Chapter 12 notes
advertisement

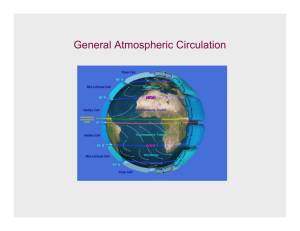
Chapter 12 Section 1 Three types of Meteors Hydrometeors- consist of cloud droplets and all forms of precipitation Lithometeors- consist of smoke and haze and dust Electrometeors- thunder and lightening Weather vs. Climate Weather is the current state of the atmosphere (short term) Climate is the average over a period of time (long term) Air Masses There are 5 different types Continental Tropical- hot and dry; Arizona Maritime tropical- warm and moist; Southern tip of Florida Continental Polar- cold and dry; Canada Maritime Polar- cold and moist; Alaska Artic- much colder and dry; around the north pole Air Mass Modification When an air mass moves to a different area and takes on different characteristics Weather Systems Section 2 Global Wind Systems Earth rotates from West to East The direction of Earth’s winds are influenced by rotation Coriolis effect is the movement of fluids and objects in a curved path and not a straight line Curves right in the North and Left in the South Global wind systems result from heat imbalance and the Coriolis effect They equalize thermal energy on Earth 3 basic wind systems: o Polar Easterlies o Prevailing Westerlies o Trade Winds Polar Easterlies 60 N latitude and north pole 60 S latitude and south pole Cold Winds Weak and sporadic Polar fronts are areas of stormy weather Prevailing Westerlies 30 N-60 N 30 S-60 S Originate in the west Steady winds that move most weather across the U.S. and Canada Trade Winds 30 N- 30 S Two circulation belts Air sinks, warms, and moves toward the equator in an easterly direction Once at the equator it moves back north and south Describe the horse latitudes and the inter-tropical convergence zone Horse Latitudes- Near 30 N and 30 S latitude; area of high pressure causing weak surface winds Inter-tropical Convergence Zone- Near equator; low pressure regions; forms bands of cloudiness and storms to deliver moisture to rain forests Jet Streams A jet stream is a narrow band of fast westerly wind; the strongest core of winds Polar jet streams o Separates the polar easterlies form the prevailing Westerlies Subtropical jet streams o Located where trade winds meet prevailing Westerlies o Weather systems usually follow the path of the jet streams Fronts 4 types of fronts: o Cold- cold, dense air displaces warm air and forces the warm air up along a steep front o Warm- advancing warm air displaces cold air o Stationary- two air masses meet and neither advances into the other’s territory. Frequently occurs when two air masses have become so modified in their travels that the temperature and pressure gradients between them are small o Occluded- sometimes when cold air mass moves so rapidly that it overtakes a warm front. The advancing cold air wedges the warm air upward. Pressure Systems Air always flows from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure Low-pressure systems are associated with cloudy weather and precipitation; air rises; counter- clockwise movement High-pressure systems are associated with fair weather; air sinks; clockwise movement