Basic Chemistry Review Packet Key
advertisement
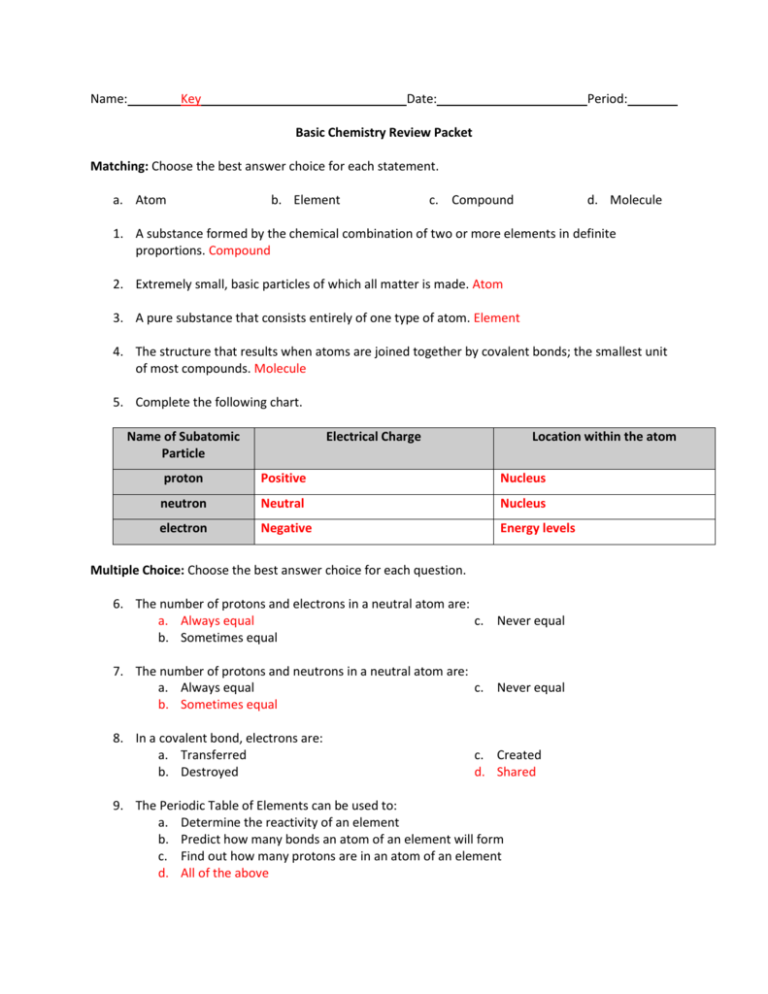
Name: Key Date: Period: Basic Chemistry Review Packet Matching: Choose the best answer choice for each statement. a. Atom b. Element c. Compound d. Molecule 1. A substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in definite proportions. Compound 2. Extremely small, basic particles of which all matter is made. Atom 3. A pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom. Element 4. The structure that results when atoms are joined together by covalent bonds; the smallest unit of most compounds. Molecule 5. Complete the following chart. Name of Subatomic Particle Electrical Charge Location within the atom proton Positive Nucleus neutron Neutral Nucleus electron Negative Energy levels Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer choice for each question. 6. The number of protons and electrons in a neutral atom are: a. Always equal c. Never equal b. Sometimes equal 7. The number of protons and neutrons in a neutral atom are: a. Always equal c. Never equal b. Sometimes equal 8. In a covalent bond, electrons are: a. Transferred b. Destroyed c. Created d. Shared 9. The Periodic Table of Elements can be used to: a. Determine the reactivity of an element b. Predict how many bonds an atom of an element will form c. Find out how many protons are in an atom of an element d. All of the above 10. What are the five most common elements found in living things? H, O, N, C, P Use the Periodic Table of Elements to answer the following questions (#11-16). 11. What is the atomic number of Neon (Ne)? 10 12. How many protons are in one atom of Neon (Ne)? 10 13. How many electrons are in one atom of Neon (Ne)? 14. What is the atomic number of Boron (B)? 10 5 15. How many protons are in one atom of Boron (B)? 16. How many electrons are in one atom of Boron (B)? 5 5 Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer choice for each question. 17. What is the number marked by the arrow? a. Mass number b. Atomic number c. Number of neutrons 18. Which subatomic particle(s) can be found in the nucleus? Circle your answer(s). a. Electron c. Neutron b. Proton 19. Which subatomic particle has a charge of -1? a. Electron b. Proton c. Neutron 20. Which subatomic particle has the lowest mass? a. Electron b. Proton c. Neutron 21. In the spaces below you will see the Bohr Model of energy levels for two different atoms. a. Fill in the blank information at the top of the space. (Some of the information has been filled in for you.) b. Draw and label each atom as they would exist in their elemental state. Include the number of protons and the locations of electrons. Name Beryllium Name _____oxygen_______________ # protons ____4______ # protons ___8__________ # electrons ____4_______ # electrons 8 4p 8p Diagrams: For #22-24, draw diagrams for the assigned compound: OCl2. You only need to show electrons and protons (you can omit neutrons). 22. Draw a Lewis Dot diagram for each of the atoms in this compound Cl O Cl Cl O Cl 23. Draw a full Bohr model for each of the atoms in the compound. 17p 8p Cl 17p O Cl 24. Draw the simplified structural formula of this compound. Cl O Cl 25. Chloroform is a common anesthetic. It has a chemical formula of HCCl3. a. How many atoms of each element are found in one molecule of chloroform? Hydrogen=1 carbon=1 chlorine=3 b. Draw the structural formula for chloroform Cl Cl C H Cl 26. A common element has 16 electrons surrounding its nucleus. a. What is the name of the element? sulfur b. How many bonds will this element form in order to become stable? 2 c. This element will join with 2 hydrogen atoms to become stable. What is its chemical formula? SH2 d. Draw its structural formula H S H Matching: Choose the best answer choice for each vocabulary word. 27. Products C 28. “yields” or “produces” E 29. Reactants B 30. Subscript D 31. Coefficient A 32. Is the equation above properly balanced? Circle your choice: YES NO 33. Complete the following chart. Chemical Formula H2O CaCO3 Numbers and types of atoms in the compound Two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. 1 calcium atom, 1 carbon atom, 3 oxygen atoms Six hydrogen atoms, 3 oxygen atoms 3H2O 4H2SO4 8 hydrogen atoms, 4 sulfur atoms, 16 oxygen atoms 34. Calculate how many atoms of each element are present in the following compounds. a. NaHCO3 1 sodium atoms, 1 hydrogen atom, 1 carbon atom, 3 oxygen atoms b. C2H4O2 2 carbon atoms, 4 hydrogen atoms, 2 oxygen atoms c. Mg(OH)2 1 magnesium atom, 2 oxygen atoms, 2 hydrogen atoms d. 3H3 PO4 9 hydrogen atoms, 3 phosphorus atoms, 12 oxygen atoms 35. Complete the chart below. EQUATION BALANCED? (Y/N) yes H2 + O2 --> H2O2 no H2O2 --> H2O + O2 yes 4Na + O2 --> 2Na2O no N2 + H2 --> NH3 36. What is the difference between reactants and products in a chemical equation? Reactants enter the reactions (starting point), products is what is made at the end of the reaction (ending point) 37. Which number indicates the number of atoms of each element in a molecule of a substance? subscript 38. Which number indicates the number of molecules? coefficient 39. Why must chemical equations always balance? Law of conservation of matter: matter (atoms/elements) cannot be created or destroyed. If you start with 5 hydrogen atoms, you must end with 5 hydrogen atoms 40. If an atom is reactive, how does it become stable? a. Joins a water molecule b. Forms bonds with other reactive atoms c. Forms energy levels with other subatomic particles d. Joins the nuclei of other atoms