natural disaster
advertisement

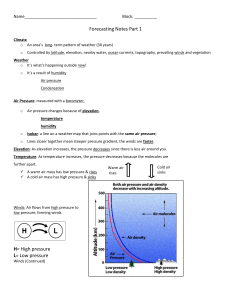
Weather & Climate Study Guide Name ______________________________ 6th Grade PSI Science 1. What is the difference between weather and climate? Weather is the current conditions of a location. Climate is the average weather for a location. 2. What is radiation? Radiation is the transfer of electromagnetic energy to Earth's surface. 3. How does sunlight affect Earth’s climate? Electromagnetic waves from the sun travel through Earth's atmosphere. This energy is absorbed by the atmosphere but the rest strikes Earth, warming it. This helps to drive our weather cycle. 4. How do the oceans affect Earth’s climate? The oceans absorb, maintain, and transport energy. This helps to regulate our weather. Ocean currents circulate energy and moisture between different areas of the world. 5. How do the oceans moderate coastal climates? The ocean has a steady temperature despite the seasons. Oceans absorb heat in the summer from the sun and release it very slowly during the winter. This helps to moderate temperature. People who live in costal regions experience warmer winters and cooler summers than inland regions. 6. In what layer of the atmosphere does weather occur? The troposphere is the layer closest to Earth's surface. This is the layer in which weather occurs. 7. What effect do greenhouse gases have on Earth’s climate? Greenhouse gases in the troposphere, such as CO2, retain heat and warm the planet. www.njctl.org 6th Grade PSI Weather & Climate and Natural Disasters 8. What causes the wind? Convection currents that affect ocean water also affect air currents in the atmosphere. We feel this as the wind. Convection currents are a result of less dense hot air rising and more dense cold air sinks. 9. What are prevailing winds? Prevailing winds are winds that travel from one direction. 10. How does moisture level in prevailing winds differ? Moisture content in prevailing winds is affected by location. Winds traveling over land are dry while winds traveling over water are moist. 11. How does ice affect Earth’s climate? The presence of ice and snow helps to regulate Earth's climate. Without them, Earth would absorb additional radiation and become much warmer. Because ice and snow are white in color, they do not absorb electromagnetic radiation from the sun. Instead, they reflect this energy back into space. 12. How do mountains affect local weather? As warm, moist air encounters the mountain, it is forced to rise, where it cools. As it cools, it condenses and releases moisture. 13. How do hills and valleys create wind patterns? Hills and valleys create wind patterns due to differential heating. During the day, hilltops heat up faster than valleys. This creates low pressure that pulls air (wind) up from the valley. At night, hilltops cool off faster than valleys. This creates high pressure that sends air (wind) down into the valley. www.njctl.org 6th Grade PSI Weather & Climate and Natural Disasters 14. What is an example of living things affecting climate? Humans increased use of greenhouse gases has led to global warming. 15. Why do different areas of the planet receive different amounts of sunlight? Because of Earth's tilt, different areas of the planet receive different amounts of sunlight. 16. Describe polar, temperate and tropical latitudes. Polar: Cold all year Temperate: Warm in summer, cold in winter Tropical: Warm all year 17. How does altitude affect temperature? As altitude increases, pressure decreases. This means that as altitude increases, temperature decreases. 18. Why do meteorologists use probability forecasting? Because they never know exactly what will happen, they use probability forecasting. 19. Compare high pressure and low pressure. What symbols are used to show each on a weather map? High Pressure System: Cool, dry air: Fair weather and light winds www.njctl.org 6th Grade PSI Weather & Climate and Natural Disasters Low Pressure System: Warm moist air: Storms and strong winds 20. What is a front? A front is a boundary between cold and warm air. 21. What are the differences between cold, warm and stationary fronts? What symbols are used to show each on a weather map? Front What is it? Conditions Symbol on map Storms replaced by lower temperatures and high pressure. Precipitation replaced by increased temperatures and low pressure. Cold Cold air replaces warm air. Warm Warm air replaces cold air. Stationary Two air Prolonged masses do precipitation and not move. storms. 22. What is a natural disaster? A natural disaster is a catastrophic event that occurs as a result of natural processes. www.njctl.org 6th Grade PSI Weather & Climate and Natural Disasters 23. What natural disasters are predictable? Volcanoes and Severe Weather 24. What natural disasters are unpredictable? Earthquakes and Tornados 25. What is unpredictable for all natural disasters? Even for a predictable natural disaster, the exact timing and magnitude is often unpredictable. Just like with weather, probability forecasting is used in predictions. www.njctl.org 6th Grade PSI Weather & Climate and Natural Disasters