Molar Conversion Graphic - Greer Middle College || Building the
advertisement

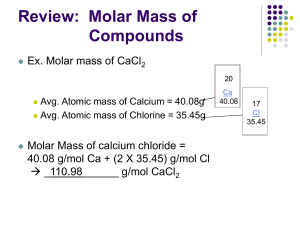
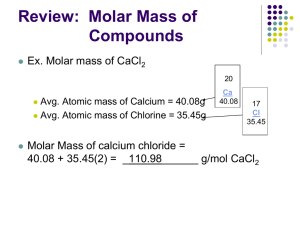
THE “MOLE” - NOTES Standard C-4: Apply the concept of moles to determine the number of particles of a substance in a chemical reaction, the percent composition of a representative compound, the mass proportions, and the mole-mass relationships. Notes/Q’s Objective: By the end of this lesson I will be able to explain the “mole,” “molar mass,” and “Avogadro’s number.” I will also use these concepts to do the following conversions: Appetizer: # particles moles moles mass (g) mass (g) How do we count atom, molecule, and formula units? 1.Take a guess of how many items are in the container. __________ 2. How many atoms of copper do you think there are in 63.546 g of copper wire? # particles We use the ______________. What is the mole? n The amount of substance that contains as many particles as there are atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12. n A counting number (like a dozen or a pair) n Avogadro’s number (NA) (6.022 1023) or (6.022 E23) ____________________________________________________ n 1 mole = 6.022 1023 items (of anything) ____________________________________________________ n Abbreviation = “mol” n Variable = “n” ___________ 3. Discuss with the person beside you whether a single dozen of different items would have the same mass._________________ Molar Mass Examples: 1 dozen # of Pumpkins 12 1 mol # of Pumpkins 6.022 E23 5 dozen (5 x12) 1.5 dozen (1.5 x 12) 60 18 5 mol 5 x (6.022 E23) 1.5 mol 1.5 x (6.022 E23) 3.011 E24 9.033 E23 1 mole of hockey pucks would equal the mass of the moon! 1 mole of basketballs would fill a bag the size of the earth! 1 mole of pennies would cover the Earth 1/4 mile deep! n Molar mass = mass of 1 mole of an element or compound. n Atomic mass on the P.T. tells the... atomic mass units per atom (amu) grams per mole (g/mol) Ex: 6.022 E23 C atoms = 1 mol C atoms = 12.011g C Examples: Substance Molar mass Aluminum 26.982 g/mol Zinc 65.409 g/mol 1 mol C = 12.011 g *Simply look at the atomic mass on the P.T. This is also equal to the molar mass of that element. THE “MOLE” - NOTES Molar Mass of Compounds Notes/Q’s n n Ex: Magnesium Acetate Formula = Mg(C2H3O2)2 The molar mass of a compound is equal to the sum of all the element’s molar masses in the compound. Mg = H= Chemical Formula – a combination of symbols and numbers to represent a substance. Subscripts right after a symbol indicates the number of atoms in that compound. C= O= If no subscript is written, you assume “1.” Subscripts right after parentheses apply to everything in parentheses. (multiply each subscript by the subscript outside parentheses. Name Formula Water H2O Sodium Bicarbonate NaHCO3 Magnesium Acetate Mg(C2H3O2)2 Sucrose C12H22O11 Calculation Molar Mass = Molar Conversions #1 How many moles of carbon are in 26 g of carbon? Molar Conversions #2 How many molecules are in 2.50 moles of C12H22O11? Molar Conversions #3 Molar Conversions #4 Find the mass of 2.1 1024 molecules of NaHCO3. Find the # of oxygen atoms in 5.00 grams of NaHCO3.