Your exam will be 80 Multiple Choice Questions. Each
advertisement

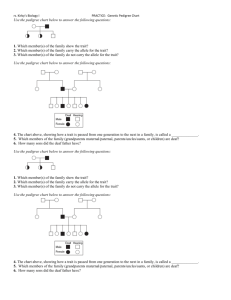
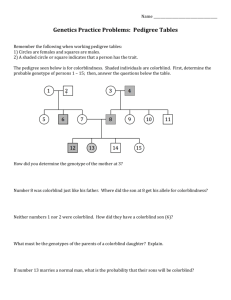
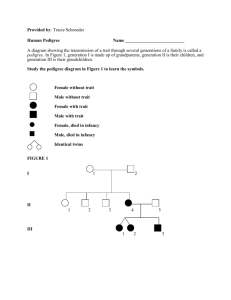
Biology – Semester 2 Exam Review Your exam will be 80 Multiple Choice Questions. Each question will be worth 1.25 points for a total of 100 points. You will only have the time allotted for the exam to take it. Most of the questions on this study guide will appear on your exam. Know the correct answers to them before your exam begins. 1. Who discovered the cell? What was he looking at when he discovered the cell? 2. Which cell parts are not found in animal cells? 3. What is the difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? 4. What is the chloroplasts used for? If an organism has that cell part, what can it do? 5. What do all cells have in common? 6. What are the three ways in which cells can replicate? 7. Which process immediately follows Mitosis? 8. What type of cells divide by binary fission? 9. What are the steps to mitosis? What are some examples of cells that undergo mitosis? 10. How is meiosis different from mitosis? 11. How are plant cells different from animal cells? Name 3 ways. 12. What stage of interphase is chromosomal DNA copied? 13. What happens during each phase of mitosis? 14. What are the common cell organelles to all eukaryotic cells? 15. What are the differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms? 16. If you are looking at a round cell and it has a nucleus, a small vacuole, and cilia, what type of cell is it? 17. What is the job of chloroplasts? 18. The cristae has a special structure that allows the mitochondria to perform more work than the regular allowable surface area of the cristae would allow. How? 19. How are plant vacuoles different when there is plenty of water vs when there is scarcely any water? 20. What are secretory vesicles? 21. What are the 3 ways in which cells replicate? 22. What controls most of the cell processes and contains the hereditary information of DNA 23. What is a cell membrane? What is its job? 24. What is the main function of the cell wall? 25. Which organelle makes food for the cell? 26. What is the job of the organelles in the cell? What does each one do? 27. What is the difference between a plant cell and an animal cell? 28. What organelle is only found in plant cells, provides a protected framework, and gives plants their shape? 29. The cell organelle that acts like the powerhouse of the cell also does what other job? 30. Refer to the illustration above. Which cell is most likely to lose both water molecules and solute molecules as the system approaches equilibrium? 31. Refer to the illustration above. Which direction are water molecules in this system most likely to diffuse? 32. What are the characteristics of facilitated diffusion? 33. What is the name of the process by which water passes in and out of a cell? 34. Which types of cells in your body are more likely to have more mitochondria? 35. What is the main job of vacuoles? 36. What is the form of transport in which molecules are moved down their concentration gradient? 37. What type of transport is diffusion? 38. Why do Cells Need Homeostasis? 39. What main cell organelle helps with homeostasis? 40. What types of molecules can pass through the cell membrane via diffusion? 41. Being tall or short are examples of 42. BB, Bb, and bb are examples of Use the punnett square below to answer questions 43-44. B B = Brown eyes b = blue eyes b B b 43. What is the probability of having a child with blue eyes? 44. What is the probability of a homozygous child? 45. How do you cross parents in a punnett square? 46. Does it matter whether the mom is at the top or the side? 47. If mom and dad both have blue eyes, what is the probability of their child having brown eyes? (B = Brown eyes, b = blue eyes) 48. If mom is heterozygous and dad has blue eyes, what is the probability of their child having brown eyes? (B = Brown eyes, b = blue eyes) 49. If mom and dad are both heterozygous, what is the probability of their child having brown eyes? (B = Brown eyes, b = blue eyes) 50. In a dihybrid cross (WwGg X WwGg) where W = round, w = wrinkled, G = yellow and g = green, what is the probability of obtaining an individual that is homozygous wrinkled and homozygous green? 51. The observable characteristics of an organism that result from the expression of genes is the organism’s 52. In lilies, white flowers (W) are dominant to purple flowers (w). If two plants that are heterozygous for flower color are mated, the offspring might have which genotype? 53. How many different allele combinations would be found in the gametes produced by a pea plant whose genotype was RrYY? 54. One breed of cattle can be red, white, or roan. Roan (RW) is the combination of the red allele (R) and the white allele (W). If a farmer wanted only Roan cattle, which two types of cattle should he breed together? 55. Use the information from the above question to answer this question. If a farmer wanted to breed a half red and half roan herd, what animals should be the parents? 56. A red-flowered sweet pea plant is crossed with a white-flowered sweet pea plant. All of the offspring are pink. What is the inheritance pattern being expressed? 57. Variation in human skin color is a result of 58. What is a Pedigree Chart 59. What do the symbols on a pedigree chart represent? 60. In a Pedigree, if you are tracing a trait that is dominant, what is true about one or both of the parents? 61. How can an offspring inherit a trait if neither parent is affected by the trait? 62. What does autosomal traits refer to? 63. What are the ways a male offspring will NOT inherit an X linked recessive trait? 64. What is the complete set of chromosomes in a species? 65. What is the difference between the sex chromosomes? 66. The following is the name of a karyotype: 47, XY, +18. What does the name tell scientists about this karyotype? 67. What is the difference between trisomy and monosomy? The pedigree chart below is for a family, some of whose members exhibit wooly hair. Affected individuals are indicated by a shaded square or circle. Use the chart to answer questions 68-69. 68. Is the trait dominant or recessive? Is the trait x-linked or autosomal? 69. What is the genotype of the individual 1 in row IV? 70. The karyotype shown above is named 71. The pedigree below most likely represents what type of trait? 72. What is the genotype of individual 2 in row II? 73. Examine the karyotype below. What can you determine about the individual 74. Examine the karyotype below. What can you determine about the individual 75. What is the term for a feature that allows an organism to survive better in its environment? 76. What observations did Charles Darwin make about finches in the Galápagos Islands? Use this chart to answer questions 77-80. 77. What are the sister groups? 78. Charles Darwin’s observation that finches of different species on the Galápagos Islands have many similar physical characteristics supports what hypothesis about these finches? 79. Which can be said about the members of a population that live long enough to reproduce? 80. If a mutation introduces a new skin color in a lizard population, which factor might determine whether the frequency of the new allele will increase?