Name: : :___ CELL TRANSPORT 1. Which of the following describes

Name: _______________________________________________________________Date: __________________________Block:___
CELL TRANSPORT
1. Which of the following describes active transport?
A. Water moves across the cell membrane.
B. Small molecules are pushed into the tissue fluid by blood pressure.
C. Molecules are moved against the concentration gradient using energy.
D. Molecules are moved with the concentration gradient without using energy.
Use the following list to answer question 2.
2. How many of the conditions would affect the rate of diffusion across a semipermeable membrane?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Use the following diagram to answer question 3.
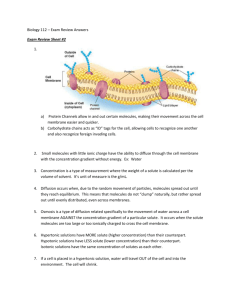
3. What is the next step in the process shown above?
A. Water is drawn into the cell.
B. Enclosed substances leave the cell.
C. A lysosome fuses with the vacuole.
D. A vesicle fuses with the cell membrane.
4. Compare the process of facilitated transport with that of active transport. ( 3 marks)
• Facilitated transport does not use energy (ATP).
• Active transport uses energy (ATP). either one for 1 mark
• Facilitated transport uses protein carriers and active transport uses protein carriers. (1 mark)
• During facilitated transport material moves from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration (with the concentration gradient).
• During active transport material moves from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration (against the concentration gradient). either one for 1 mark
• Both move amino acids and glucose.
(1 mark)
5. Phagocytosis involves the infolding of what structure?
A. the nucleolus
B. the mitochondria
C. the cell membrane
D. the smooth endoplasmic reticulum
6. By what process do lipid-soluble molecules and gases cross the cell membrane?
A. osmosis
B. diffusion
C. pinocytosis
D. active transport
7. a) Why do oxygen molecules enter a cell at a different rate than protein molecules. (1 mark)
• Oxygen molecules are smaller.
• Oxygen molecules enter by diffusion.
• Oxygen is a gas and gases diffuse across the cell membrane more quickly.
• Oxygen is neutral / unchanged / non-polar.
• Protein molecules are larger.
• Protein molecules enter by endocytosis.
Note to markers:
Do not accept different sizes. any one for 1 mark b) State two ways to increase the rate of oxygen movement into a cell. (2 marks)
• increase the temperature
• increase the concentration gradient OR explanation of oxygen gradient OR increase the respiratory rate
• increase the metabolic rate of the cell
• increase cytoplasmic streaming
Mrs. N Gill Biology 12
Name: _______________________________________________________________Date: __________________________Block:___
• secretion of thyroxin
Note to markers:
Do not accept increase in surface area.
any two for 1 mark each
Use the following diagram to answer question 8.
8. The diagram shows a white blood cell ingesting a bacterium. By what process does the bacterium enter the white blood cell?
A. pinocytosis
B. phagocytosis
C. active transport
D. facilitated transport
9. Facilitated and active transport both
A. require ATP.
B. require protein carrier molecules.
C. operate in the sodium-potassium pump.
D. move molecules against the concentration gradient.
10. Materials move across the cell membrane either actively or passively. Complete the following table to compare and contrast these two ways of moving materials . (4 marks) any four pairs with 1 mark for each pair
Use the following diagram to answer question 11.
11. The diagram shows a white blood cell ingesting a bacterium. The bacterium enters the white blood cell by
A. diffusion.
B. pinocytosis.
C. phagocytosis.
D. active transport.
12. Which of the following moves material against a concentration gradient?
A. osmosis
B. diffusion
C. active transport
D. facilitated transport
13. The secretion of noradrenalin into the synaptic cleft occurs by which of the following processes?
A. exocytosis
B. pinocytosis
C. endocytosis
D. active transport
14. What will happen to an animal cell when it is placed into a concentrated salt solution?
Mrs. N Gill Biology 12
Name: _______________________________________________________________Date: __________________________Block:___
A. It will excrete salt.
B. Its volume will decrease.
C. It will absorb more water.
D. Its volume will remain the same.
Use the following diagram to answer question 15.
15. a) Identify the process shown in the diagram. (1 mark)
• active transport (1 mark) b) Give one example in which this process is used in the body. (1 mark)
• Nerve impulse transmission.
• Reabsorption and tubular excretion.
• Absorption of nutrients in the small intestine.
• Active transport of sodium ions into the medulla of the kidney. c) Describe the function of the molecule represented: (1 mark)
• Provides energy for the process. (1 mark) d) What is the function of molecule X ? (1 mark)
• Transports (or carries) sodium ions. (1 mark)
Use the following information to answer question 16.
1. Vesicle fuses with a lysosome.
2. Bacterium is taken into the macrophage.
3. Digestion of the bacterium occurs.
4. Vesicle is formed around the bacterium.
16. Which of the following is the correct sequence to describe what happens to a bacterium after a type of white blood cell called a macrophage encounters it?
A. 1, 3, 2, 4
B. 1, 4, 2, 3
C. 2, 3, 4, 1
D. 2, 4, 1, 3
Use the following diagram to answer question 17.
17. Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z ?
A. exocytosis and diffusion
B. endocytosis and diffusion
C. exocytosis and facilitated transport
D. endocytosis and facilitated transport
Use the following diagram to answer question 18.
18. The diagram above represents the initial conditions of an experiment.
Which of the following graphs most accurately represents the change in the net rate of osmosis over time? C
Mrs. N Gill Biology 12
Name: _______________________________________________________________Date: __________________________Block:___
19. When Na+2(sodium ions) are moved across the cell membrane against the concentration gradient,
A. ATP is used.
B. osmosis occurs.
C. diffusion occurs.
D. vesicles are formed.
20. Which of the following molecules will pass through a cell membrane by simple diffusion?
A. water
B. an enzyme
C. nucleic acid
D. carbohydrate
21. Describe the following mechanisms of transport across cell membranes. (3 marks: 1 mark each) osmosis:
¥ The net diffusion of water from the area of high water concentration to the area of lesser concentration of water.
¥ The net diffusion of water from the area of lower solute concentration to the area of greater solute concentration.
¥ The movement of water according to osmotic pressure / gradient (or diffusion). any one for 1 mark facilitated transport:
¥ The net movement of molecules, using a carrier protein, from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
¥ The net movement of molecules down the concentration gradient, using a carrier protein. either one for 1 mark active transport:
¥ The use of a carrier protein and an energy source to move molecules from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration.
¥ The movement of molecules, against the concentration gradient, using a protein carrier and ATP as an energy source. either one for 1 mark ote
Examples of exocytosis, endocytosis, pinocytosis or phagocytosis were not acceptable.
22. Facilitated transport may be described as the movement of particles from an area of
A. low to high concentration using protein carriers.
B. low to high concentration without using protein carriers.
C. high to low concentration using protein carriers.
D. high to low concentration without using protein carriers.
Use the following diagram to answer question 23.
23. What could the structure labelled X contain?
A. bacteria
B. glycogen
24. What process does not require the use of ATP?
A. exocytosis
B. pinocytosis
C. active transport
D. facilitated transport
25. Which of the following is an example of pinocytosis?
A. Transport vesicles are formed at the Golgi bodies.
B. Small particles move because of osmotic pressure.
C. small molecules are engulfed and brought into the cell.
D. A white blood cell forms a vacuole around a bacterium.
C. white blood cells
D. protein molecules
Mrs. N Gill Biology 12
Name: _______________________________________________________________Date: __________________________Block:___
Use the following diagram to answer questions 7 and 8.
7. The process shown is an example of
A. exocytosis.
B. pinocytosis.
C. endocytosis.
D. phagocytosis.
8. The material labelled X could be
A. water.
B. insulin.
C. amino acids.
D. sodium ions.
Use the following diagram to answer question 25.
25. The organelle ON THE LEFT is abundant in cells involved in
A. active transport.
B. diffusion of oxygen.
C. transport of hemoglobin.
D. transport of lipid-soluble molecules.
Mrs. N Gill Biology 12