word that you plan on synthesizing: ___________________________ b. Write out the chemical reaction: _____________________________________________________________ c. Name the compound word that you plan on digesting: __________________________ d. Write out the chemical reaction: _____________________________________________________________ e. Create your posters. Part 2: Investigating the Enzyme Catalase Metabolic activities of the cell often produce waste products that are toxic, like hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). a. How does the cell avoid being poisoned by these waste products? __________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ b. Write out the chemical reaction that is sped up by catalase: ________________________________________ c. Prepare a sample of potato and a sample of apple. d. Add a small amount of hydrogen peroxide to the potato sample. Do the same to the apple sample. e. Record your observations below Potato Sample Apple Sample f. In which sample was catalase present? How do you know? ________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ g. In the sample with catalase, identify what gas (bubbles) and liquid were produced: Gas = _______________________ Liquid = ________________________ h. Prepare two more samples of potato. i. Begin heating one potato sample in the water bath. j. Make a prediction: How will heating the potato sample change its reaction to hydrogen peroxide? _________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ k. Make a prediction: How will adding an acidic solution to the potato sample change its reaction to hydrogen peroxide? _________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ l. Add a small amount of acid to your hydrogen peroxide. Use pH paper to record the pH: _________________ m. Add the acidic hydrogen peroxide solution to your potato sample. n. Remove the potato sample from the water bath. Add hydrogen peroxide. o. Record your observations below: Acidic Potato Sample Heated Potato Sample Conclusion 1. Explain the effect that changing the pH had on Catalase activity: ___________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the effect that changing the temperature had on Catalase activity: ____________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Label the diagram below with the following terms: enzyme, substrate, active site, products











