File
advertisement

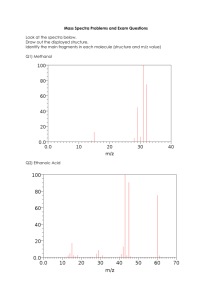
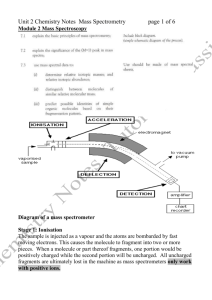
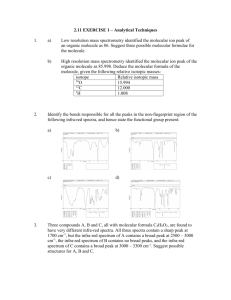
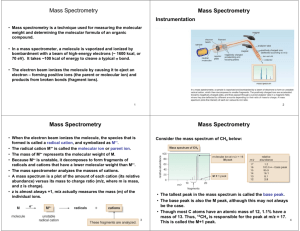
WORKSHEET ONE Mass spectrometry 1. State the main aim of mass spectrometry. 2. Fill in the following boxes by choosing from the words below to show how a mass spectrum is obtained. Smaller ions electrons vaporised positive ion graph Bombarded with Pure compound Detected and printed Breaks down into as a 3. Molecule loses 1 electron to form a Write an equation to show how a molecule, M, reacts to form a radical cation (positive ion). 4. Explain two uses or applications of mass spectrometry. 5. What is the m/z value for the molecular ion produced by the loss of 1 electron from: (a) Methane: (b) Propanone: (c) Ethanol: 6. Above is the mass spectrum for hexane C6H14. (a) List the peak number that relates to the: Molecular ion peak: Base peak: (b) State what the following peaks correspond to: 86 57 43 7. A hydrocarbon that does not react with bromine water gave a molecular ion peak at 114 and a base peak at 85. Give formula for: 8. (a) The molecular ion peak: (b) The base peak: A compound has an empirical formula C2H4O and a molecular ion peak at 132. Write the molecular formula for the compound.