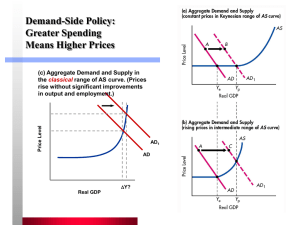
Unit 5.1 Government Economic Policy
advertisement

Unit 5.1 Government Economic Policy Macroeconomic Objectives: Low & stable inflation: To keep ____________ under control. Low employment: Unemployment is a waste of resources and means the economy is under producing. Economic growth: this increases the standard of ____________ as more goods and services are produced A balance in the balance of payments: A deficit means more money is leaving the country than is coming in; a surplus means another country has a deficit. A balance may be desirable. Types of policy: Demand side policies: attempts to influence aggregate ______________ Supply side policies: attempts to increase the quantity and _________ of the factors of production specifically labour, capital and enterprise- this will increase an economy’s ability to produce (affecting aggregate _____________). Expansionary policies: increasing aggregate demand e.g. lower tax rates, higher _______________ spending, lower interest rates. Contractionary policies: decreasing aggregate demand e.g. higher tax rates, lower government spending, higher interest rates. Instruments of government policy: Demand side policies: 1. Fiscal Policy: Fiscal Policy is an instrument of DEMAND MANAGEMENT which seeks to control the level of economic activity in an economy through the control of TAXATION and GOVERNMENT EXPENDITURE. Quite simply, if a government spends more, without increasing taxes, then aggregate demand increases. For example, if the government spends more on defence then government purchases will increase on military goods and more people will be employed either directly or indirectly. If the government reduces taxes (e.g. income tax, corporation tax) or increases transfer payments (pensions, unemployment benefit etc) without reducing its own spending, then aggregate demand will increase. Reduced taxes and increased spending increase people’s ________________________- they have more money in their pockets to spend. Problems with fiscal policy? Time delays- any change in policy will take time to work through the economy, by which time the policy change may no longer be needed. Information problems- it is difficult to know the exact position of the economy at any moment Government intervention either overshoots or undershoots i.e. increases AD too much or too little because of time lags and poor information; this can destabilise the economy. Some items of spending are very difficult to reduce due to political sensitivity e.g. education and ___________ spending- to cut back on these would be politically unwise. 2. Monetary Policy Monetary Policy is a tool of MACROECONOMIC POLICY which involves the regulation of the MONEY SUPPLY and/or INTEREST RATES in order to control the level of expenditure in an economy. Interest rates affect household spending and _____________ spending. If the Central Bank raises interest rates, it increases the cost of borrowing money and thus consumer durable spending will fall, investment spending will fall and saving becomes more attractive. Supply-side policies Supply side policies can involve both fiscal and monetary policies. They include ‘interventionist’ policies such as government spending to improve infrastructure making it cheaper to move goods and people around and spending on education and training of the labour force. There are also market based policies use to encourage competition and increase the incentive to work. For example: 1. 2. 3. 4. Reduction in income taxes: Reduction in business (profits) tax: Reductions in unemployment benefits: Deregulation & privatization: