Electron Cloud
advertisement
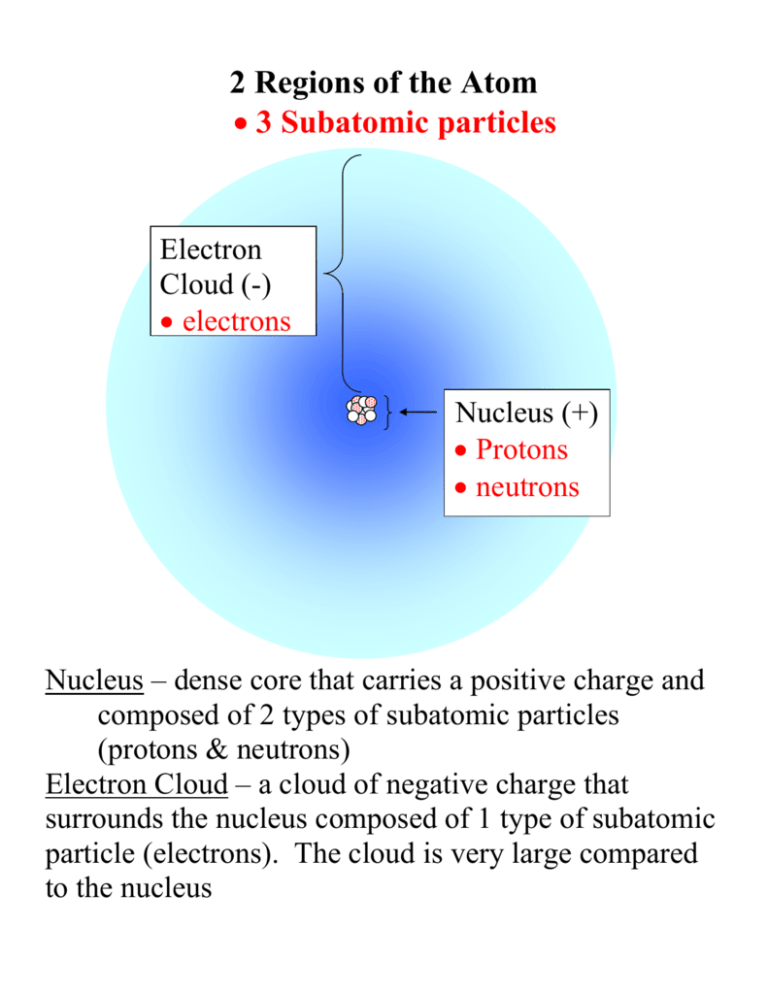
2 Regions of the Atom 3 Subatomic particles Electron Cloud (-) electrons Nucleus (+) Protons neutrons Nucleus – dense core that carries a positive charge and composed of 2 types of subatomic particles (protons & neutrons) Electron Cloud – a cloud of negative charge that surrounds the nucleus composed of 1 type of subatomic particle (electrons). The cloud is very large compared to the nucleus Region 1 – The Nucleus + + carries a positive 0 + (+) charge 0 dense and tiny + compared to the entire atom contains protons and neutrons which only come in whole numbers (can’t have ½ proton) Protons (abbv. P or +) postively charged (gives nucleus its positive charge) mass of 1 P = 1 amu (1.673 x 10-24 g) Atomic # = # of P # of P gives the element its identity all atoms of the same element have the same # of P atoms of different elements have different # of P Neutrons (N or 0) particle in the nucleus that has no charge neutral mass of 1 N = 1 amu (about the same as a P) The number of N in an element can vary Region 2 – The Electron Cloud e- cloud density decreases probability e- energy increases cloud contains electrons (e-) density of the ↑ density cloud ↓ e- energy most dense at ↓ density ↑ e- energy the center least dense toward the outside electron energy e- energy is greatest toward the outside e- energy is least at the center Electron negatively charged particle that moves around the nucleus forming a cloud of negative charge mass of 1 e- = 0 amu 1800 times smaller than a Proton (9.10953 x 10-28 g) # e- = # P in a neutral (uncombined) atom Energy Levels not circular orbits not all e- have the same energy each e- has different energy levels it can occupy in the electron cloud Energy Level Capacities 1st Energy Level s closest to the nucleus 1 spherical in shape (s orbital) holds a maximum of 2 ep 2nd Energy Level holds a maximum of 8 electrons o 1 spherical shape (s – orbital holds 2 e -) o 3 sets of 2 teardrop shapes (p – orbitals holds 2 e- each) 3rd Energy Level can hold up to 18 eo s orbital (2 e-) o p orbital with 3 - suborbitals (2 e- each) o d orbital with 5 - suborbitals (2 e- each) 4th Energy Level can hold up to 32 eo s orbital (2 e-) o p orbital (6 e-) o d orbital (10 e-) o f orbital with 7 suborbitals (2 e- each) p s p p p p Electron Cloud - Energy Levels continued Lowest energy level fills first, then second Atoms seek a stable number of e- in their outer energy level o the most stable e- arrangement in an outer energy level is an octet 8 e- in the outer energy level o 2e- in the outer energy level or a filled outer energy level are the next most stable arrangements + 8 outer e most stable condition won’t react + 2 outer e somewhat stable will react but usually slowly or needs energy