2nd Semester Review Guide
advertisement

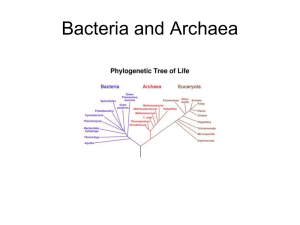
Honors Biology Second Semester Study Guide Biotechnology (12 & 13) 1. Explain the use of restriction enzymes, vectors, and plasmids in making recombinant DNA. 2. Explain how gel electrophoresis works and how it is applied in DNA identification. 3. Explain how biological technologies and research such as gene splicing, mammalian cloning, and stem cells impact human society. Restriction enzyme Electrophoresis Plasmid Transgenic organisms Restriction site DNA fingerprinting Gene splicing Transformation Sticky ends Gene cloning Recombinant DNA Stem cell Evolution (14-16) 1. Explain the theory of endosymbiosis and how it details the formation of Eukaryotes. 2. Distinguish between scientific ideas about evolution. a. Lamarck's idea of inheritance of acquired characteristics b. Darwin's idea of descent with modification 3. Analyze the reasoning in Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection. a. Overproduction of offspring b. Genetic variation c. Adaptations d. Differential reproduction (survival & reproduction) 4. Explain how the following show evidence of evolution a. Morphology: analogous & homologous structures, vestigial structures b. Biochemistry: DNA, RNA, proteins 5. Compare and contrast divergent and convergent evolution 6. List the conditions under which evolution may take place (Hardy-Weinberg: genetic equilibrium) Fossil record Vestigial structure Natural Selection Species Radiometric dating Analogous structure Hardy-Weinberg conditions Population Descent with Modification Biochemistry Genetic Drift Morphology Molecular comparison Gene flow Homologous structure Embryology Mutation Classification (17) 1. Use hierarchical categories of classification to illustrate the biodiversity on this planet: Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species 2. Use proper binomial nomenclature in describing organisms: Latin, italicized, avoid confusion with common name 3. Based on given data, construct a phylogenetic tree: shows chronological sequence of organism's appearance 4. Differentiate between the organisms found in different domains and kingdoms based on characteristics such as cell type, cell wall, body plan, and nutrition. Domain Genus Homo Archaea Chemoheterotroph Kingdom Animalia Species Homo sapiens Eukarya Chemoautotroph Phylum Chordata Species identifier Protista Photoheterotroph Class Mammalia Systematics Fungi Photoautotroph Order Primates Phylogenetic tree Plantae Family Hominidae Bacteria Animalia Bacteriology (23) 1. Describe the internal and external structure of bacteria: peptidoglycan, endospores, cilia, cell wall, capsule. 2. Morphology: spirillum, coccus, bacillus in various configurations 3. Describe the environments bacteria live in: obligate aerobic &anaerobic, facultative anaerobes. 4. Significance of Bacteria 5. Explain how bacteria develop new traits (including antibiotic resistance) via mutation, transformation, conjugation, and transduction Decomposition Facultative anaerobe Gram – Spirillum Transformation Fermentation Obligate anaerobe Capsule StreptoConjugation Nitrogen fixation Peptidoglycan Pilus StaphyloEndospore Antibiotics Gram stain Coccus Binary fission Exotoxin Obligate aerobe Gram + Bacillus Plasmid Endotoxin Virology (24) 1. Describe why viruses are not considered living things. 2. Describe the structure of a virus: Nucleic Acid, Capsid, Envelope 3. Replication: Lytic Cycle (virulent viruses) & Lysogenic Cycle (temperate viruses) 4. Pathology: HIV/AIDS, vaccines, influenza, HPV/cervical cancer Nucleic Acid Envelope Lytic Cycle Capsid Virulent Temperate Botany (28-30) 1. Name three adaptations plants have made to live on land a. reproduction (spores & seed) b. vascular tissue (phloem & xylem) c. limiting desiccation (cuticle) 2. Summarize the classification of plants: a. nonvascular (moss), b. vascular spore producers (ferns) c. vascular seed producers non-flowering (gymnosperms) & flowering (angiosperms) 3. Explain how angiosperm reproduction takes place 4. Compare and contrast monocotyledons and dicotyledons Fruit Stoma Sink Dicot Vegetable Vascular System Moss Taproot Root Vascular bundle Fern Apical meristem Stem Xylem Gymnosperm Vascular cambium Leaf Phloem Angiosperm Secondary growth Cuticle Source Monocot Springwood Zoology 1. Identify key characteristics of animals that distinguish them from other organisms 2. Identify the significance of symmetry and cephalization in animal behavior 3. Describe components and function of digestive system a. Primitive systems (intracellular and gastrovascular cavities) b. Dental variations c. Mammalian digestion d. Herbivorous adaptations 4. Describe components and function of circulatory system a. Primitive systems (diffusion and open circulation) b. Vertebrate variations (Fish, Amphibian, Bird/Mammal) c. Pathway of blood through heart (chambers, valves) and major vessels Differentiation Annelida Mammary Glands Specialization Closed circulation Esophagus Porifera Complete gut Peristalsis Filter feeding Mollusca Stomach Cnidaria Open circulation Pancreas Radial symmetry Closed circulation Liver Nerve net Gills Gallbladder Gastrovascular cavity Arthropoda Small intestine Platyhelminthes Exoskeleton Large intestine Cephalization Chitin Heart Bilateral symmetry Chordata Atria Central nervous system Mammalia Ventricles Lysogenic Cycle Vaccine Summerwood Cone Flower Septum Pulmonary loop Pulmonary artery Pulmonary vein Systemic loop Inferior vena cava Superior vena cava Aorta Red blood cell White blood cell Platelet