Weather Test Review Packet--
advertisement
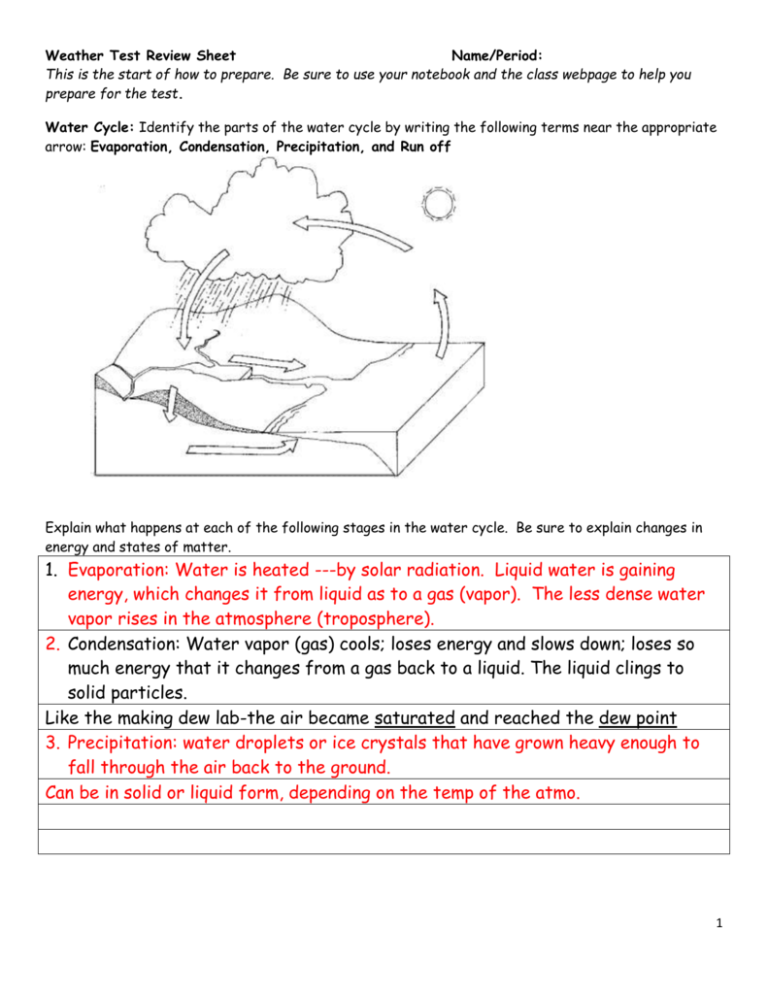
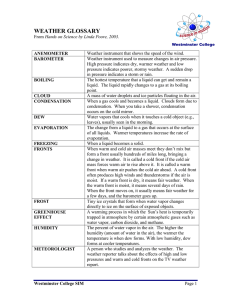
Weather Test Review Sheet Name/Period: This is the start of how to prepare. Be sure to use your notebook and the class webpage to help you prepare for the test. Water Cycle: Identify the parts of the water cycle by writing the following terms near the appropriate arrow: Evaporation, Condensation, Precipitation, and Run off Explain what happens at each of the following stages in the water cycle. Be sure to explain changes in energy and states of matter. 1. Evaporation: Water is heated ---by solar radiation. Liquid water is gaining energy, which changes it from liquid as to a gas (vapor). The less dense water vapor rises in the atmosphere (troposphere). 2. Condensation: Water vapor (gas) cools; loses energy and slows down; loses so much energy that it changes from a gas back to a liquid. The liquid clings to solid particles. Like the making dew lab-the air became saturated and reached the dew point 3. Precipitation: water droplets or ice crystals that have grown heavy enough to fall through the air back to the ground. Can be in solid or liquid form, depending on the temp of the atmo. 1 Weather Instruments: Name 4 and what they measure. Instrument 1.Barometure 2.Anemometer 3. Wind Vane 4. Thermometer 5. Psychrometer What it measures? Air Pressure Wind Speed Wind Direction Temperature Relative Humidity Precipitation-how does each type form? Rain-cloud is made of liquid water b/c air above 32°F; droplets cling together and fall to earth as a liquid Sleet-starts out as rain; falls through a layer of below-freezing air; land as solid pellets Freezing Rain-start out as ran; falls to ground as a liquid; freezes upon contact with belowfreezing ground/objects. Snow-air is below-freezing; form in cloud as ice crystals; falls to the ground as a solid. Hail-Form in cumulonimbus clouds; rise and fall because of updrafts and downdrafts of warm and cold air, which forms layers of ice Fronts-What types of clouds are associated with each? What type of weather do they bring? What is the weather like following the front? Clouds Weather at the front Weather following front Clouds, precipitation, or Clear skies, cooler Cold Cumulonimbus thunderstorms-can happen temps, lower humidity quickly. Stratus/nimbostratus Gray skies, drizzle or rain Warmer temps and Warm for a longer period of time higher humidity (maybe a day or two) Low clouds, rain possible Depends on which front Stationary Stratus/nimbostratus/fog for several days takes over Moderate to heavy precip Occluded Nimbostratus or cumulonimbus Cooler temps and lower humidity Define the following: The temperature at which the air is saturated and condensation begins. Dew Point Relative Humidity The % of water vapor in the air compared to the maximum amount the air can hold at a certain temperature Air is full of water vapor; rel. humidity = 100%; WV condenses Saturated 2 Reading a Weather Map 1. Near which city would you expect to find (circle one for EACH): a. A storm or quick downpour Atlanta b. Several hours of drizzly precipitation Seattle c. Several days of overcast, rainy weather Detroit Denver Atlanta Denver Chicago Phoenix Boston 2. What is happening to the air masses at Front B? a. A warm air mass is slowly moving up and over a cold air mass b. A cold air mass is moving under a warm air mass and pushing it upwards c. Neither air mass is moving 3. Atlanta is currently experiencing a ___warm_____ front. 4. Write “true” or “false” on the line for the following statements. a. _false_____ A cold front is moving towards Detroit. b. ___false____ Salt Lake City and Phoenix most likely have higher temperatures than Denver right now. c. ___true____ The weather system in Chicago will last for a day or two. 3 Winds Review 1. What causes winds? Differences in air pressure; the unequl heating of Earth. 2. Global Winds-name the 3 wind belts and 2areas of calm Wind Belts Areas of Calm Trade Winds Horse Latitudes Prevailing Westerlies Doldrums Polar Easterlies 5. In the boxes below, illustrate the four types of LOCAL WINDS. Be sure to represent whether it is day or night, and COLOR warm air currents RED and cold air currents BLUE. Heat Transfer: Identify which type of heat transfer. R-radiation CV-Convection CD-Conduction __CD___George burns his hand touching his tray of tater tots without an oven mitt! __CV___Angela always keeps the heating vents in her car pointed at her feet because she knows that her face will feel it soon ___R__Natalie gets an early start on her tan by sunbathing in her living room under the skylight ___CD/R__Jimmy fries an egg on a rock in Death Valley, CA only to realize he has been scarred by blistering sunburn 4