Economic Growth
advertisement
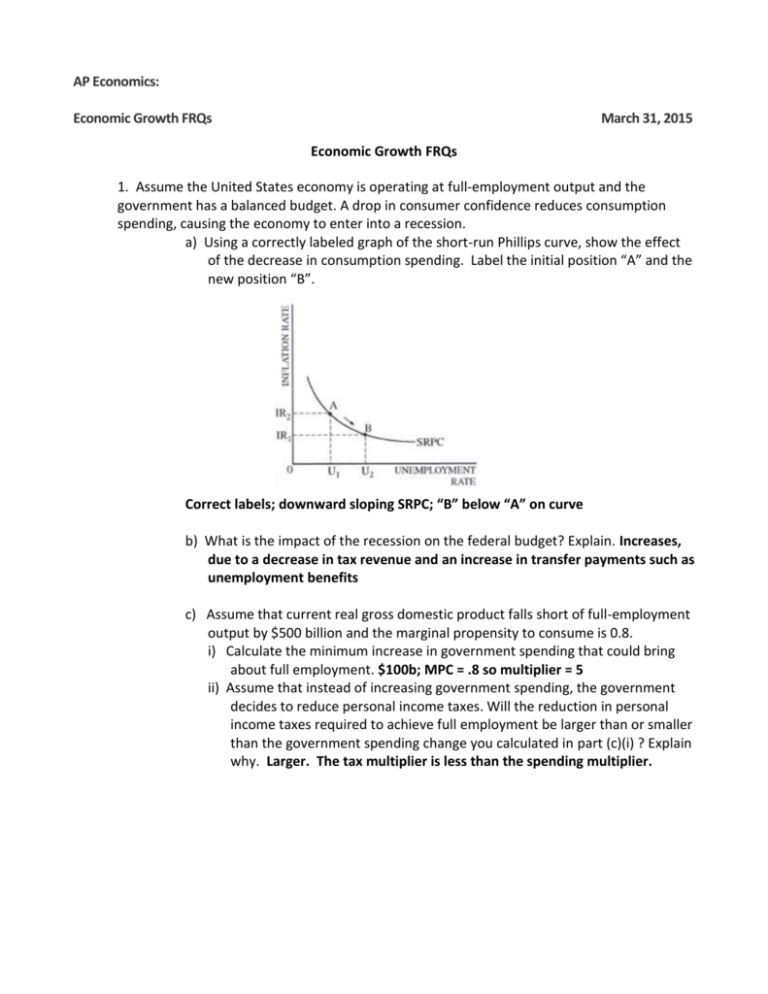
AP Economics: Economic Growth FRQs March 31, 2015 Economic Growth FRQs 1. Assume the United States economy is operating at full-employment output and the government has a balanced budget. A drop in consumer confidence reduces consumption spending, causing the economy to enter into a recession. a) Using a correctly labeled graph of the short-run Phillips curve, show the effect of the decrease in consumption spending. Label the initial position “A” and the new position “B”. Correct labels; downward sloping SRPC; “B” below “A” on curve b) What is the impact of the recession on the federal budget? Explain. Increases, due to a decrease in tax revenue and an increase in transfer payments such as unemployment benefits c) Assume that current real gross domestic product falls short of full-employment output by $500 billion and the marginal propensity to consume is 0.8. i) Calculate the minimum increase in government spending that could bring about full employment. $100b; MPC = .8 so multiplier = 5 ii) Assume that instead of increasing government spending, the government decides to reduce personal income taxes. Will the reduction in personal income taxes required to achieve full employment be larger than or smaller than the government spending change you calculated in part (c)(i) ? Explain why. Larger. The tax multiplier is less than the spending multiplier. d) Using a correctly labeled graph of the loanable funds market, show the impact of the increased government spending on the real interest rate in the economy. Correct labels; increase in G causes increase in D, shown by shift to the right; causing increase in real interest rates e) How will the real interest rate change in part (d) affect the growth rate of the United States economy? Explain. Growth rate declines because rise in real interest rates causes decrease in Investment. 2. Over the past two years, the unemployment rate in Country X has risen from 5 percent to 9 percent. As the leader of Country X, you have been presented with two policy options to address the unemployment problem. Policy 1: Use tariffs and quotas to restrict imports and thus protect jobs in Country X Policy 2: Use monetary and fiscal policies to solve the unemployment problem without resorting to trade restrictions a) Explain two disadvantages of selecting Policy 1. Creates deadweight loss which reduces efficiency; other countries may retaliate and cause job losses in exporting sector; consumers have lower quality products and fewer choices b) Describe in detail one specific monetary policy action and one specific fiscal policy action you would take to reduce unemployment. Explain how each of these actions would affect each of the following in the short run: Monetary policy: 1) Increase MS by buying securities in Open Market Operations, 2) Reduce Reserve Requirements or 3) Reduce Discount Rate. Fiscal Policy: 4) Increase spending or (5) decrease taxes. i) aggregate demand Monetary policies 1-3: reduces interest rates which causes increase in Investment which causes increase in AD; Fiscal policy 4: increase in G increases AD; Fiscal policy 5: decrease in taxes causes increase in disposable income, which causes increase in C which causes increase in AD ii) output and the price level All actions above increase AD, which increases both output and price level iii) real interest rates Monetary policies 1-3: interest rates decrease; Fiscal policies 4-5: the higher output and price level increase demand for money which causes an increase in interest rates c) If the interest rate effects you identified in part b) continues in the long run, explain the impact of these effects on economic growth. Monetary policies 13: reduced interest rates lead to an increase in I, which causes an increase in productivity and results in long run growth; Fiscal policies 4-5: higher interest rates lead to a decrease in I, causing a decrease in long run growth 3. Suppose that the following statements describe the current state of the United States economy: • the economy is at full employment • the consumer price index is rising at 2 percent annually • the federal government budget deficit is equal to $200 billion (5 percent of gross national product) a) Legislation is just been passed which holds government spending constant and raises personal income taxes enough to balance the budget. Explain briefly how and why this policy will affect output and employment in the short run. Increase in taxes will reduce disposable income, reducing AD, reducing output and employment in the short run b) Following the income tax increase, the Federal Reserve announces a goal of significantly increased growth rates in the money supply. If the Federal Reserve achieves its goal, explain in detail the short run effects of the Federal Reserve’s actions on each of the following: i) interest rates Buying bonds causes shift to right in MS, intersecting downward sloping MD curve at lower interest rate ii) output and employment decrease in interest rate leads to increase in Investment, causing increase in AD, causing increase in output and employment iii) prices Increase in AD causes increase in price level c) Summarize the combined effects of the federal government’s actions and the Federal Reserve’s actions on long-run growth. It is indeterminant if the tax decrease will reduce AD more or less than the increase in AD resulting from the increase in MS. However, both policies reduce interest rates, causing an increase in I, which leads to productivity gains and therefore long-term growth 4. Assume the economy of Andersonland is in a long-run equilibrium with full employment. In the short run, nominal wages are fixed. a) Draw a correctly labeled graph of short-run aggregate supply, long-run aggregate supply, and aggregate demand. Show each of the following. i) Equilibrium output, labeled Y1 ii) Equilibrium price level, labeled PL1 Correct lables; Y1 and PL1 at intersection of SRAS, AD and LRAS b) Assume that there is an increase in exports from Andersonland. On your graph in part (a), show the effect of higher exports on the equilibrium in the short run, labeling the new equilibrium output and price level Y2 and PL2, respectively. Show rightward shift in AD and new Y2 and PL2 levels at intersection of AD’ and SRAS c) Based on your answer in part (b), what is the impact of higher exports on real wages in the short run? Explain. Increase in XN leads to rightward shift in AD, which causes PL to rise. Nominal wages are sticky in the short run, so rise in PL means real wages fall. d) As a result of the increase in exports, export-oriented industries in Andersonland increase expenditures on new container ships and equipment. i) What component of aggregate demand will change? I ii) What is the impact on the long-run aggregate supply? Explain. The LRAS will shift to the right due to the increase in I.