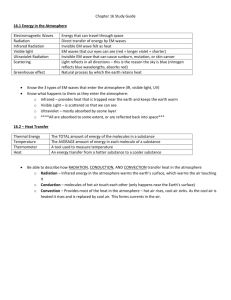
Grudgeball Questions How does the sun contribute to the creation of
advertisement

Grudgeball Questions 1- How does the sun contribute to the creation of wind? Uneven heating creates areas of different air pressures. 2- Which is more dense, cold air or warm air? Cold air 3- In terms of pressure differences, which way does air move? From high pressure to low pressure 4- How would the winds blow if the Earth did not rotate? A straight line 5- In the southern hemisphere, which way does the Coriolis Effect cause the wind to curve? Left 6- These global winds are found between 30 and 60 degrees latitude in both hemispheres. Westerlies or Prevailing Westerlies 7- These winds were used by European Sailors to get from Europe to the New World. Trade winds 8- These winds carry cold, arctic air to the United States. Polar Easterlies 9- These areas of calm winds are found at 30 degrees latitude in both hemispheres. Horse Latitudes 10- What area of calm winds is found near the Equator? Doldrums 11- Which direction do the Jet Streams blow? West to East 12- Name the 2 Jet Streams. Subtropical and polar 13- In a sea breeze, where is the higher pressure, over the land or the sea? Sea 14- In a land breeze, where is the air more dense, over the land or the sea? Land 15- In a valley breeze, from where is the wind blowing, and is it daytime or nighttime? Valley, daytime 16- In a mountain breeze, when night falls, which area cools faster, on the mountain or in the valley? Mountain 17- What is the term for an increase in volume that results from an increase in temperature. Thermal expansion 18- What is the term for the curving of the path of a moving object as a result of the earth’s rotation? Coriolis Effect 19- What type of heat transfer does the sun use to warm the Earth? Radiation 20- What gas is the most prevalent in the Earth’s atmosphere? Nitrogen 21- At 30 degrees south latitude, do we find a band of high pressure or low pressure? High Pressure 22- What is the definition of weather? Condition of the Earth’s atmosphere at a certain time and place 23- What is humidity? The amount of water vapor in the air 24- Define relative humidity. The amount of water vapor in the air compared to the amount of water vapor the air can hold 25- What is the term used when air evaporation and condensation are the same and the air can’t hold any more water vapor? Saturation 26- What is the term for the temperature at which, if air is cooled further, condensation will exceed evaporation. Dew point 27- What is precipitation? Any form of water that falls to the earth from clouds 28- Name the 5 types of precipitation we talked about. Rain, snow, sleet, hail, freezing rain 29- This type of precipitation begins as snow, melts, and then refreezes in the air before it hits the ground. Sleet 30- This type of precipitation begins as snow, melts, and doesn’t refreeze until it hits the ground or some of surface that is below freezing. Freezing rain 31- What is air pressure? The force of air molecules pushing on an area 32- As altitude increases, what happens to air pressure? It decreases 33- What is the term for measuring the transparency of the atmosphere, describing how far we can see? Visibility 34- What is the name for the layer of the atmosphere where most of Earth’s weather takes place? Troposphere 35- If a wind is blowing from north to south, which region has the lower air pressure, the north or the south? South 36- Using the relative humidity chart, determine the relative humidity if the dry bulb temperature is 20 deg. C and the wet bulb temperature is 15 deg. C. 58% relative humidity 37- Using the relative humidity chart, determine the wet bulb temperature if the dry bulb is 16 deg. C and the relative humidity is 80%. Wet bulb is 14 deg. C 38- Look at the diagram; what is responsible for the bands of high and low pressure every 30 degrees of latitude? Convection or convection cells 39- Show how the winds in the area between 30 deg. and 60 deg. South latitude are moving. 40- Show how the winds between 60 deg. and the north pole are moving. 41- Look at the image: what is the instrument and what does it measure?