Ch24Mg
advertisement
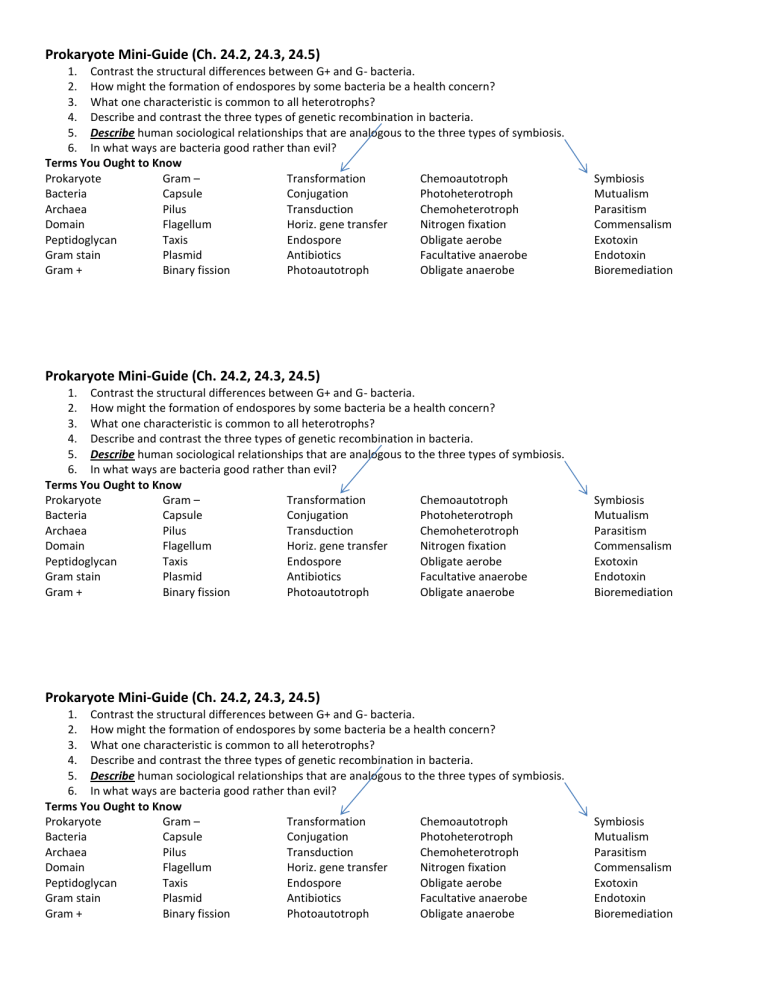
Prokaryote Mini-Guide (Ch. 24.2, 24.3, 24.5) 1. Contrast the structural differences between G+ and G- bacteria. 2. How might the formation of endospores by some bacteria be a health concern? 3. What one characteristic is common to all heterotrophs? 4. Describe and contrast the three types of genetic recombination in bacteria. 5. Describe human sociological relationships that are analogous to the three types of symbiosis. 6. In what ways are bacteria good rather than evil? Terms You Ought to Know Prokaryote Gram – Transformation Chemoautotroph Bacteria Capsule Conjugation Photoheterotroph Archaea Pilus Transduction Chemoheterotroph Domain Flagellum Horiz. gene transfer Nitrogen fixation Peptidoglycan Taxis Endospore Obligate aerobe Gram stain Plasmid Antibiotics Facultative anaerobe Gram + Binary fission Photoautotroph Obligate anaerobe Symbiosis Mutualism Parasitism Commensalism Exotoxin Endotoxin Bioremediation Prokaryote Mini-Guide (Ch. 24.2, 24.3, 24.5) 1. Contrast the structural differences between G+ and G- bacteria. 2. How might the formation of endospores by some bacteria be a health concern? 3. What one characteristic is common to all heterotrophs? 4. Describe and contrast the three types of genetic recombination in bacteria. 5. Describe human sociological relationships that are analogous to the three types of symbiosis. 6. In what ways are bacteria good rather than evil? Terms You Ought to Know Prokaryote Gram – Transformation Chemoautotroph Bacteria Capsule Conjugation Photoheterotroph Archaea Pilus Transduction Chemoheterotroph Domain Flagellum Horiz. gene transfer Nitrogen fixation Peptidoglycan Taxis Endospore Obligate aerobe Gram stain Plasmid Antibiotics Facultative anaerobe Gram + Binary fission Photoautotroph Obligate anaerobe Symbiosis Mutualism Parasitism Commensalism Exotoxin Endotoxin Bioremediation Prokaryote Mini-Guide (Ch. 24.2, 24.3, 24.5) 1. Contrast the structural differences between G+ and G- bacteria. 2. How might the formation of endospores by some bacteria be a health concern? 3. What one characteristic is common to all heterotrophs? 4. Describe and contrast the three types of genetic recombination in bacteria. 5. Describe human sociological relationships that are analogous to the three types of symbiosis. 6. In what ways are bacteria good rather than evil? Terms You Ought to Know Prokaryote Gram – Transformation Chemoautotroph Bacteria Capsule Conjugation Photoheterotroph Archaea Pilus Transduction Chemoheterotroph Domain Flagellum Horiz. gene transfer Nitrogen fixation Peptidoglycan Taxis Endospore Obligate aerobe Gram stain Plasmid Antibiotics Facultative anaerobe Gram + Binary fission Photoautotroph Obligate anaerobe Symbiosis Mutualism Parasitism Commensalism Exotoxin Endotoxin Bioremediation









