Chemistry Name: Ms. Boon Period: ______ Date: Gas Laws 6: The
advertisement
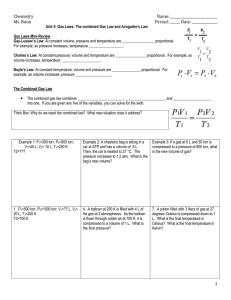
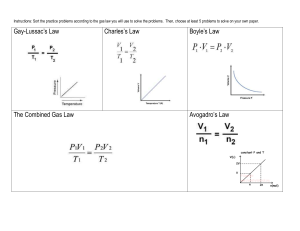
Chemistry Ms. Boon Name: ____________________________ Period: ______ Date: _______________ Gas Laws 6: The combined Gas Law and Avogadro’s Law Catalyst: What gas law was demonstrated by the can crush demonstration? Why? What gas law was demonstrated by the marshmallow video? Why? Gas Laws Mini-Review Gay-Lussac’s Law: At constant volume, pressure and temperature are _________________ proportional. For example, as pressure increases, temperature __________________. Charles’s Law: At constant pressure, volume and temperature are ________________ proportional. For example, as volume increases, temperature ____________________. Boyle’s Law: At constant temperature, volume and pressure are _______________ proportional. For example, as volume increases, pressure ___________________. The Combined Gas Law The combined gas law combines ________________________, _____________________, and ____________________ into one. If you are given any five of the variables, you can solve for the sixth. Think Box: Why do we need the combined law? What new situation does it address? Example 1: P1=300 torr, P2=900 torr, V1=40 L, V2= 10 L, T1=250 K T2=??? Example 2: A cheetohs bag is sitting in a car at STP and has a volume of .5 L. Then, the car is heated to 27 °C. The pressure increases to 1.2 atm. What is the bag’s new volume? Example 3: If a gas at 6 L and 30 torr is compressed to a pressure of 600 torr, what is the new volume of gas? 1. P1=500 torr, P2=1000 torr, V1=?? L, V2= 20 L, T1=200 K T2=100 K 4. A balloon at 200 K is filled with 4 L of He gas at 2 atmospheres. As the balloon is flown through colder air at 100 K, it is compressed to a volume of 1 L. What is the final pressure? 7. A piston filled with 3 liters of gas at 27 degrees Celsius is compressed down to 1 L. What is the final temperature in Celsius? What is the final temperature in Kelvin? 1 Chemistry Ms. Boon Name: ____________________________ Period: ______ Date: _______________ 2. P1=2.0 atm, P2=??, V1=3 L, V2= 30 L, T1=200 K T2=100 K 5. 2 Liters of a gas at STP is expanded to 4 Liters and 273 K. What is the final pressure? 8. A balloon at 546 K, 4L, and 2 atm is cooled down to STP. Find the final volume. 2. P1=4.0 atm, P2=16.0 atm, V1=3 L, V2= 30 L, T1=100 K T2=?? 6. 30 mL of gas at STP is heated to 50 degrees Celcius and the pressure is changed to 0.5 atm. Now, what is the volume of the gas? 9. A syringe is filled with 8 L of a gas at STP. The temperature is maintained at 273 K and volume is compressed to 4 L. What is the final pressure? Avogadro’s Law: The relationship between number of molecules and volume In 1811, Italian scientist Amadeo Avogadro found that equal volumes of all gases, under the same conditions, have the _______________________________________________. Specifically, at standard temperature and pressure, ___________________________________ has a volume of 22.4 L. Avogadro’s law means that gas volume is ______________________________ to the number of moles of gas at the same temperature and pressure. Example 1: V1 = 22.4 L, n1 = 1 mol, V2 = ___ , n2 = 5 mol Example 2: What is the volume of 10 mol of nitrogen gas at STP? Example 3: 6 mol of ammonia gas has a volume of 120 L. At the same temperature and pressure, what is the volume of 18 mol of ammonia? 2 Chemistry Ms. Boon Name: ____________________________ Period: ______ Date: _______________ 1. V1 = 30 L, n1 = 2 mol, V2 = ___ , n2 = 6 mol 3. What volume of carbon dioxide contains the same number of molecules as 20.0 mL of oxygen at the same conditions? 5. 15 mol of hydrogen gas has a volume of 300 L. If temperature and pressure are held constant, how many moles are in 900 L of hydrogen? 2. V1 = 10 L, n1 = 5 mol, V2 = 100 L , n2 = ___ mol 4. A very large balloon holds 224 L of helium gas at STP. If 5 moles of helium are released from the balloon, how many moles of helium remain? What is the new volume of helium? 6. A 140 mL sample of fluorine gas contains 0.7 mol fluorine. At constant temperature and pressure, what is the volume of 4.9 mol fluorine? Mixed Practice: Review with resources posted on the class website. 1. Why is it easy to compress a gas? 4. If the volume of a gas decreases by a factor of 10, what will happen to the gas pressure? (Assume temperature is held constant.) 2. What causes atmospheric pressure? 5. A student blows up a balloon in class. Then, the balloon is dipped into a container of liquid nitrogen. Liquid nitrogen has an extremely low temperature. What happened to the gas particles in the balloon? 3. The atmospheric pressure on top of Mount Everest is 58 kPa. What is this pressure in atmospheres? 6. The volume of air in a tire is 2 L at 1.00 atm and 30 °C. If the temperature decreases to standard temperature and the pressure remains constant, what is the new volume? 3